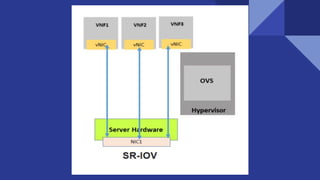
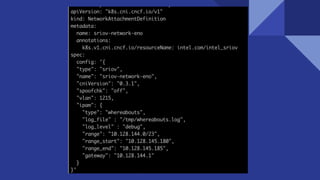
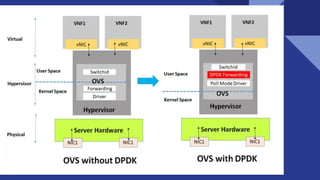
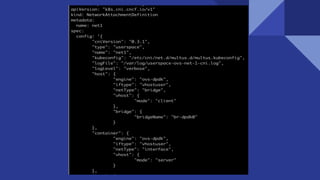
This document discusses deploying virtual network functions (VNFs) using Kubernetes pods and VMs. It covers using single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) and Open vSwitch with Data Plane Development Kit (OVS-DPDK) for high performance networking. SR-IOV allows VNFs direct access to network interface cards to bypass the hypervisor. OVS-DPDK processes packets in userspace using DPDK for accelerated performance compared to native Linux networking or SR-IOV for some workloads. The document provides configuration details for enabling SR-IOV and OVS-DPDK on the host and specifying network interfaces in KubeVirt virtual machine instances.