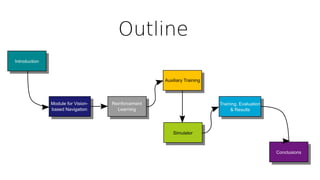
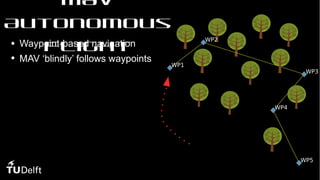
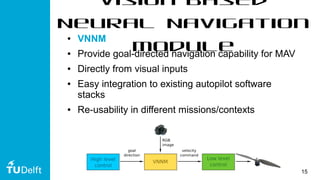
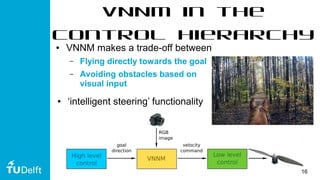
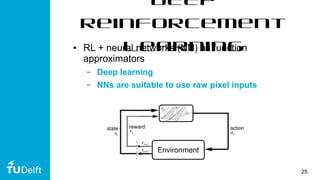
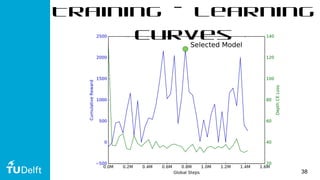
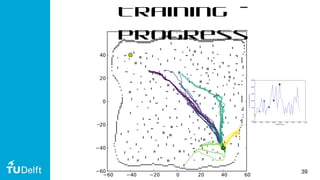
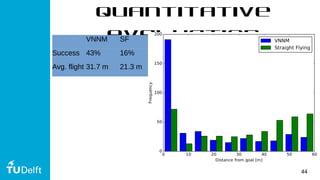
This document discusses using deep reinforcement learning for goal-directed visual navigation with micro aerial vehicles (MAVs). It presents a vision-based neural navigation module (VNNM) that provides goal-directed navigation capability for MAVs directly from visual inputs. The VNNM is trained using reinforcement learning in a simulated forest environment. Evaluation shows the VNNM can successfully navigate to goals 43% of the time, compared to 16% for straight flying, covering an average distance of 31.7 meters. While obstacle avoidance performance did not meet initial expectations, incorporating domain adaptation techniques may help address the reality gap between simulation and the real world.