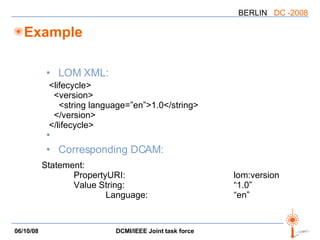
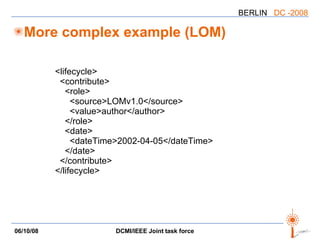
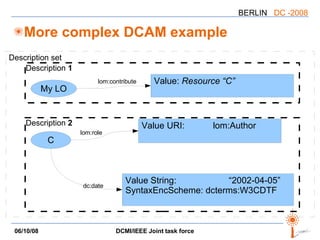
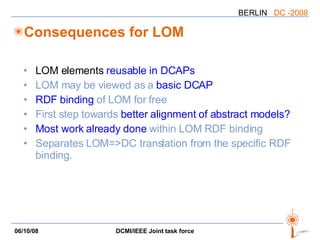
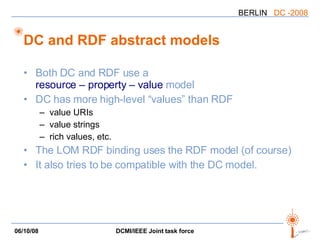
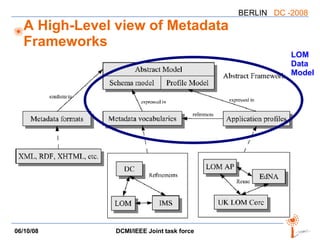
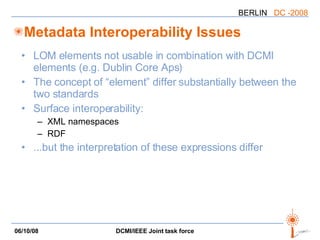
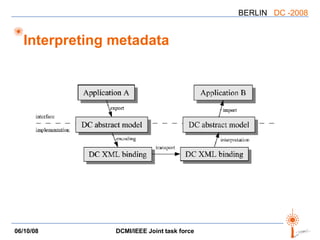
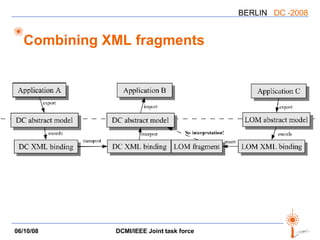
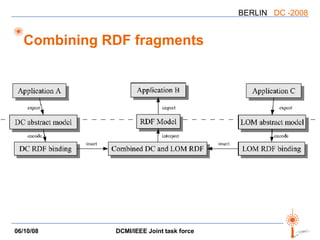
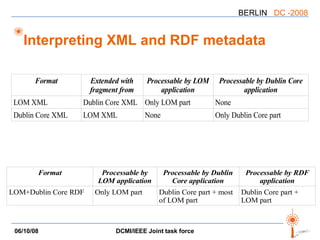
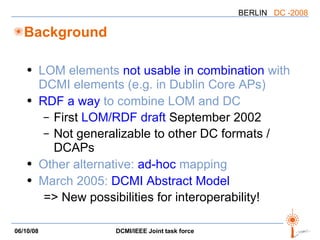
The document discusses two PARs (Project Authorization Requests) from the DCMI-IEEE LTSC Task Force regarding defining an RDF vocabulary for IEEE Learning Object Metadata (LOM) elements and a recommended practice for expressing LOM instances using the Dublin Core Abstract Model. The task force aims to improve interoperability between LOM and Dublin Core metadata by addressing differences in their abstract models and defining mappings between LOM elements and DCAM concepts. Work is ongoing to update related documents and develop an application profile and transformations based on the new recommendations.










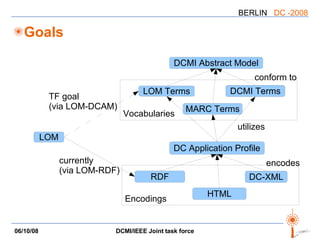

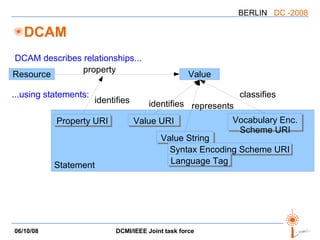
![LOM => DCAM mapping Recommendation for using LOM metadata in Dublin Core descriptions A mapping “LOM elements” => “instances of DCAM concepts” Not a binding, but a translation (lossy in part) All constructs are used: properties, value strings, value URIs, [vocabulary|syntax] encoding schemes, related descriptions, except rich representations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc-2008-dcmiieee-workshop-2695/85/DC-2008-DCMI-IEEE-workshop-17-320.jpg)