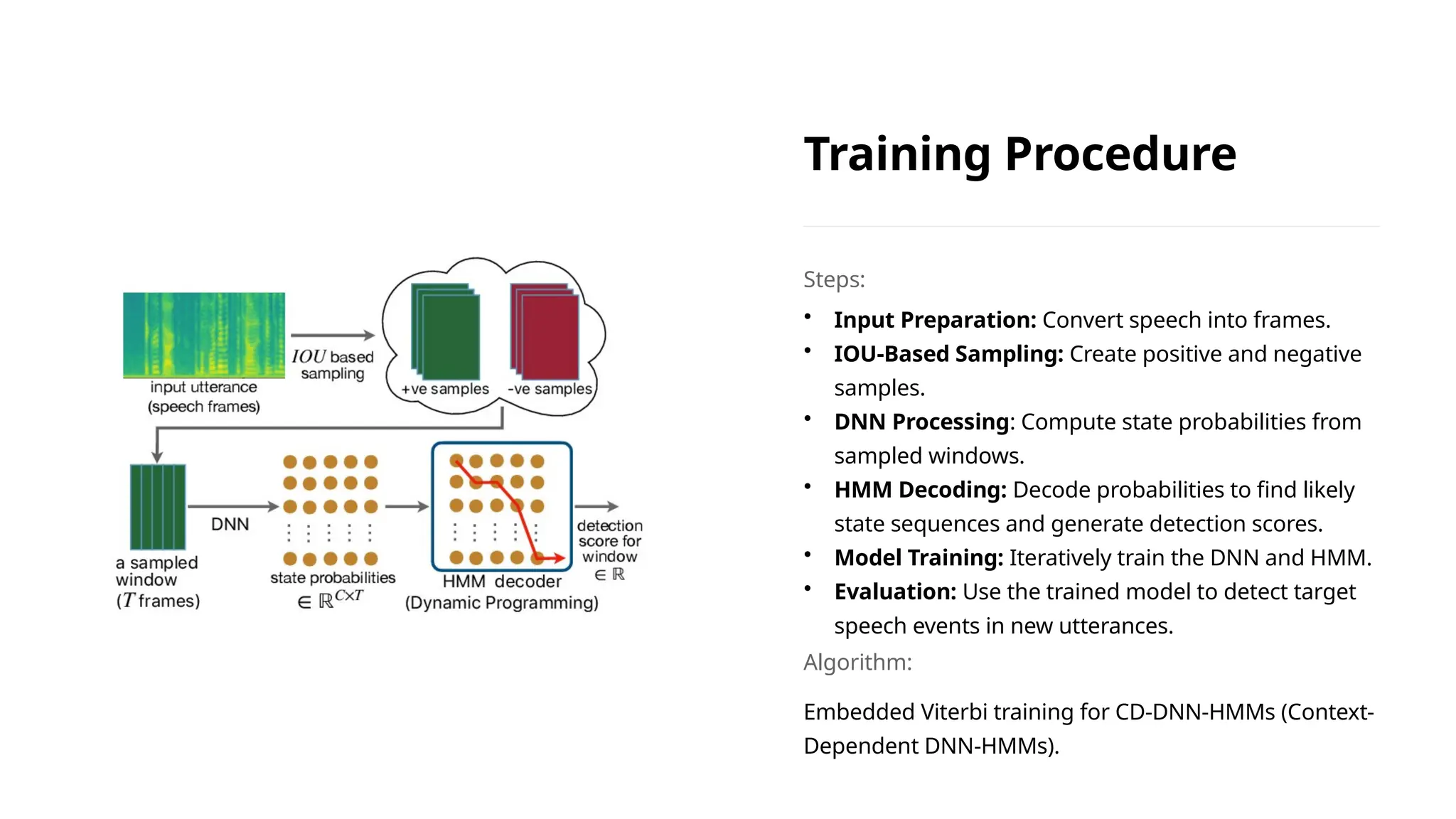
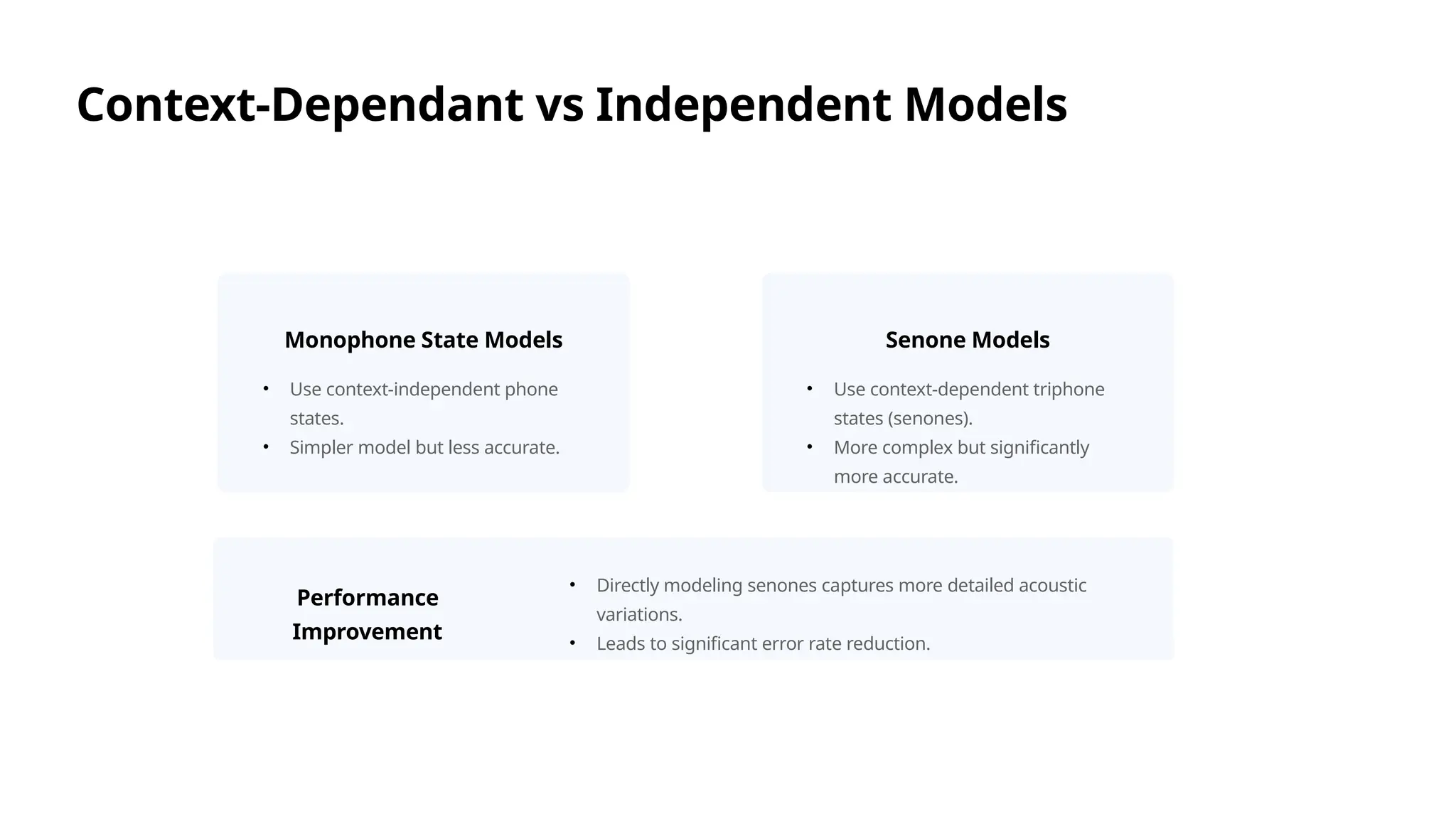
The document discusses the architecture and advantages of deep neural network-hidden Markov model (DNN-HMM) hybrid systems for speech recognition, highlighting performance improvements over traditional Gaussian mixture model-HMM systems. Key points include the effective training and decoding process utilizing the discriminative nature of DNNs and the importance of model depth and context-dependent state modeling. The findings indicate that DNN-HMM systems enable significant advancements in automatic speech recognition technology.