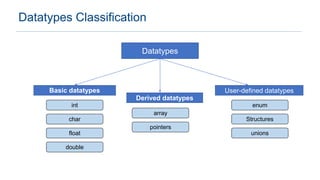
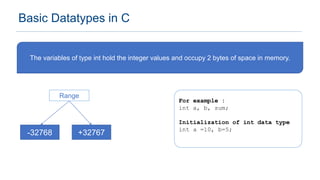
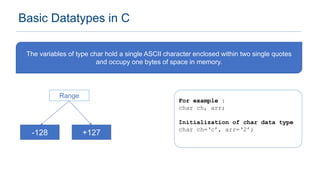
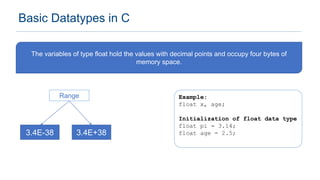
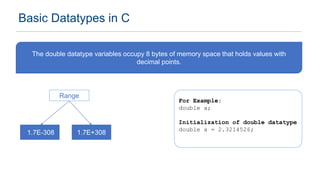
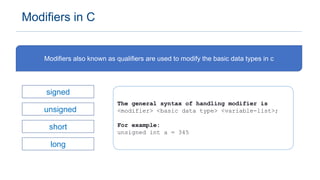
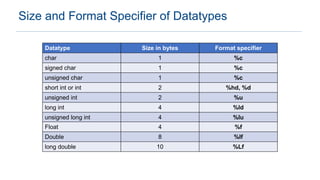
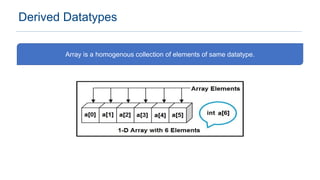
The document provides an overview of data types in C programming, detailing basic, derived, and user-defined types along with their characteristics and initialization. It covers four basic data types: int, char, float, and double, including their memory size and range. Additionally, it explains modifiers and various user-defined data types such as enum, struct, and union.