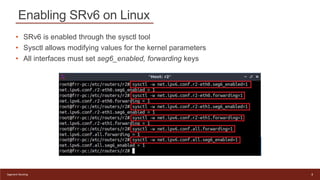
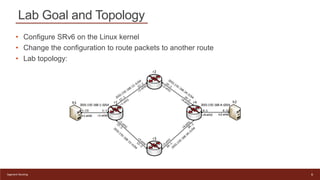
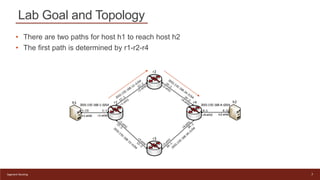
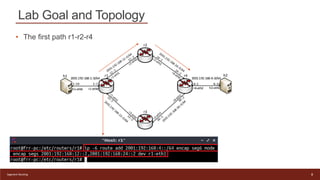
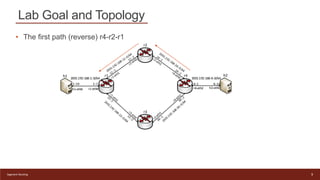
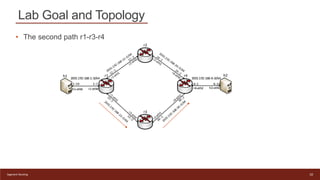
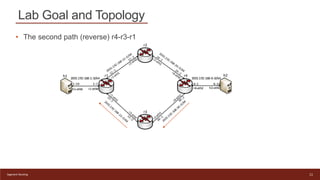
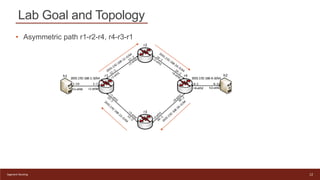
This document provides an introduction to configuring Segment Routing over IPv6 (SRv6) on Linux routers. It describes enabling SRv6 using sysctl, adding routes with segment routing headers using iproute2, and a lab topology with two paths between hosts h1 and h2 going through different combinations of SRv6-capable and non-capable routers. The goal is to configure the first path using SRv6 and then change it to use the second path instead.