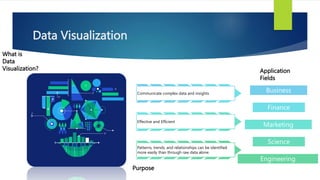
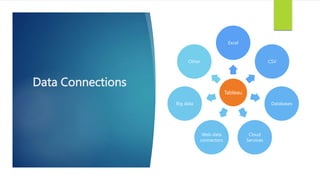
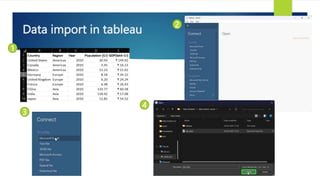
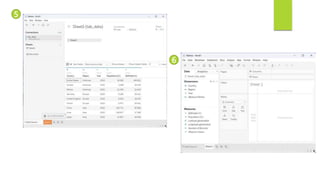
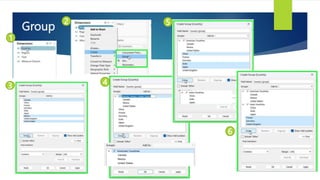
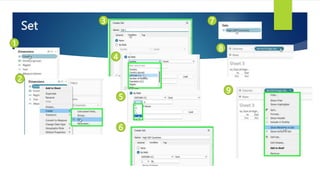
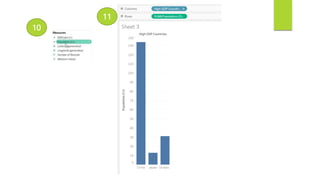
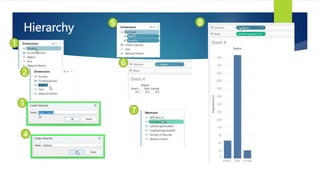
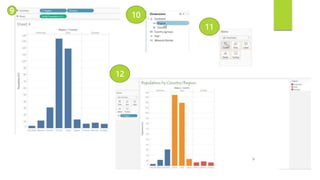
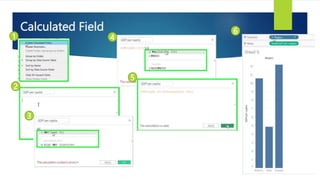
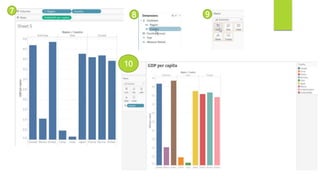
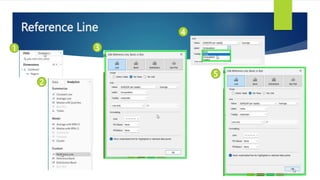
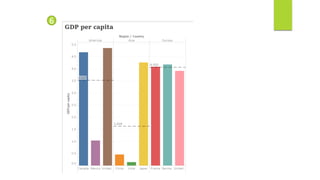
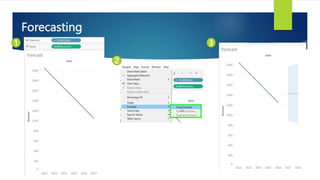
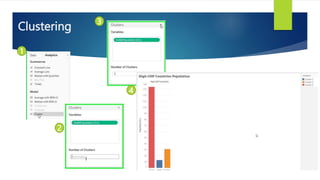
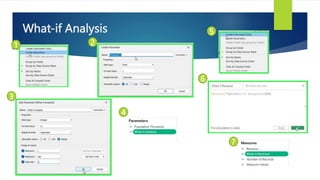
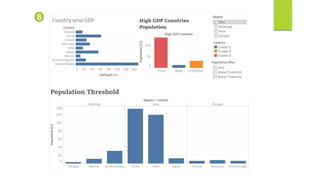
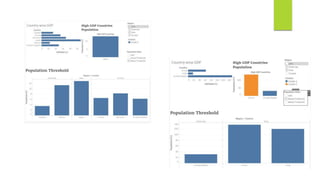
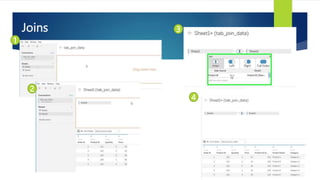
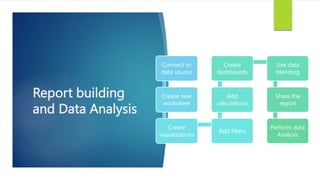
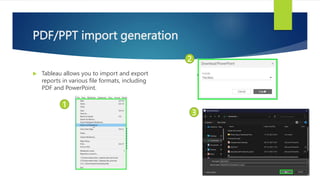
Data visualization and storytelling help communicate complex data and insights in an effective and efficient manner. Tableau is a self-service business intelligence tool that allows users to connect to various data sources, perform data preparation tasks, and create interactive visualizations, reports, dashboards, and stories. It provides features like filters, groups, sets, hierarchies, parameters, forecasting, clustering, and what-if analysis to explore and analyze data. Users can build dashboards with well-designed layouts and share reports in different file formats to facilitate data analysis and decision making.