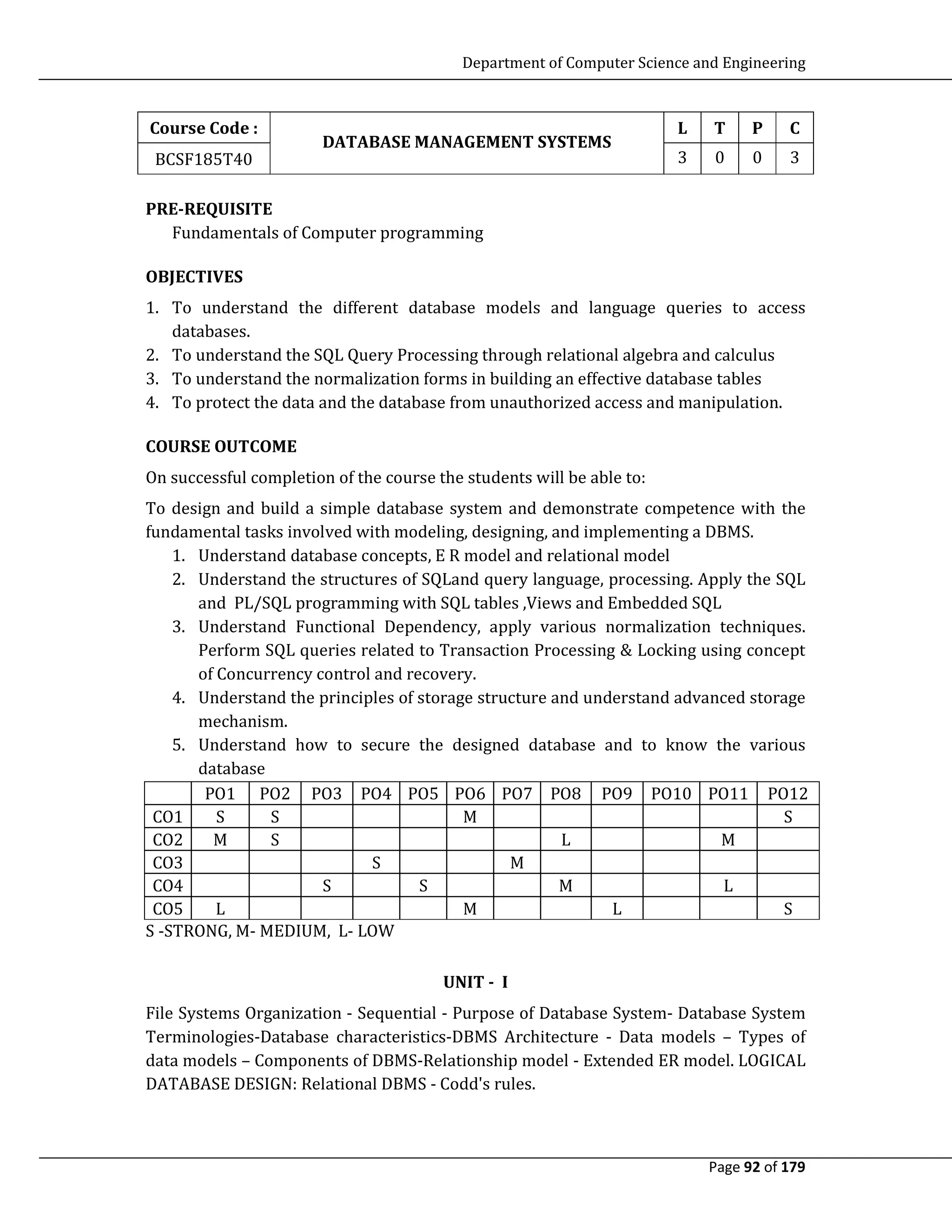
This document outlines a course on database management systems. The course objectives are to understand different database models, SQL queries, normalization techniques, and database security. The course outcomes are for students to design simple databases, understand relational models and SQL, apply normalization, and secure databases. The course covers topics like data models, relational algebra, normalization, transactions, physical storage, indexing, and security. It is a 3 credit course with prerequisites in programming fundamentals.