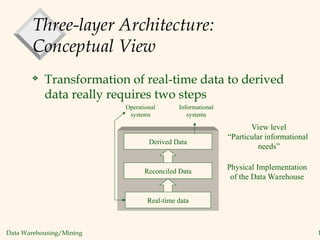
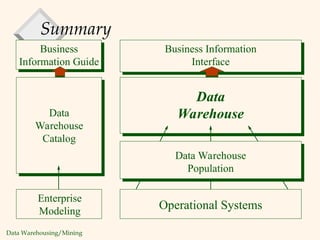
The document discusses the evolution and characteristics of data warehousing, defining it as a centralized repository for diverse data aimed at facilitating analysis and decision-making. It outlines the differences between operational databases and data warehouses, emphasizing factors such as data volume, volatility, and user engagement. The document also highlights the significance and growth of data warehousing in the industry, including examples of major implementations and architectural concepts.





![Data Warehousing/Mining
Warehousing and Industry
Warehousing is big business
– $2 billion in 1995
– $3.5 billion in early 1997
– Predicted: $8 billion in 1998 [Metagroup]
WalMart has largest warehouse
– 900-CPU, 2,700 disk, 23 TB Teradata system
– ~7TB in warehouse
– 40-50GB per day](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evolutionofdatawarehouse-250105171732-f70b1818/85/Evolution-of-Data-Warehouse-and-Data-mining-7-320.jpg)