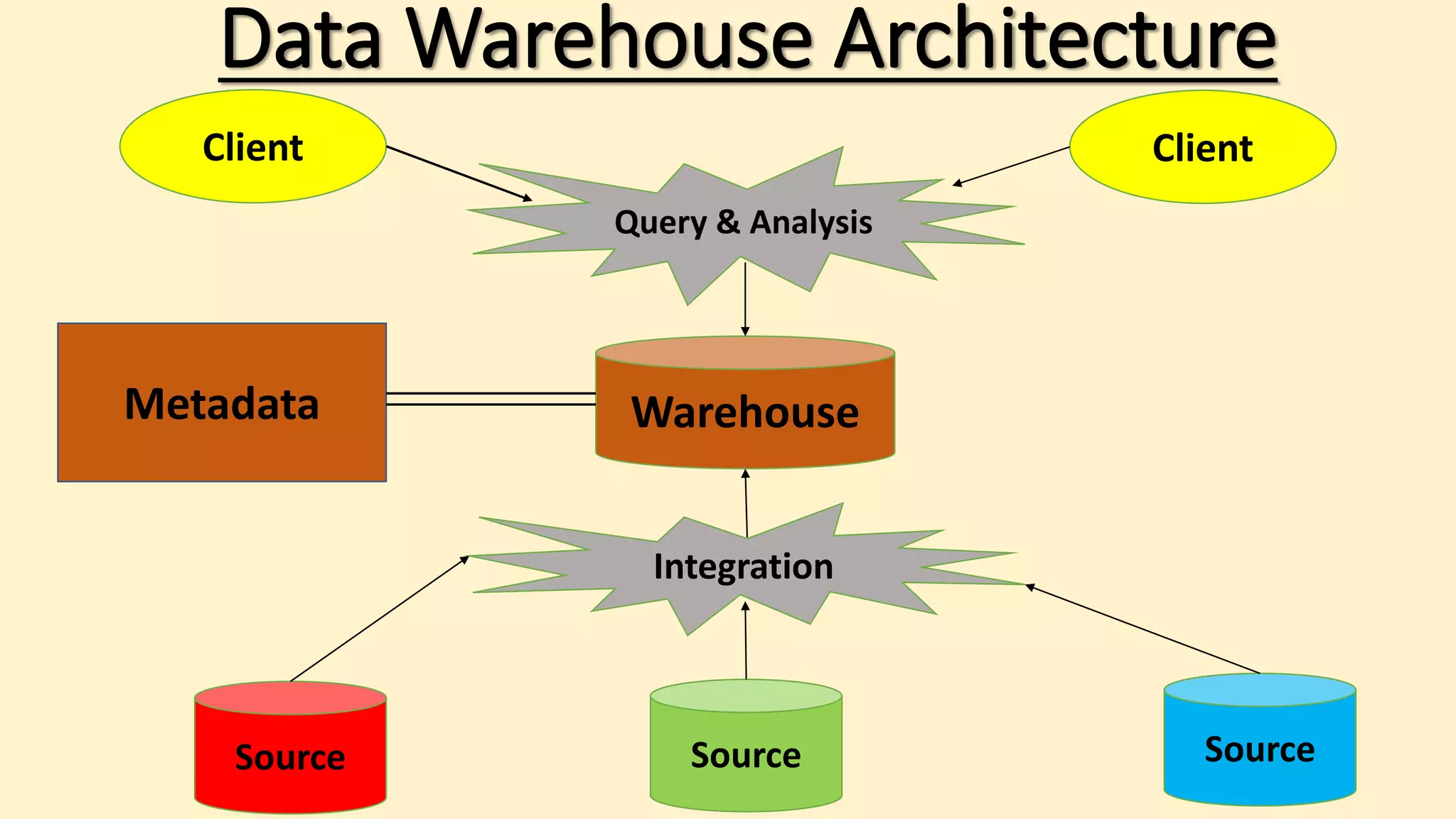
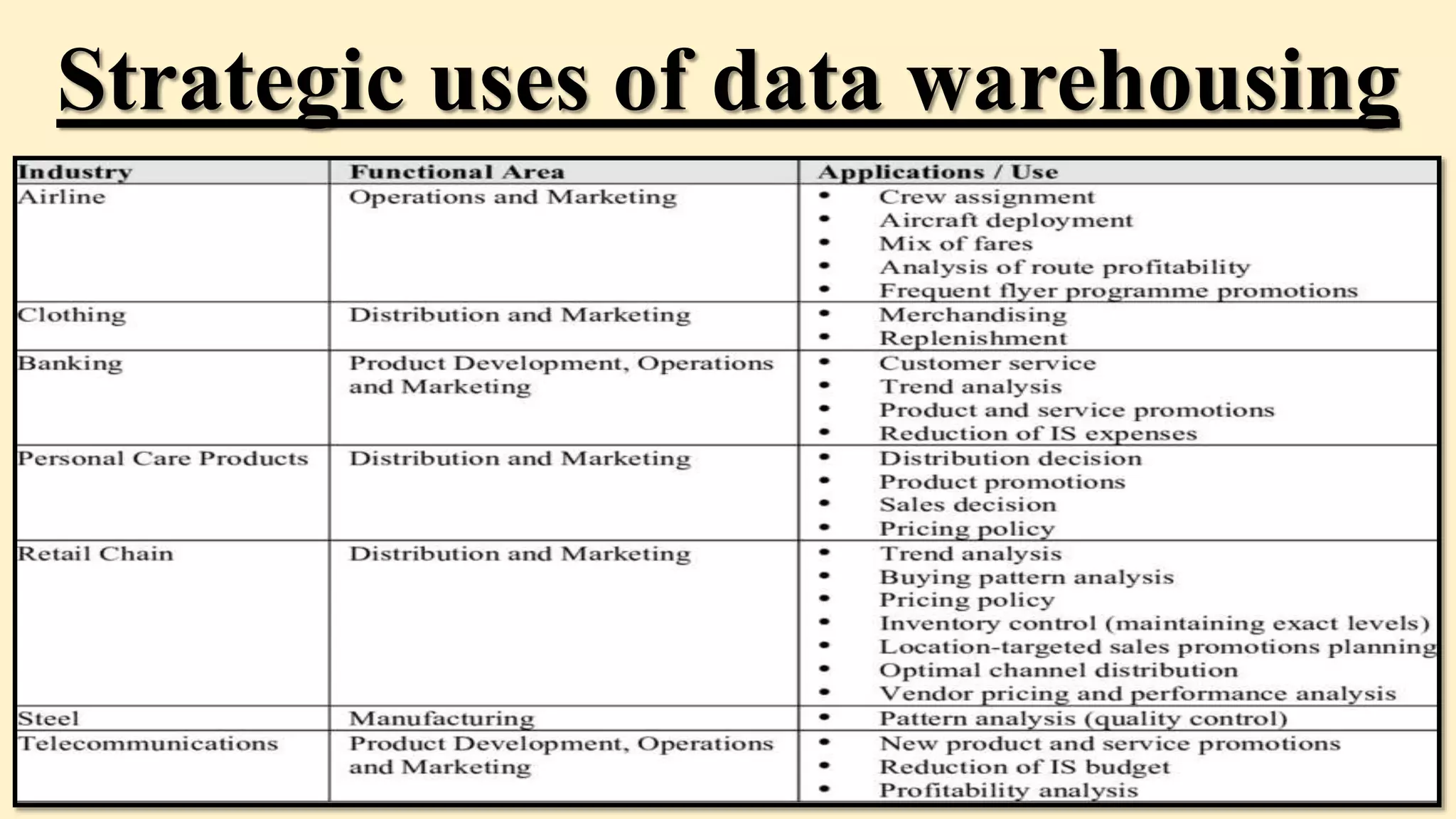
A data warehouse is a single, complete store of consistent data from multiple sources made available for business users. It transforms data into useful business information in a timely manner to support management decision making. A data warehouse uses a relational or multidimensional database to hold extracted, transformed, and loaded data from transaction systems specifically for querying and reporting. It allows businesses to answer questions that were not previously possible by assembling and managing data from various sources. The concept of data warehouses emerged in the late 1980s, with early uses in retail sales in the 1970s. A data warehouse architecture typically includes clients, a query and analysis layer, an ETL process, the warehouse itself, and source systems. While powerful, data warehouses also have