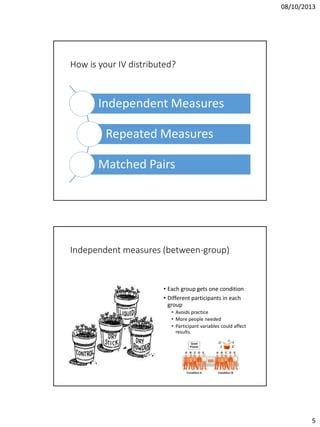
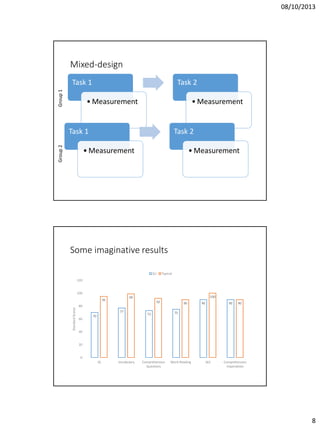
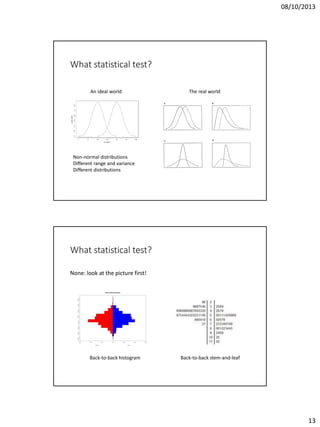
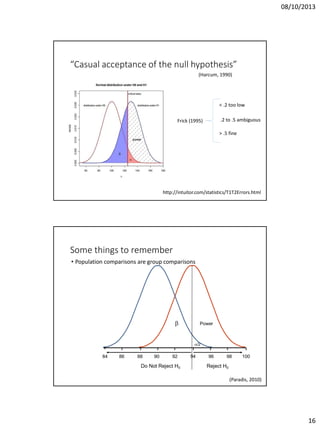
The document discusses issues in experimental design for studying atypical language development. It covers the differences between controlled experiments, field experiments, and natural experiments. Controlled experiments allow for precise control but lack generalizability, while field and natural experiments are more reflective of real life but have less control. The document also addresses within-subject repeated measures designs versus between-group independent measures designs. It notes the importance of counterbalancing to control for order effects. Additional topics covered include matching groups on relevant variables, checking the distribution of data to select appropriate statistical tests, and keeping thorough lab notes.