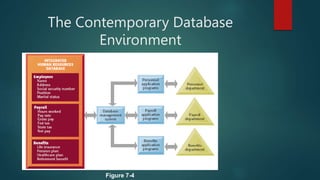
This document introduces database management systems (DBMS). It explains that a DBMS allows for the centralized management of interrelated data through a set of programs. It provides examples of common database applications in fields like banking, education, manufacturing, and more. The document then contrasts file-based systems with DBMS, noting limitations of file-based systems like data duplication, inconsistencies, and inability to perform complex queries. Key advantages of DBMS are also outlined, including reduced data redundancy, improved data integrity and security, and support for simultaneous access and transactions.