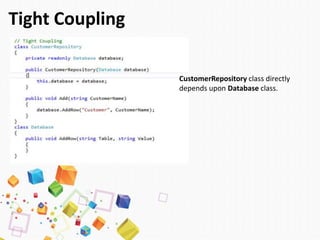
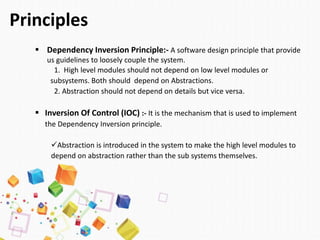
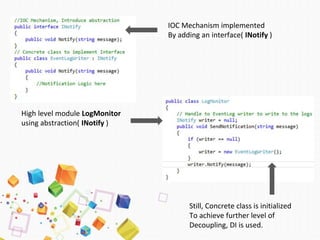
The document discusses dependency injection (DI), a software design pattern that enhances maintainability, testability, flexibility, and extensibility by promoting loose coupling between components. It outlines the principles of DI, including the dependency inversion principle and inversion of control, and describes methods of implementing DI such as constructor, method, and property injection. Additionally, it reviews the advantages and disadvantages of using DI containers for managing dependencies in software development.