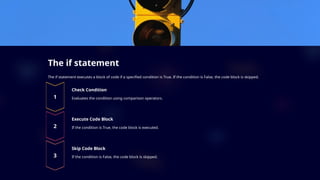
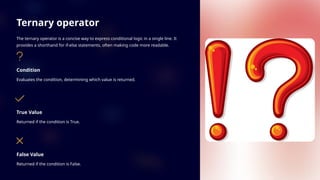
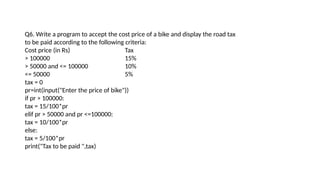
The document provides an introduction to conditional statements in Python, detailing their importance in decision-making and program flow. It covers various types of conditional statements, including if, else, and elif, as well as comparison operators, nested statements, and the ternary operator. Additionally, it discusses common use cases and provides example programs to illustrate the application of conditional logic.