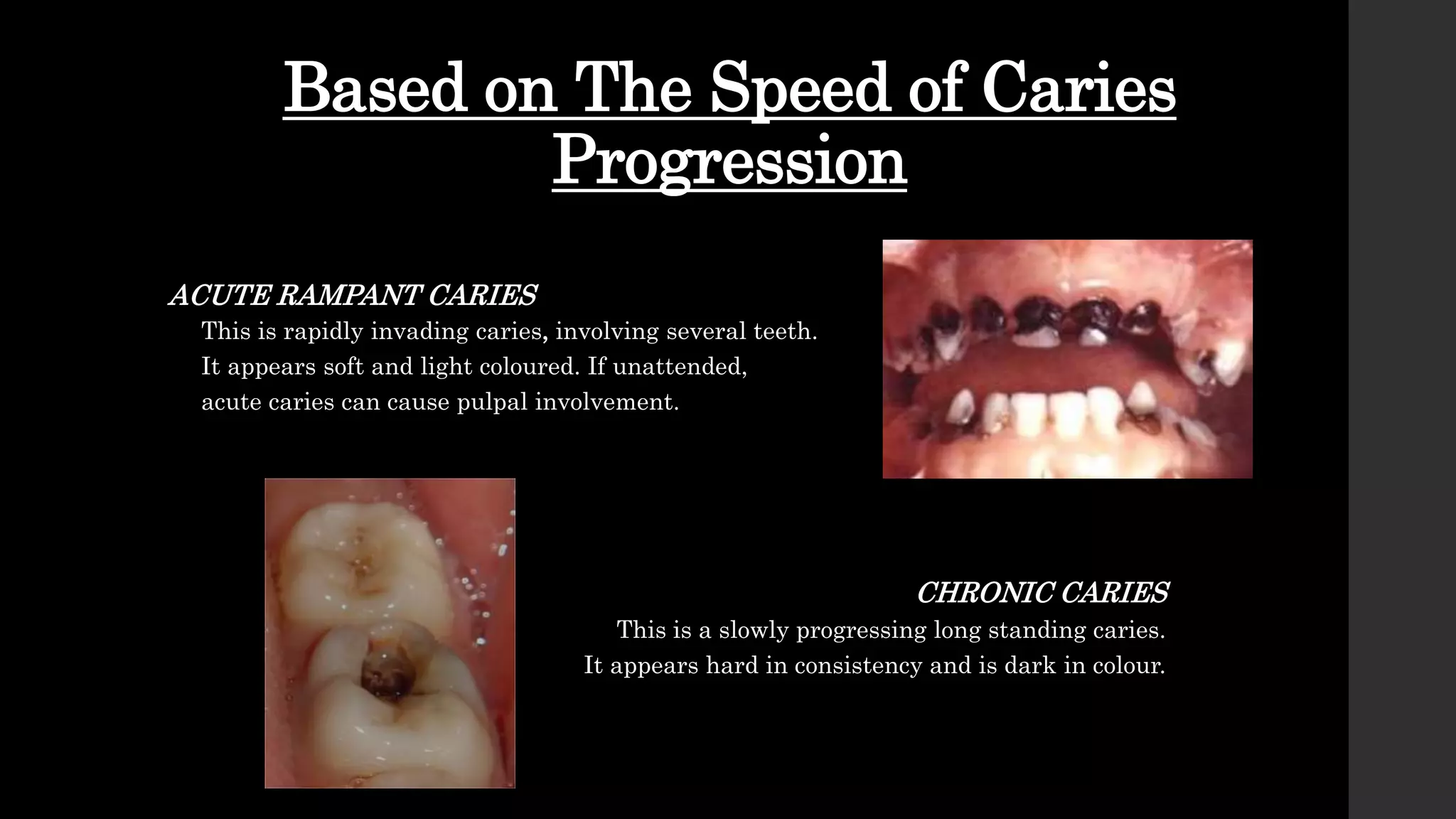
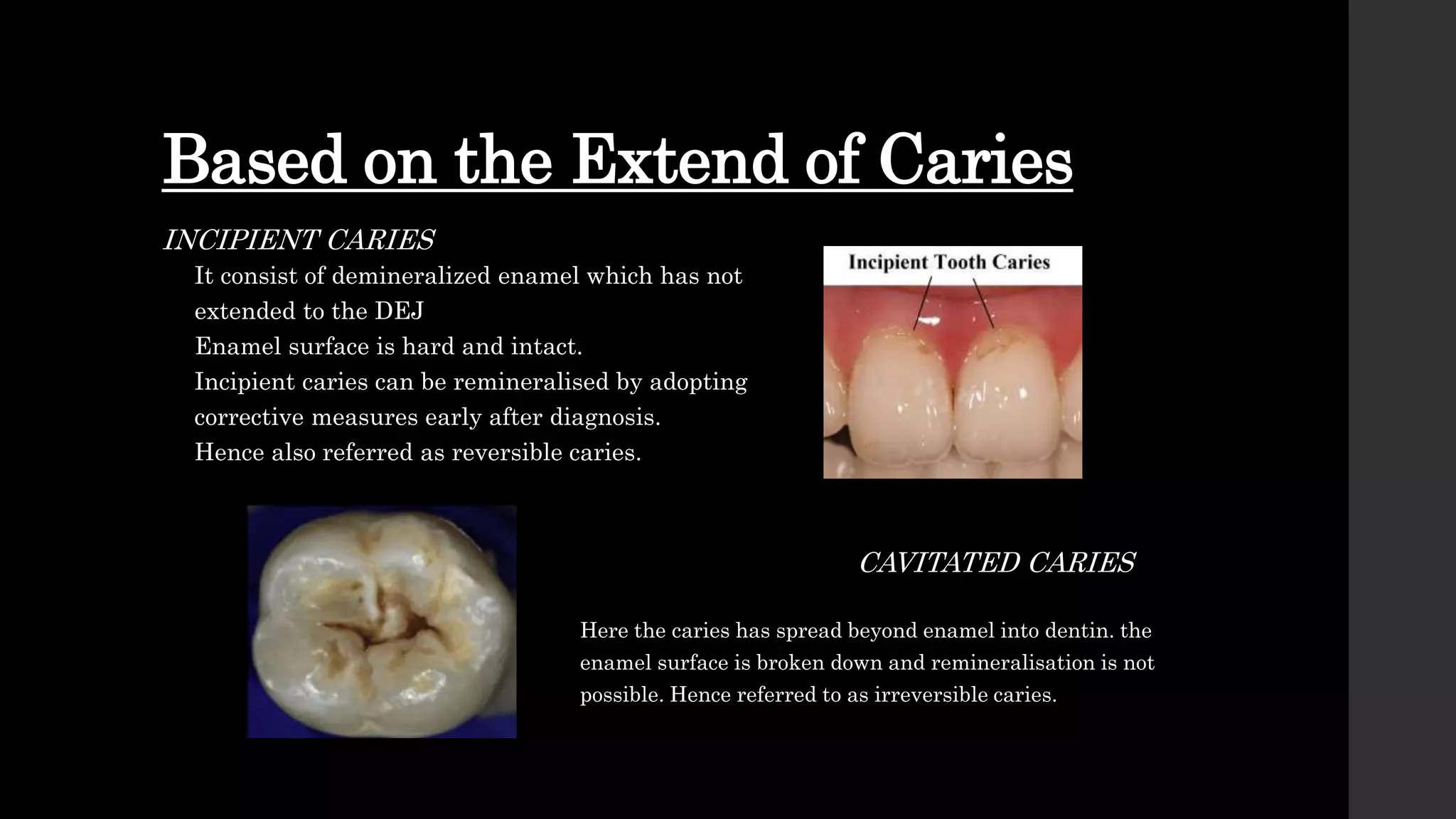
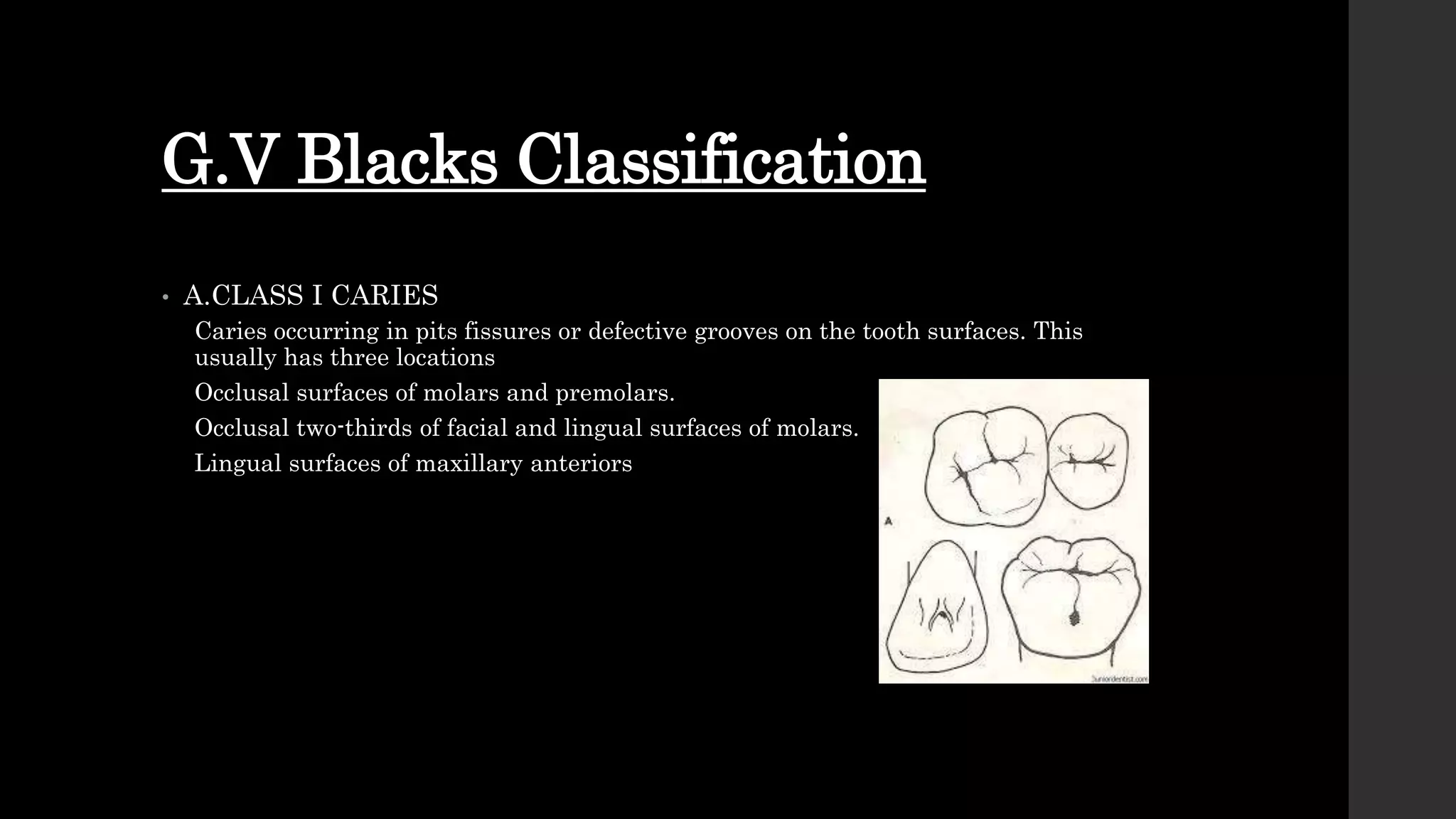
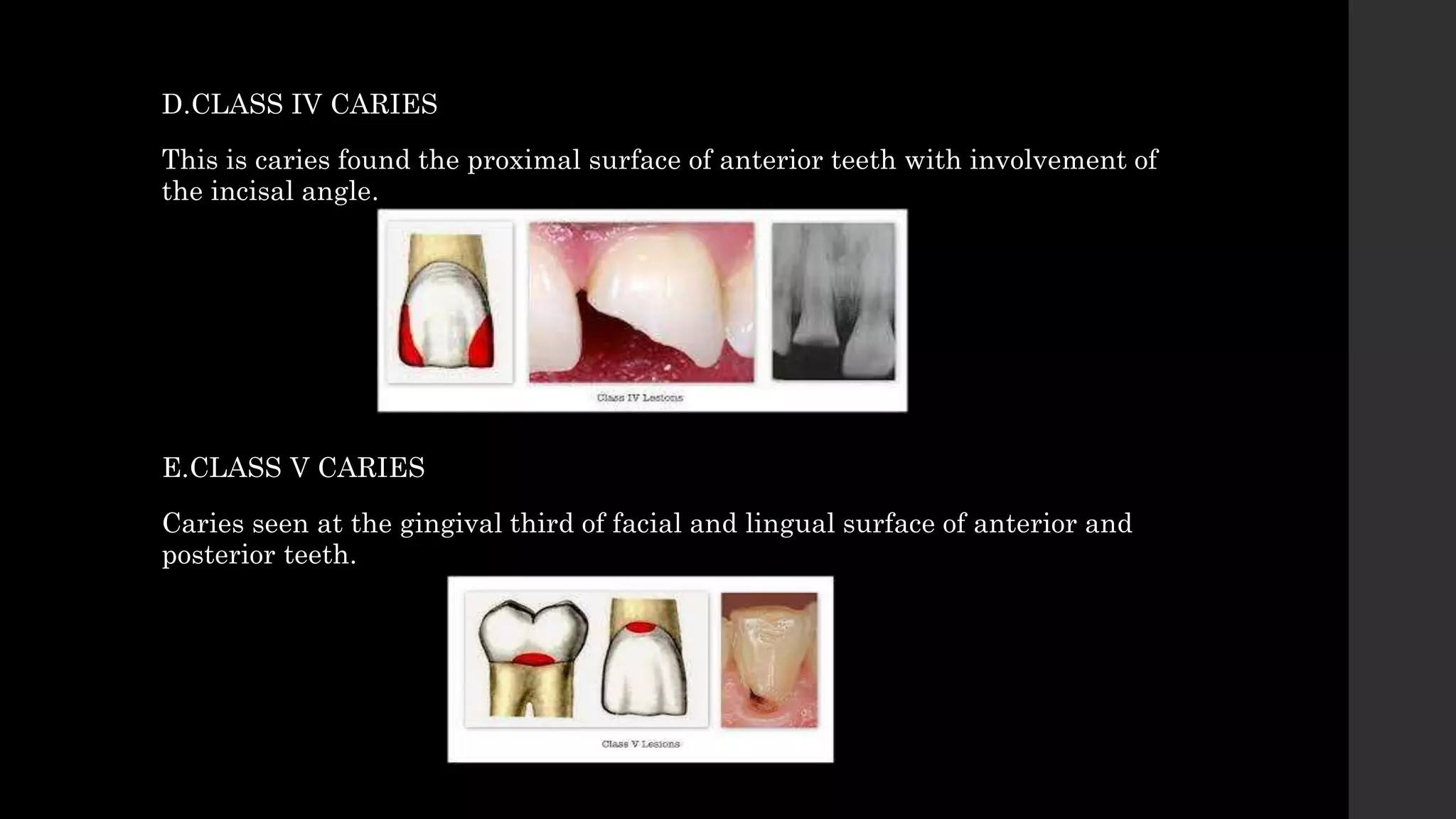
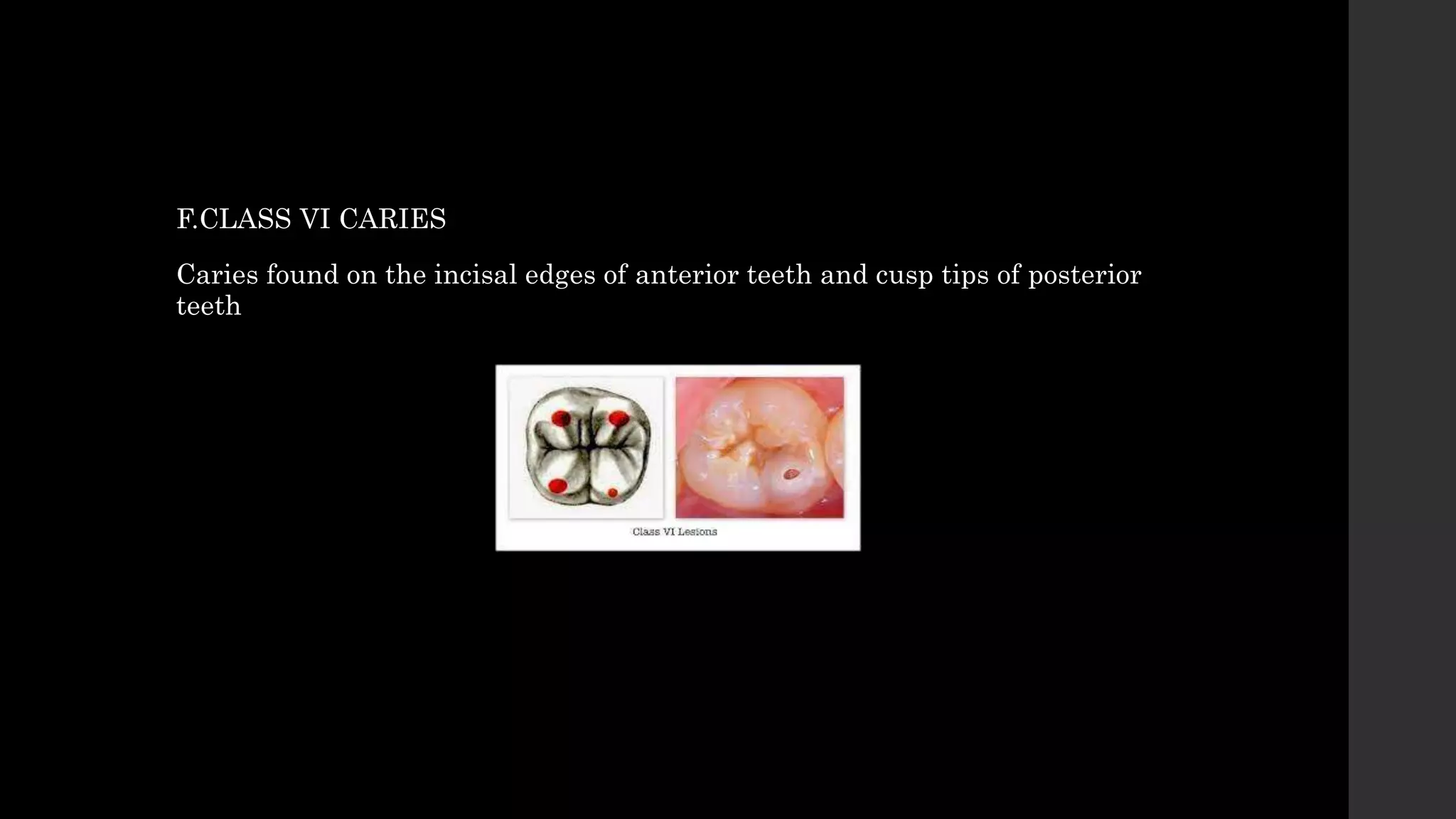
The document discusses dental caries, including its classification, etiology, pathogenesis, and prevention strategies. It highlights the multifactorial nature of caries as an infectious disease driven by bacteria, dietary factors, and tooth susceptibility. Various classification systems for caries are outlined, along with their implications for treatment and management in dental practice.



![Definition
“An irreversible, microbiologic disease of the calcified tissue of teeth,
characterised by demineralisation of the inorganic portion and
destruction of organic substance of the tooth, which often leads to
cavitation”
[Shafers]
Dental caries is an infectious microbiologic disease of teeth that
results in localised dissolution and destruction of the calcified tissues.
[Strudevant]
Localised post eruptive pathologic process of external origin involving
softening of the hard tissue and proceeding to the formation of a cavity
[WHO]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcariesclassificationmicrobiology-230728182900-f94ea3b6/75/Dental-Caries-classification-Microbiology-4-2048.jpg)