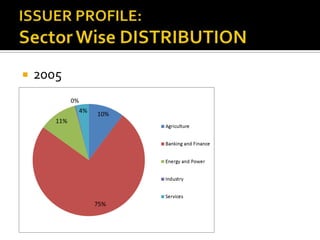
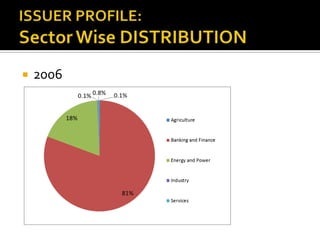
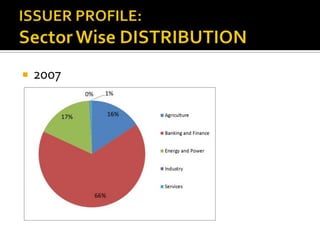
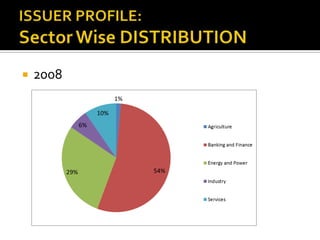
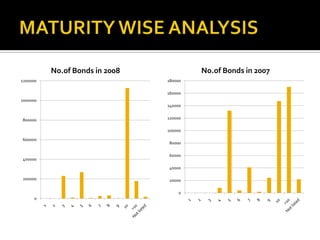
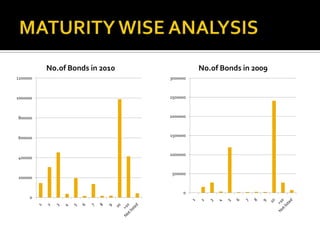
The document analyzes India's corporate bond market and suggests reforms. It notes that the corporate bond market is underdeveloped compared to the government bond market. Some key points:
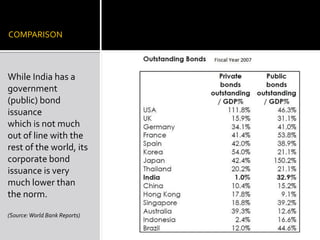
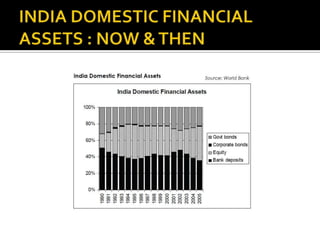
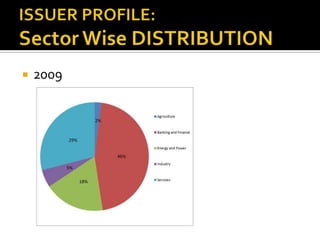
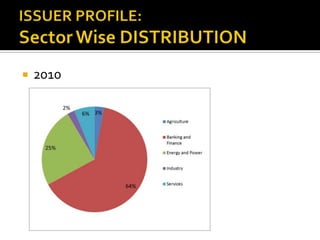
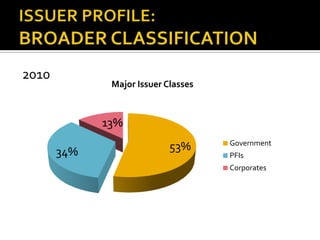
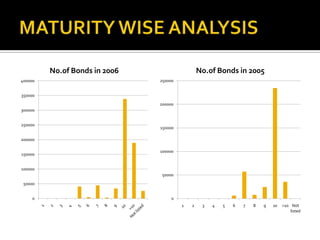
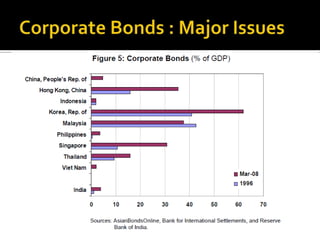
- Corporate bonds make up a very small portion of India's domestic financial assets compared to other countries.
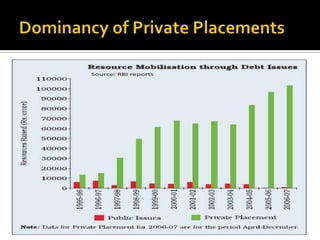
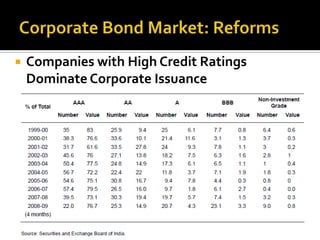
- Most corporate bond issuances are private placements rather than public issues. Trading is also over-the-counter rather than exchange-based.
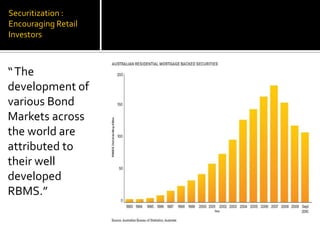
- Reforms like removing taxes on corporate bonds, giving more flexibility to investors, and allowing corporate bonds to be used as collateral could help develop the market. Expanding securitization could also encourage retail investment.