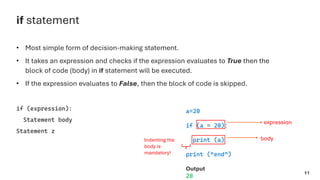
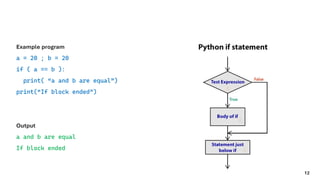
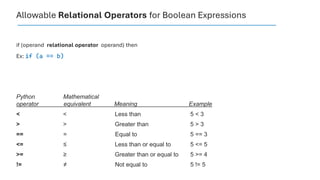
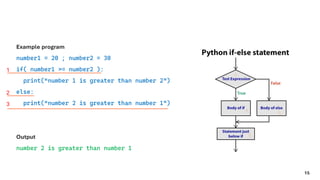
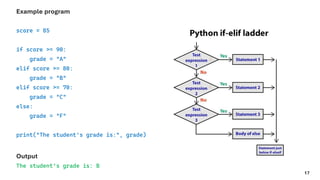
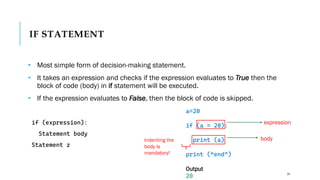
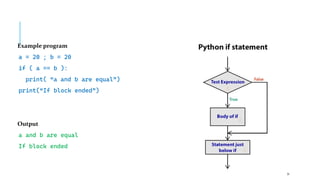
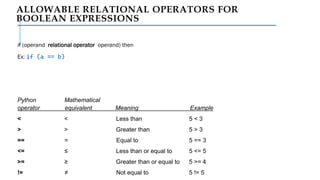
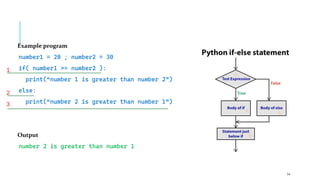
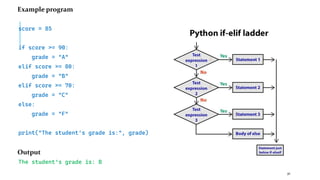
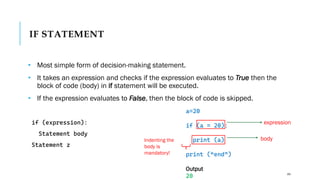
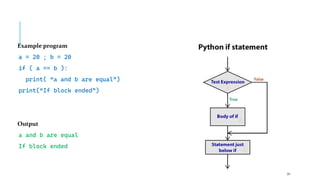
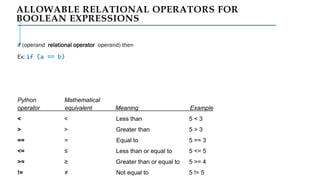
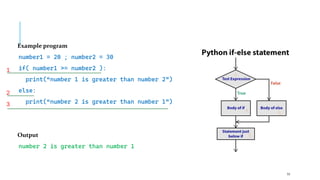
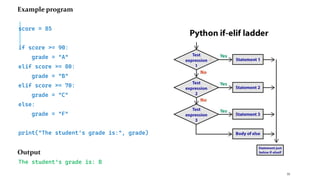
The document serves as an introduction to programming, emphasizing decision-making statements in Python. It outlines key concepts such as the basics of programming, the functionality of Python, and specific conditional statements like 'if', 'if-else', and 'if-elif'. The material also highlights the significance of these statements in automating tasks and aiding business decisions.