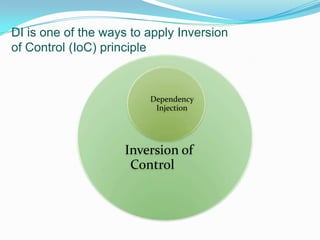
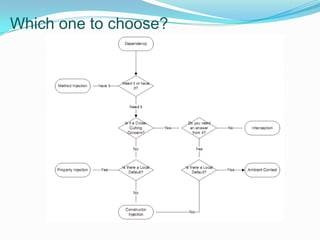
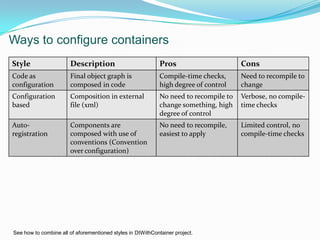
Dependency Injection (DI) is a technique for achieving Inversion of Control (IoC) by externalizing a class's dependencies, allowing them to be injected from external sources rather than being directly hard coded. DI promotes loose coupling between classes and separation of concerns by making code depend on abstractions rather than concretions. DI can be applied through constructor injection, property injection, method injection, or ambient context. Popular DI containers include Castle Windsor, StructureMap, Spring.NET, and Ninject, which help configure and manage object lifetimes and interception.