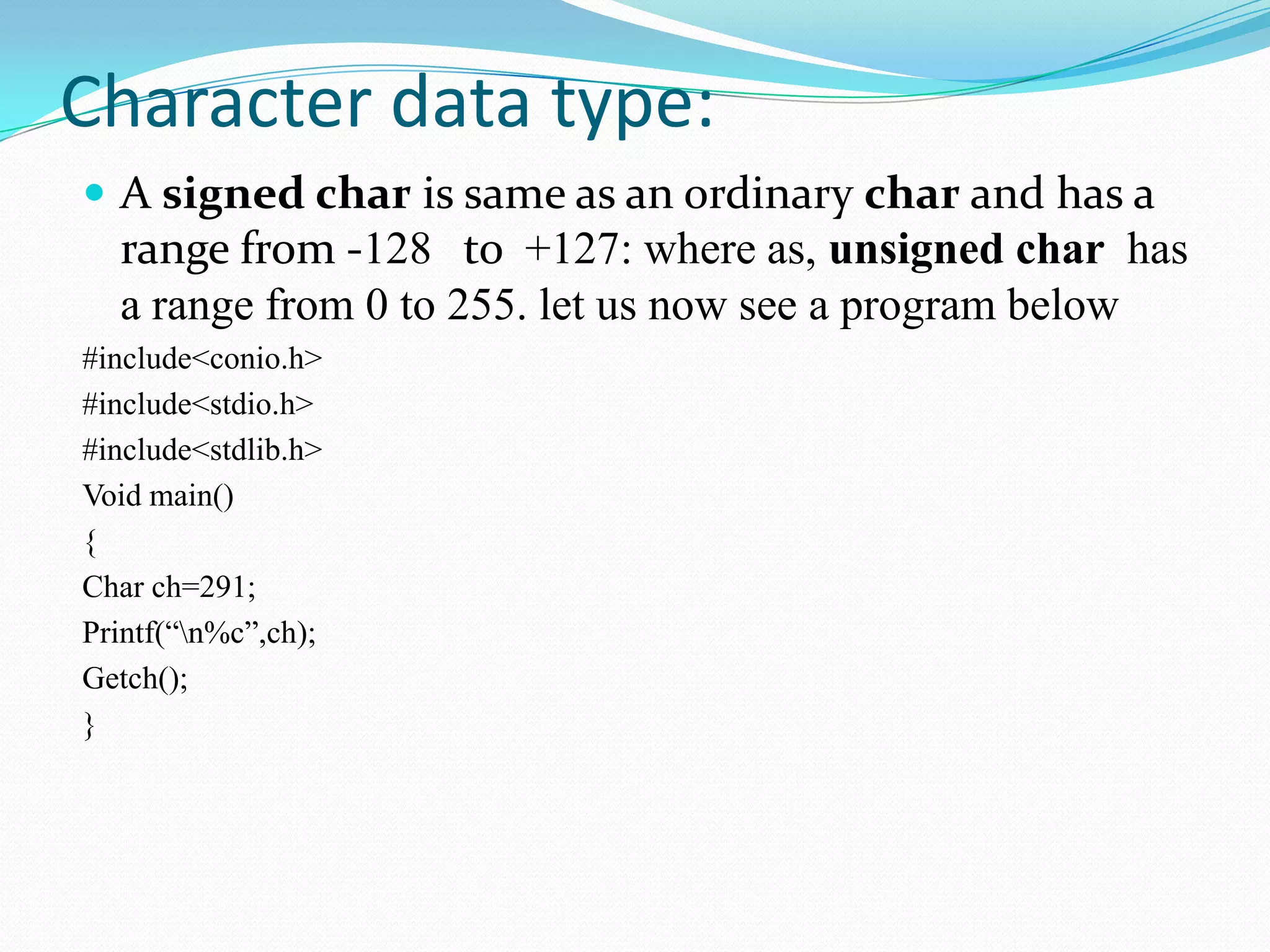
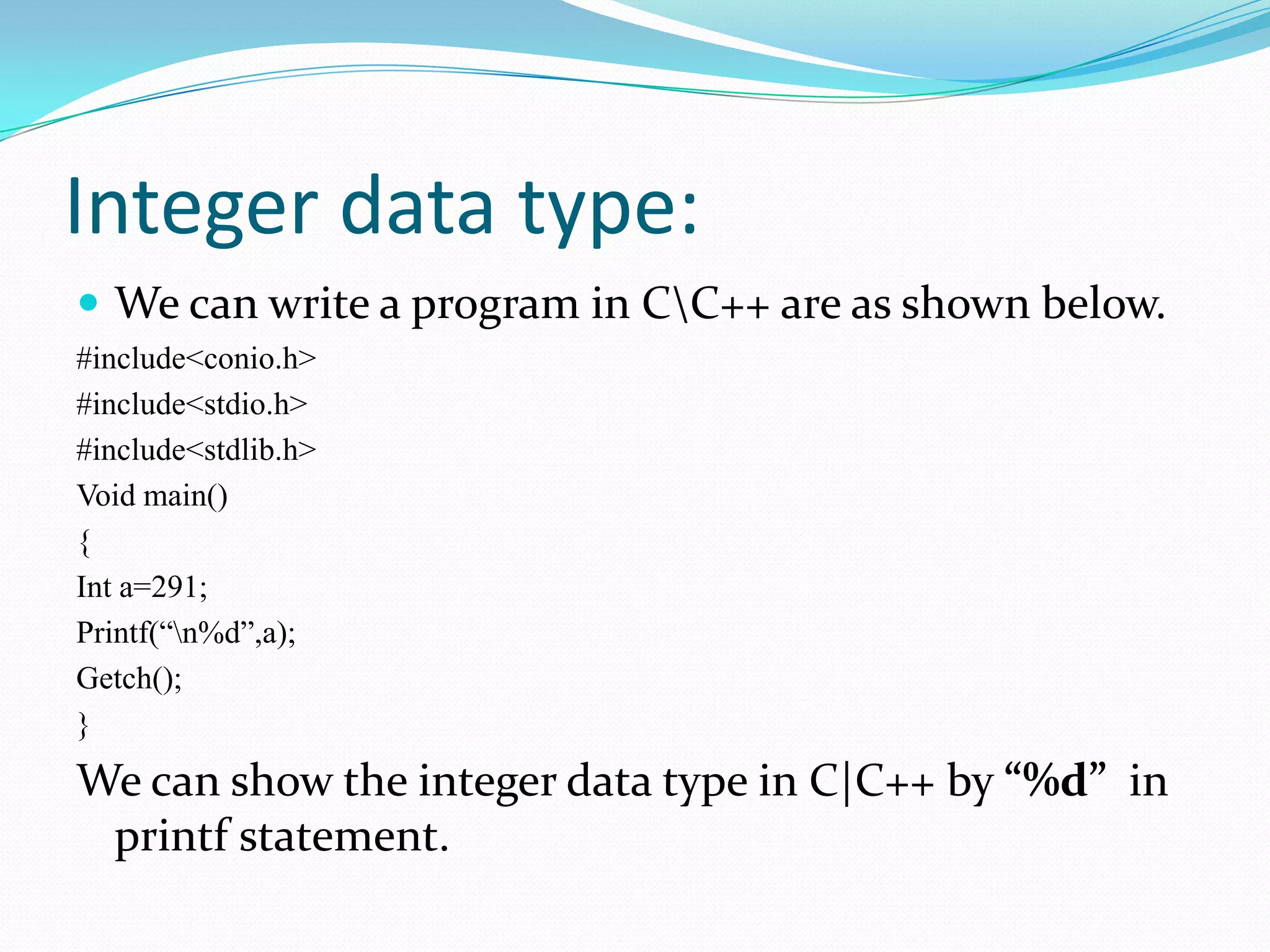
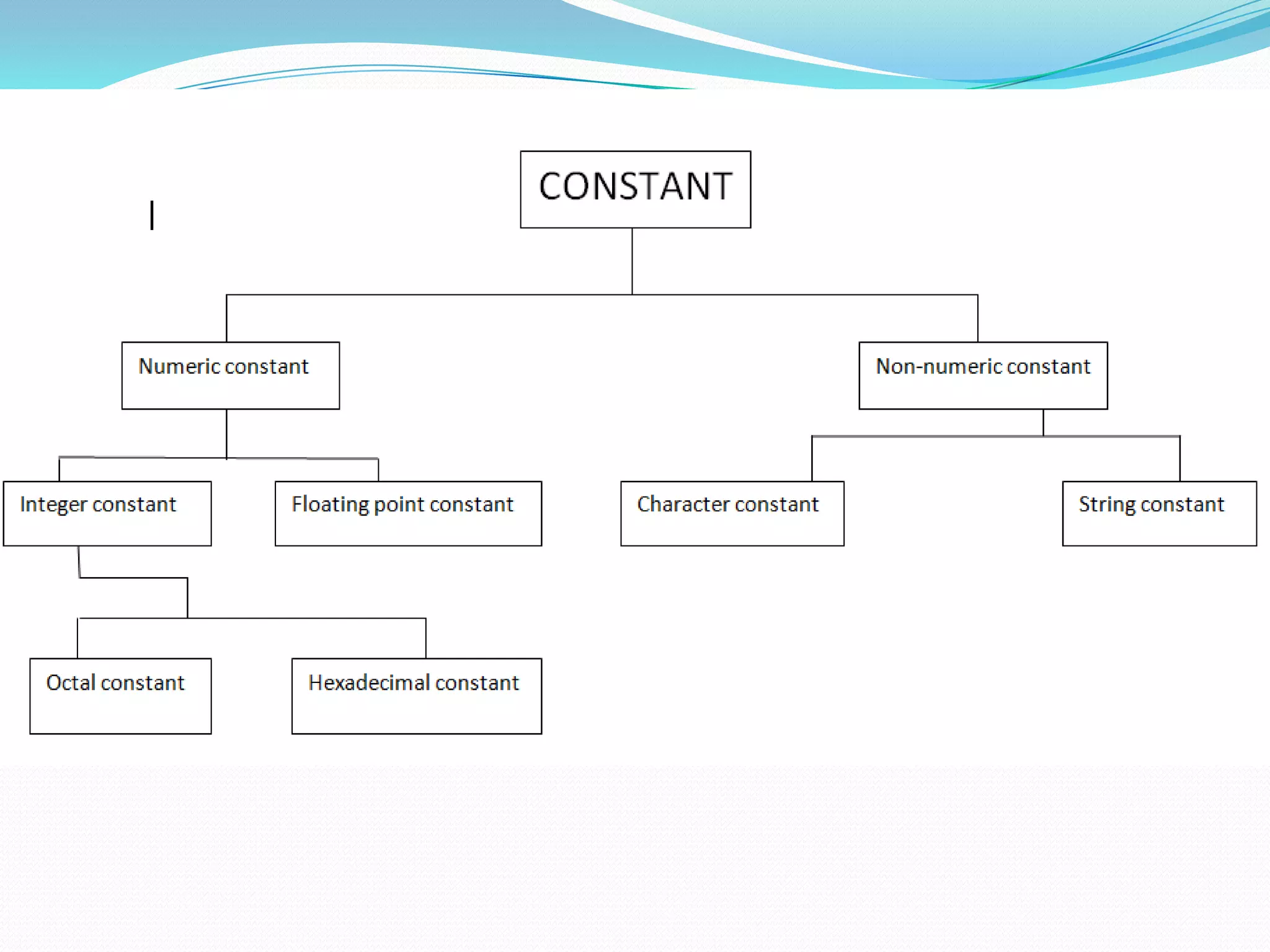
In C/C++, data types are divided into character, integer, and real (floating point) types. Character data represents letters, digits, and punctuation using the char data type. Integer data represents whole numbers using int. Real data represents decimal fractions using float. Constants represent fixed values that do not change, and can be numeric (integer, floating point, octal, hexadecimal) or non-numeric (character, string).