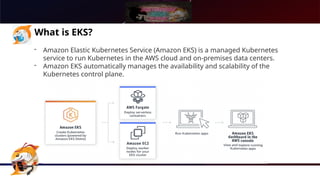
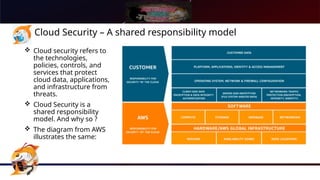
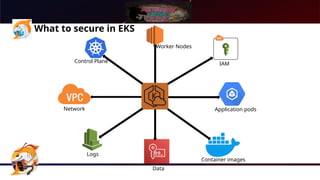
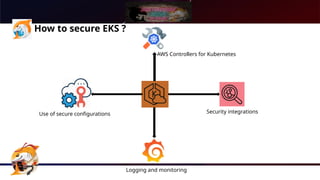
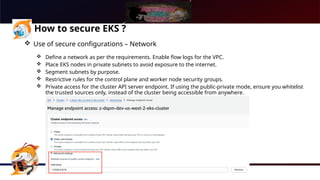
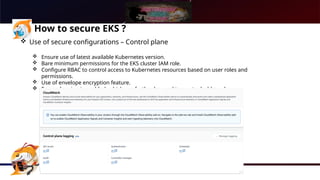
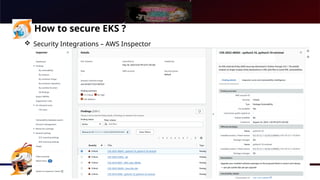
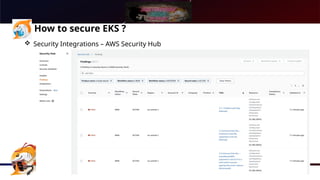
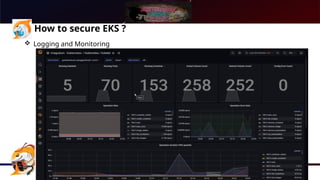
The document presents a comprehensive overview of Kubernetes security using AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), highlighting the shared responsibility model for cloud security. Key aspects include securing the network, control plane, and worker nodes through secure configurations and integrations with tools like AWS Inspector and AWS Security Hub. It also emphasizes the importance of logging and monitoring to maintain security across EKS environments.