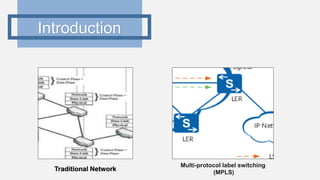
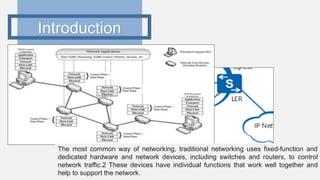
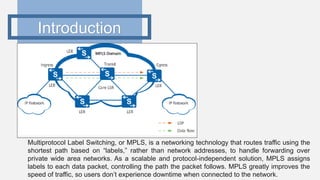
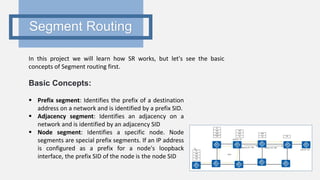
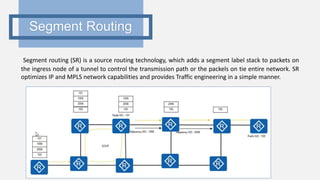
This document provides an outline for a project comparing SRv4 and SRv6. It begins with an introduction to traditional networks, MPLS, and segment routing. It explains that segment routing aims to overcome issues with MPLS while retaining its advantages. The objectives are to study traditional networks and MPLS, implement both SRv4 and SRv6, and compare the two versions of segment routing. Finally, it includes a project time plan spanning October to March.