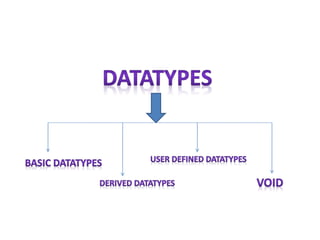
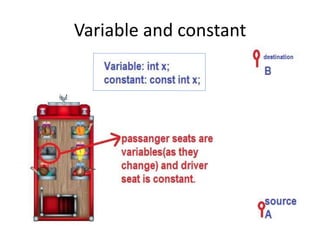
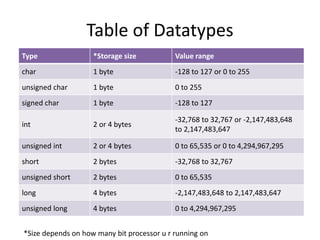
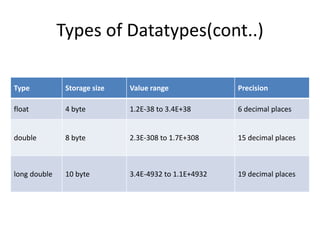
The document explains the concept of datatypes in programming, particularly in the C language, emphasizing the importance of variables and constants for holding values. It provides examples of different datatypes, their storage sizes, value ranges, and syntax for declaration and usage. Additionally, it discusses the printf function for formatted output in C with various format specifiers.