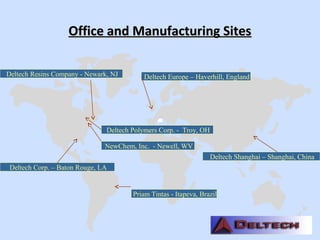
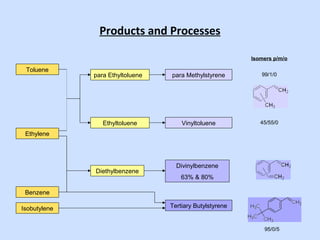
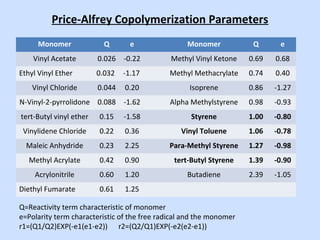
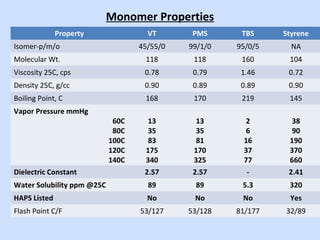
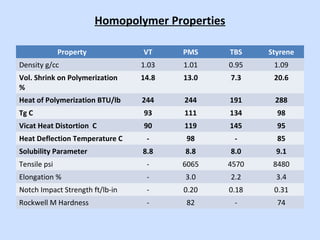
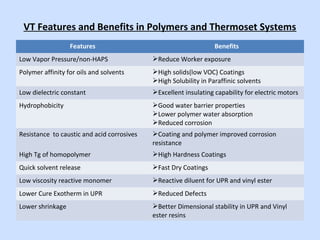
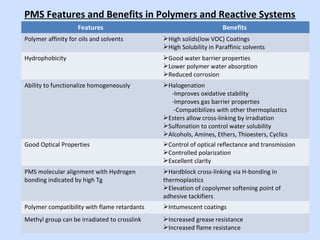
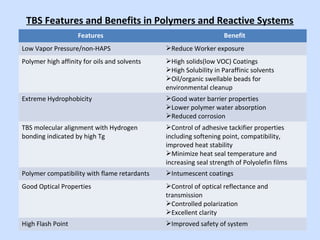
Deltech Corporation is a global supplier of monomers and polymers that was formed through a series of acquisitions between 1989-2008. It has manufacturing sites in the US, UK, Brazil, China, and sales offices in Brazil and China. The company produces a variety of monomers including vinyl toluene, para-methylstyrene, and tert-butylstyrene. These monomers are used to make polymers and resins for applications such as coatings, adhesives, composites, and functional polymers. Deltech has advantages of multi-scale production, raw material sourcing, global presence, custom capabilities, and customer support.