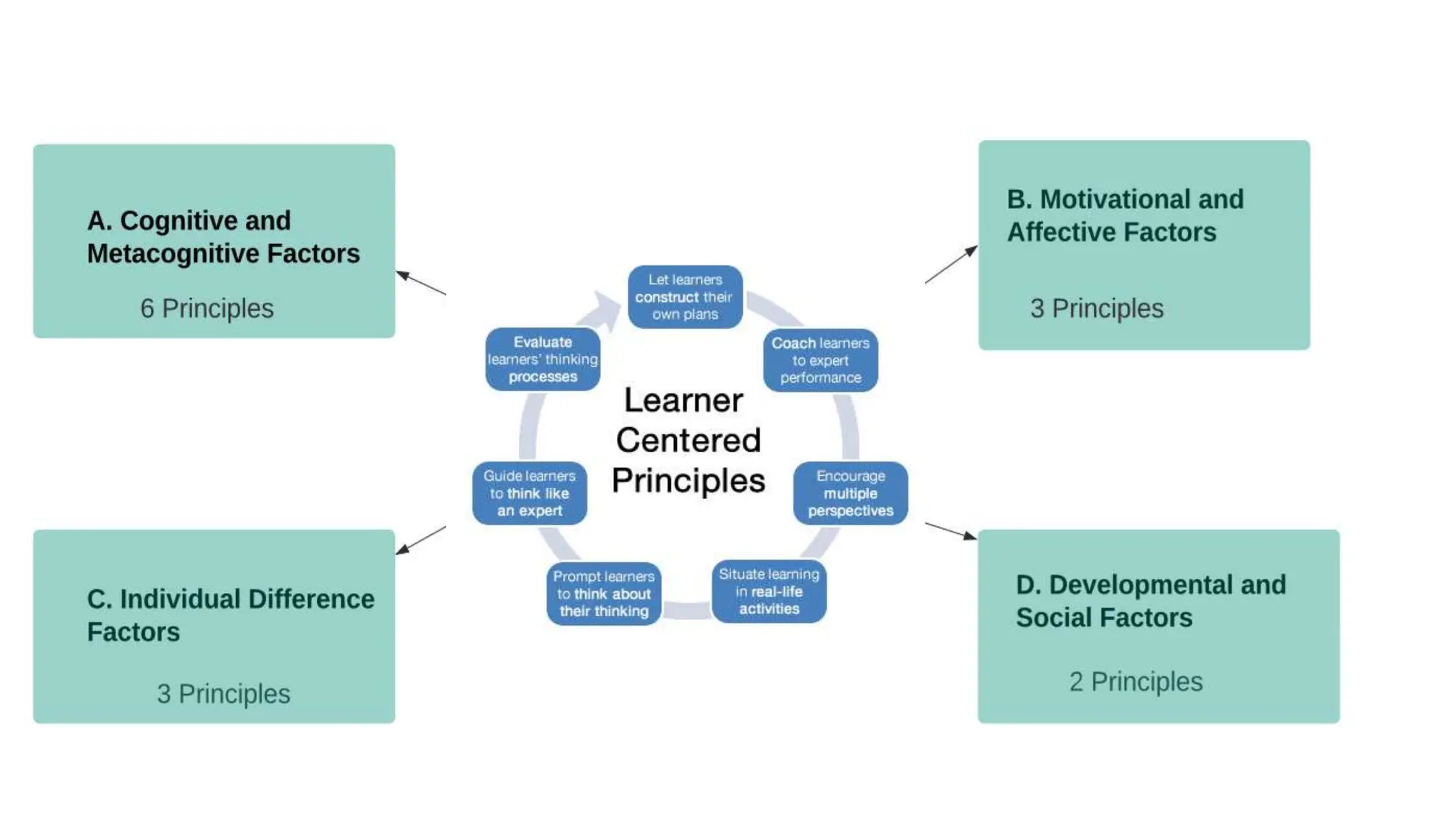
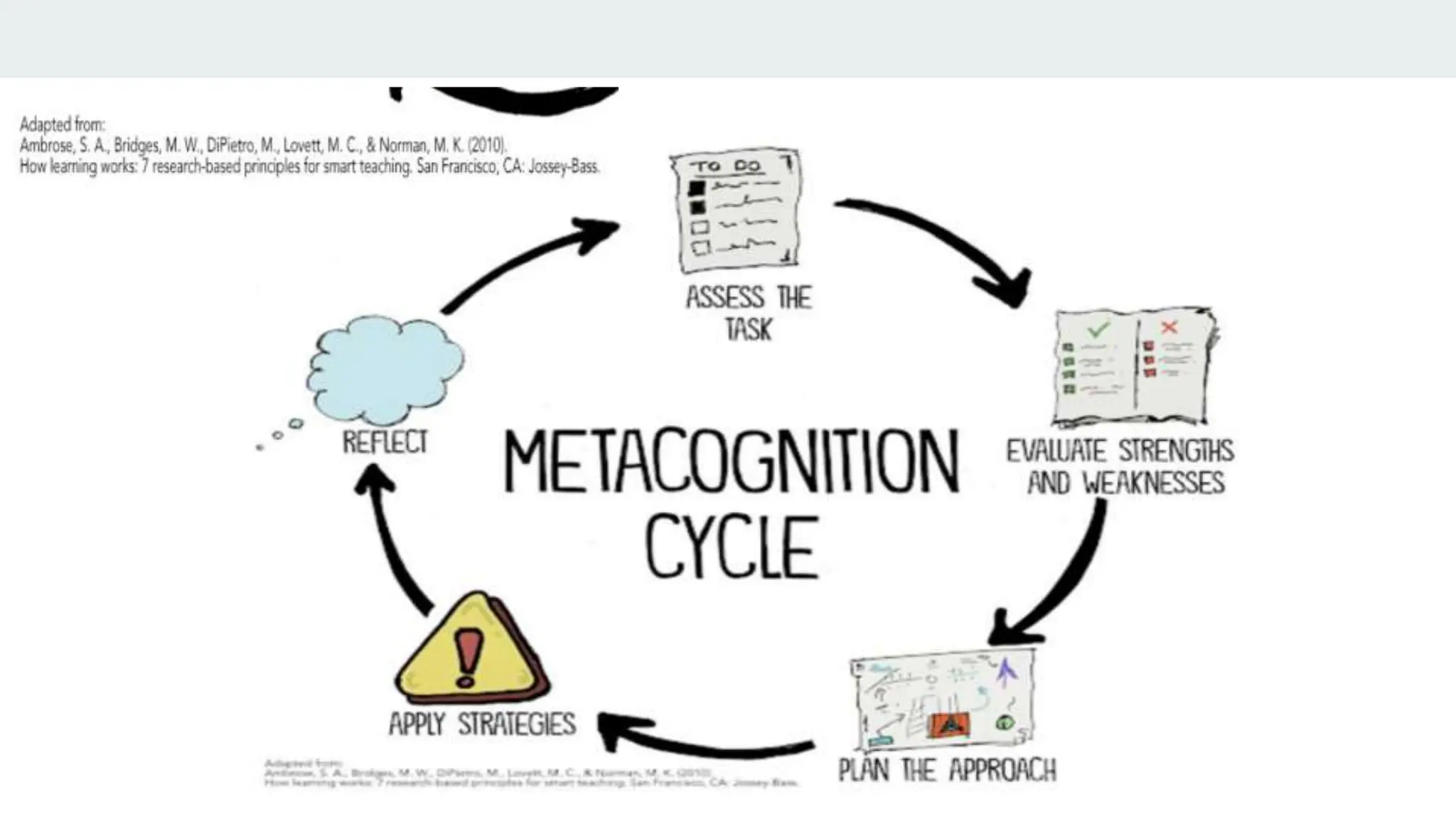
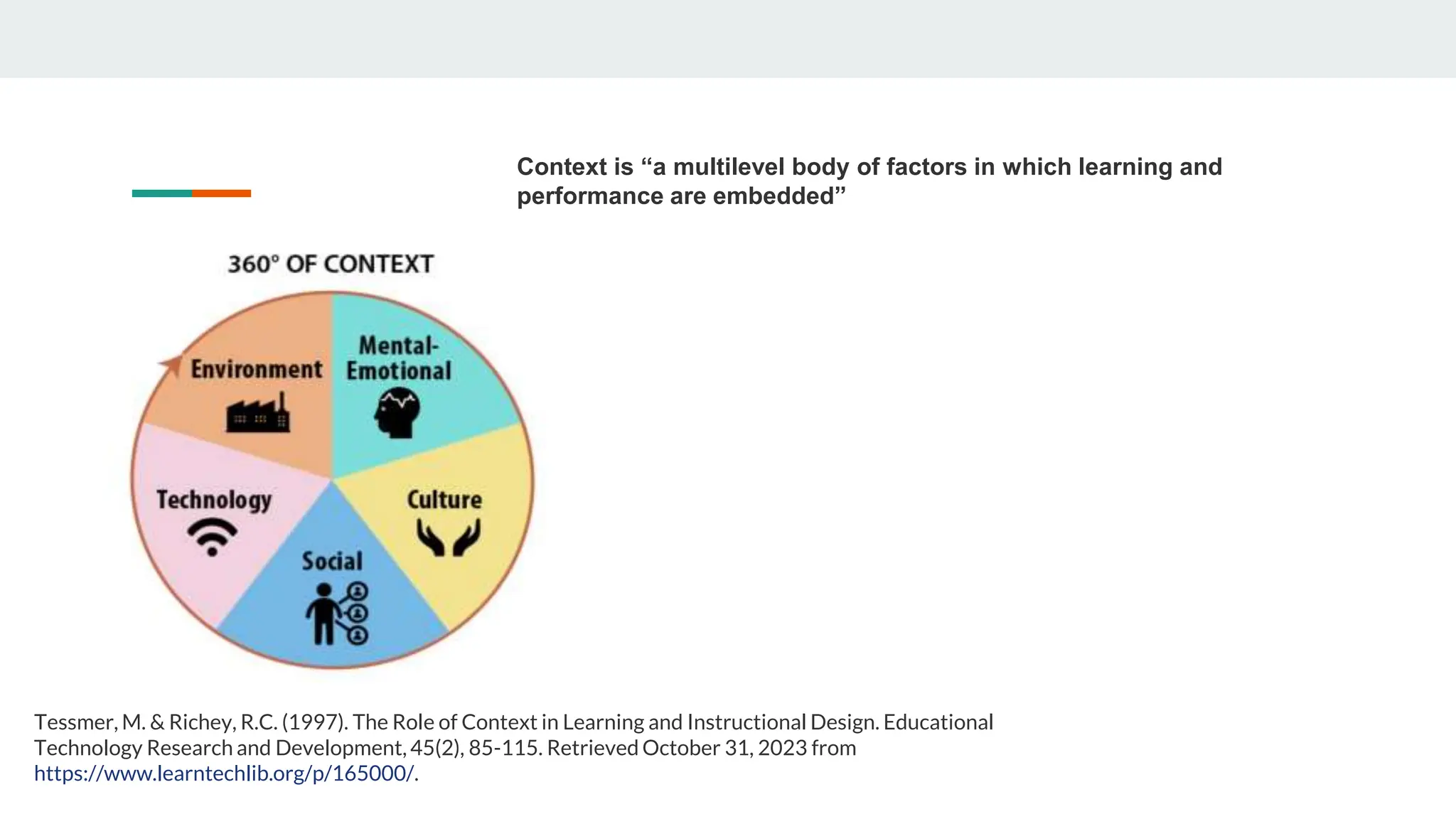
This document discusses principles of learner-centered teaching and learning. It covers cognitive and metacognitive factors like the nature of learning processes, goals of learning, and knowledge construction. It also discusses motivational and affective factors such as intrinsic motivation and the effects of motivation on effort. Additionally, it outlines individual differences factors, developmental and social influences on learning, and how the context of learning can impact the learning process. Research studies highlighted found that learner-centered teaching had a significant positive impact on students' learning outcomes and development of learning skills and strategies.