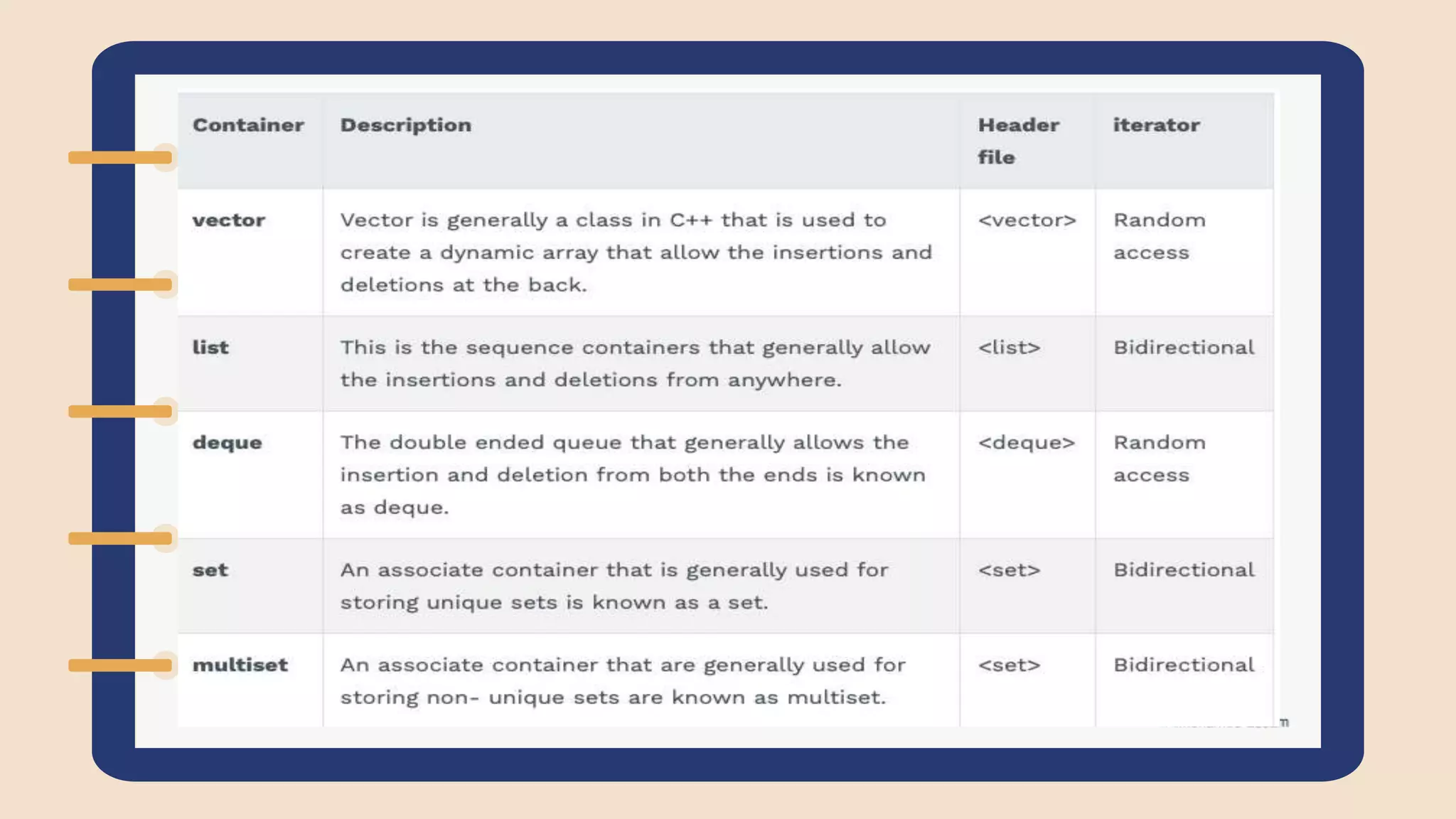
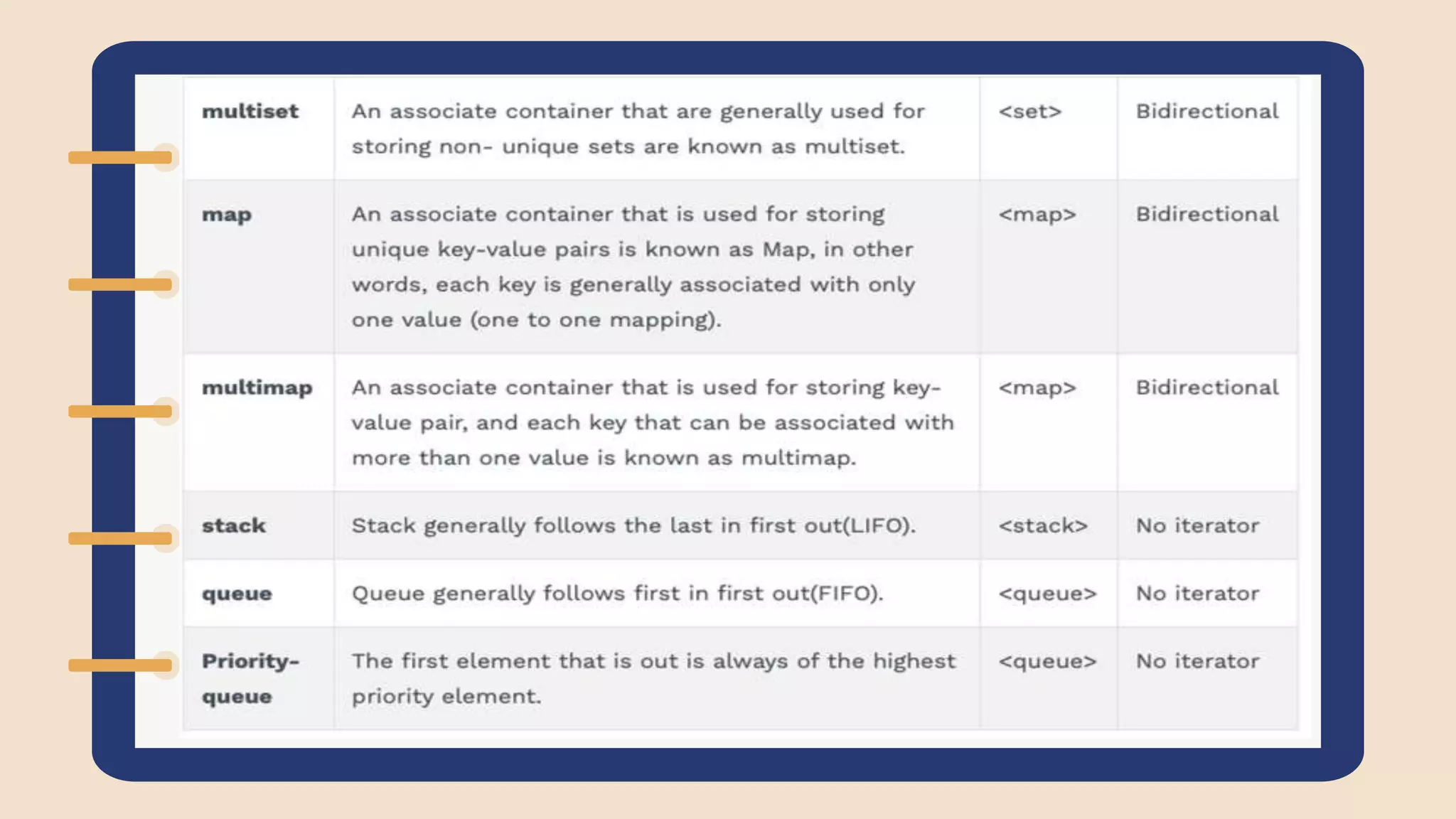
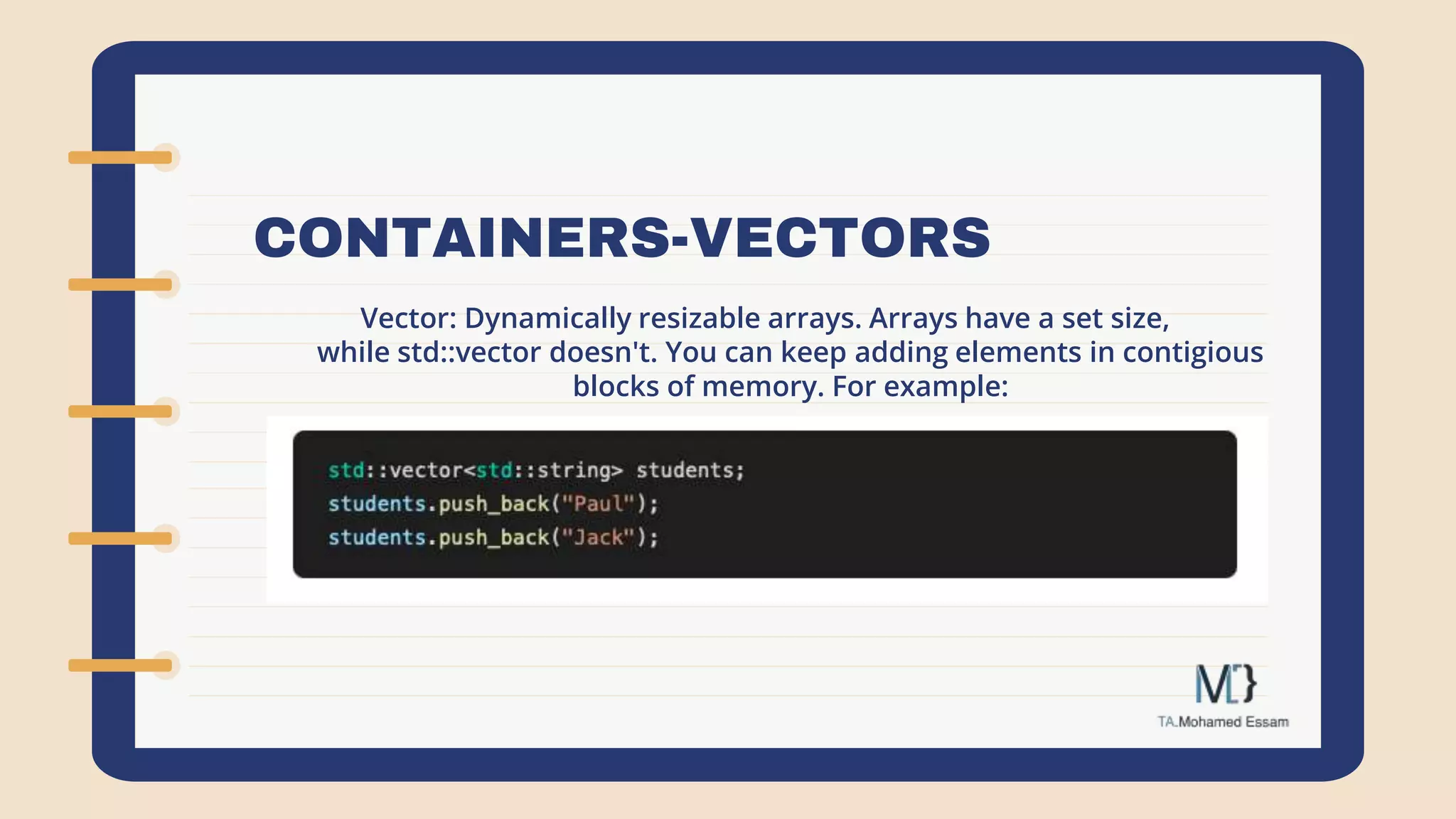
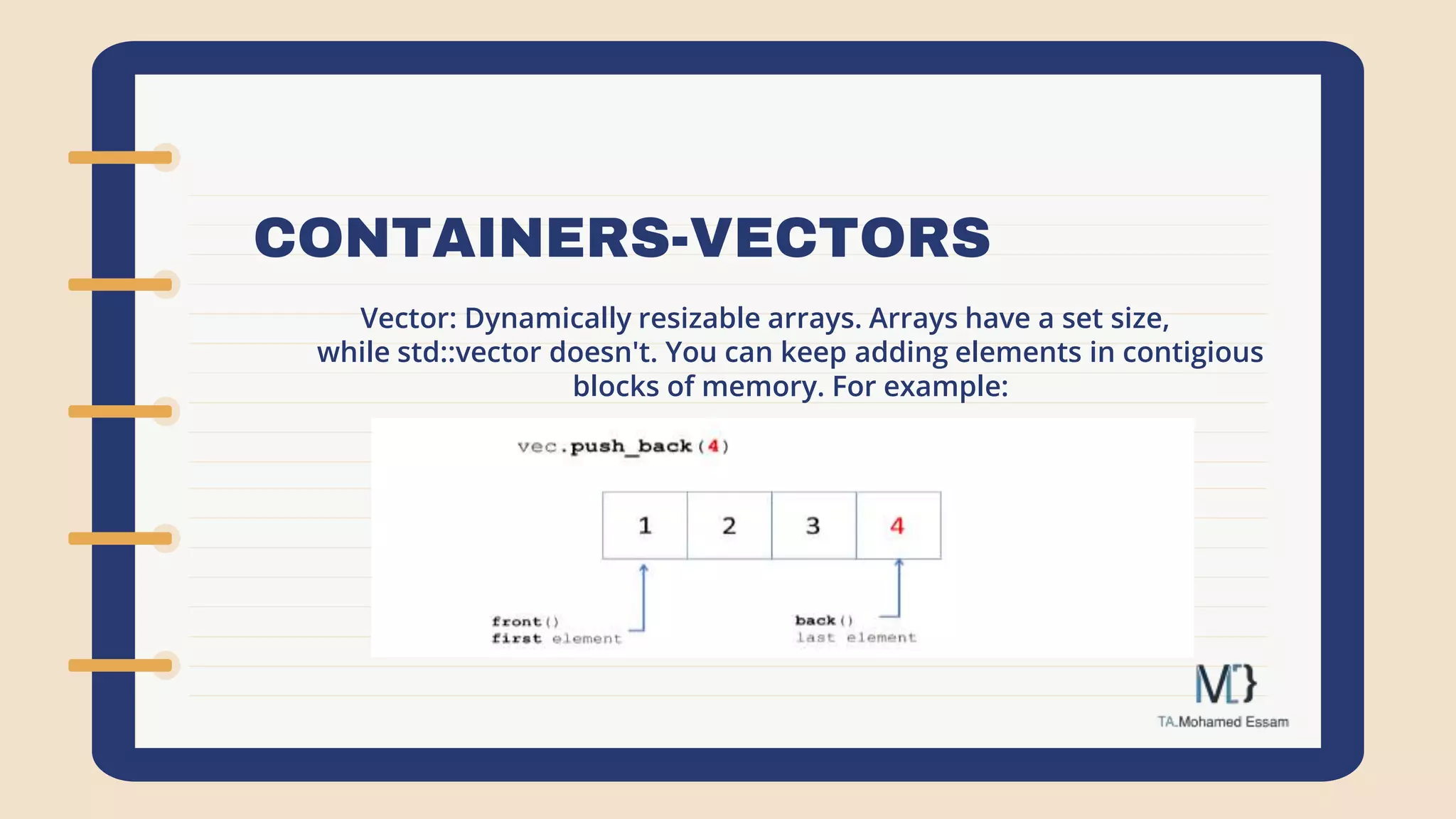
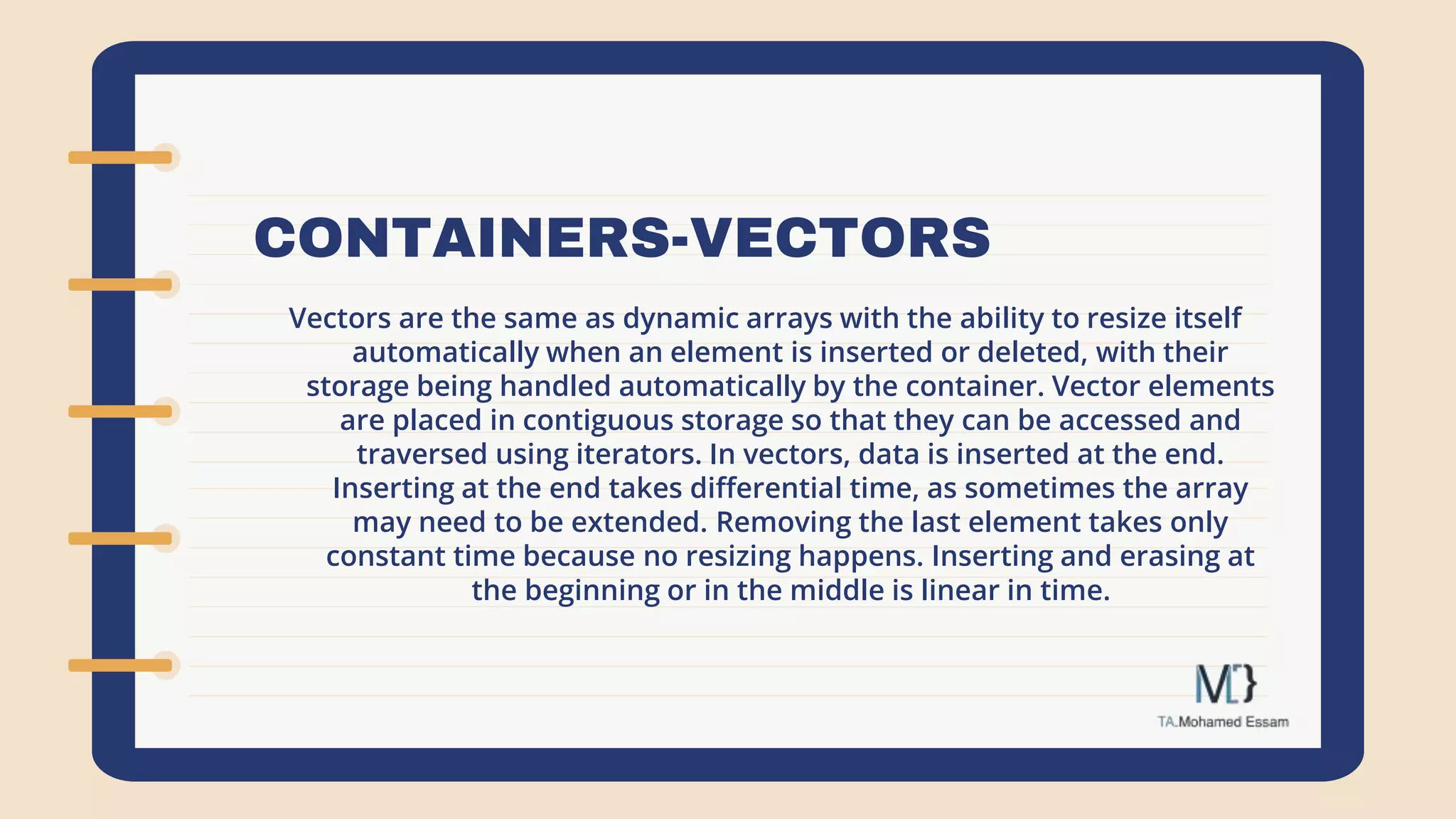
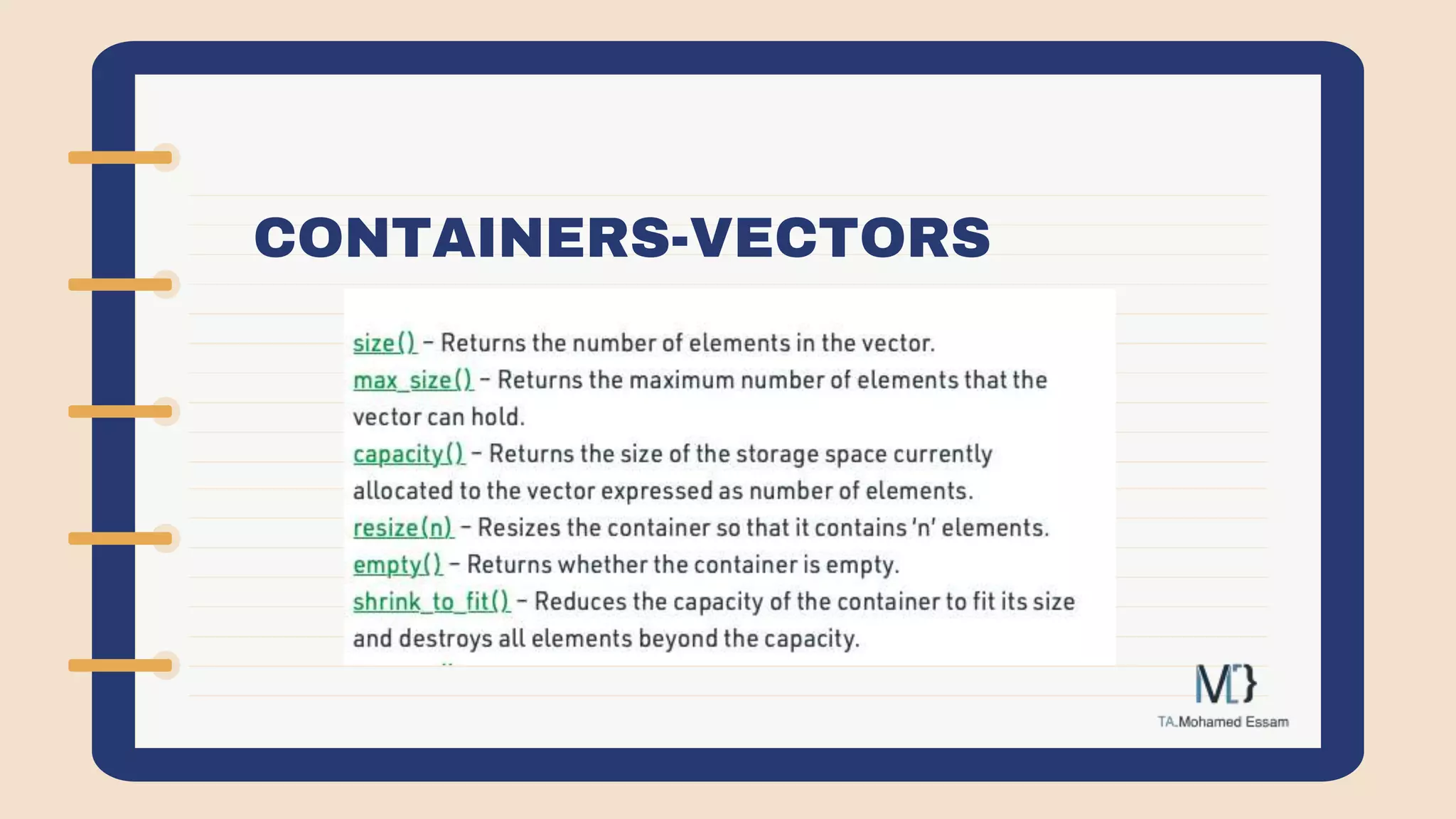
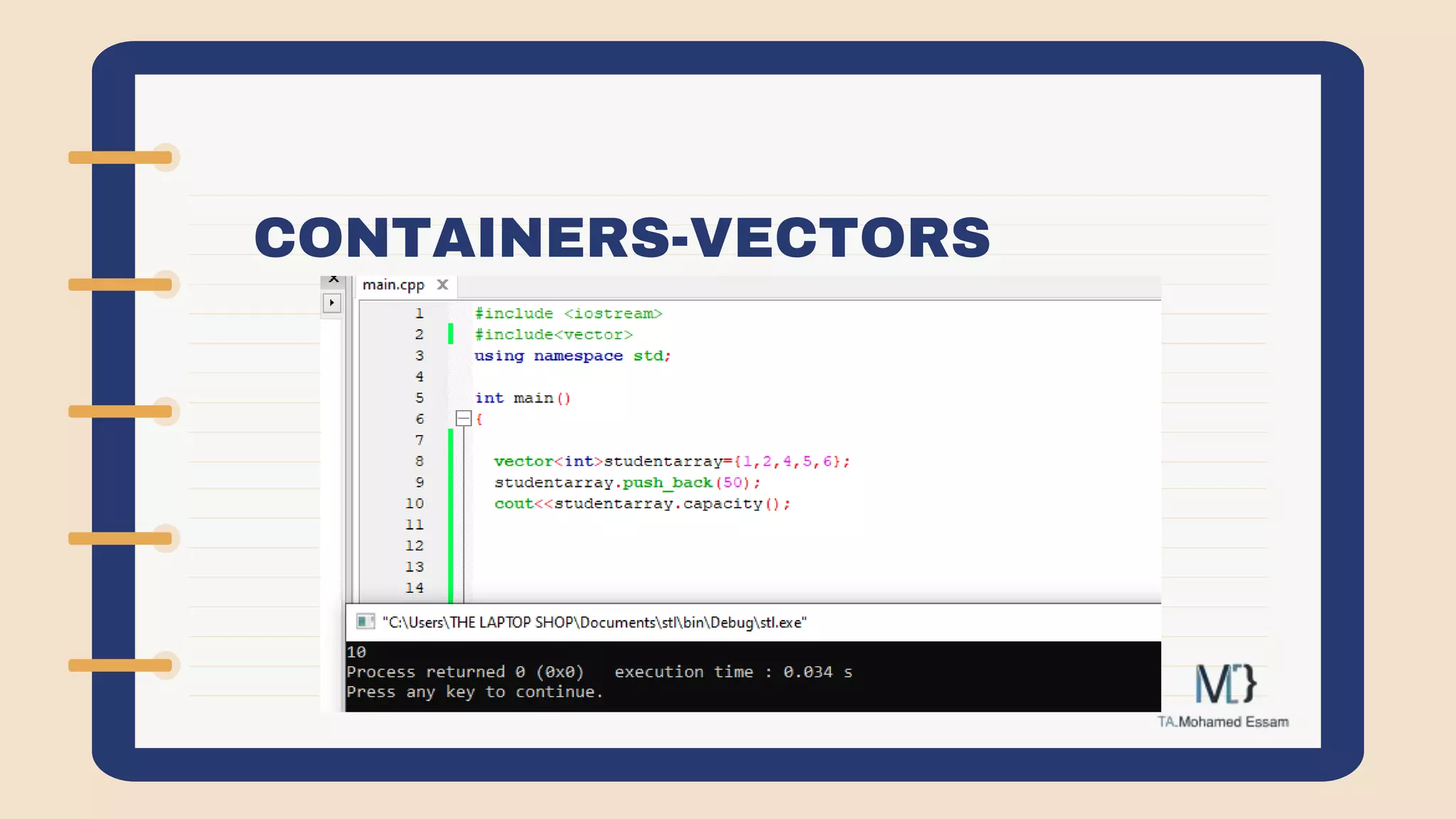
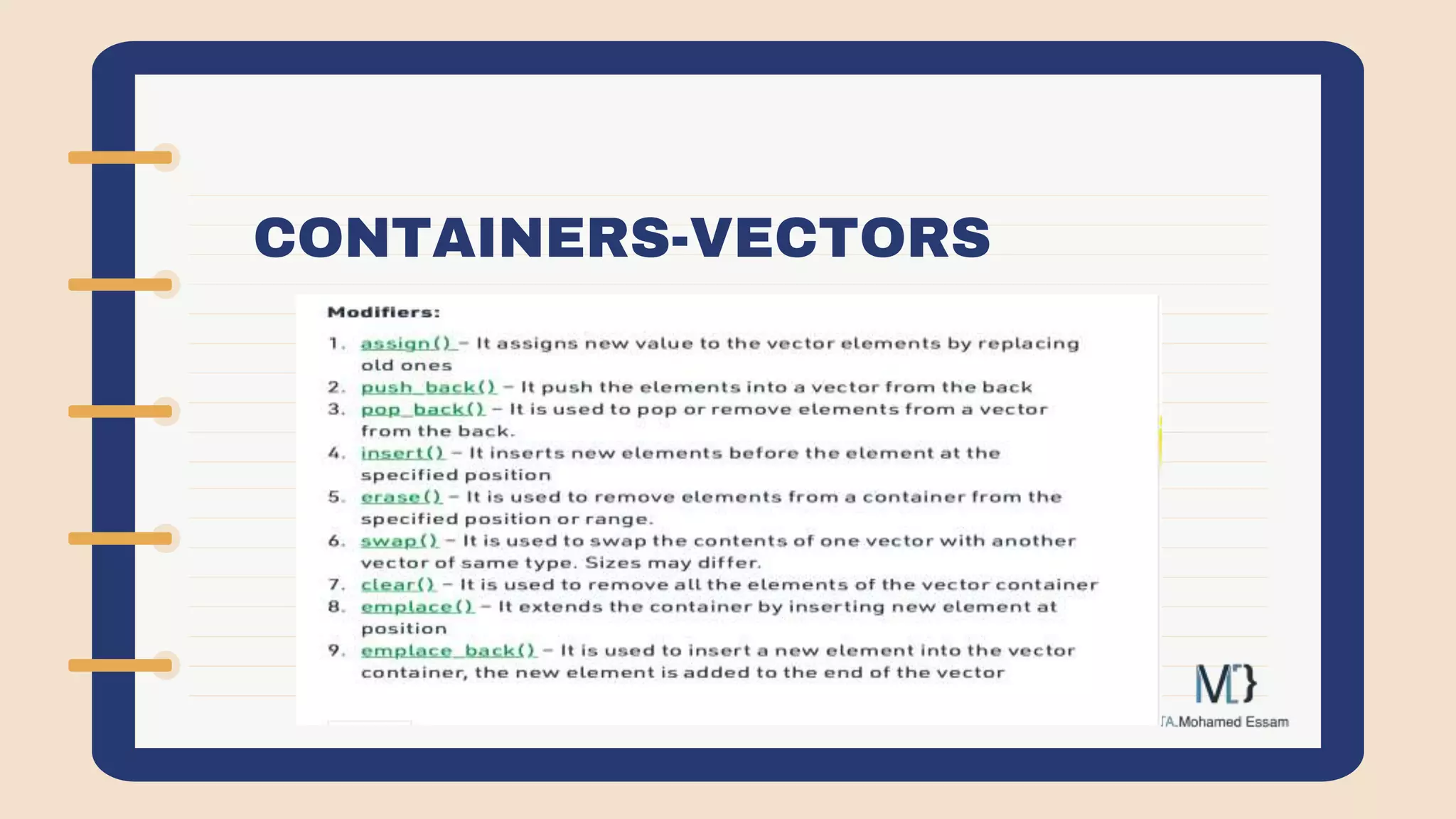
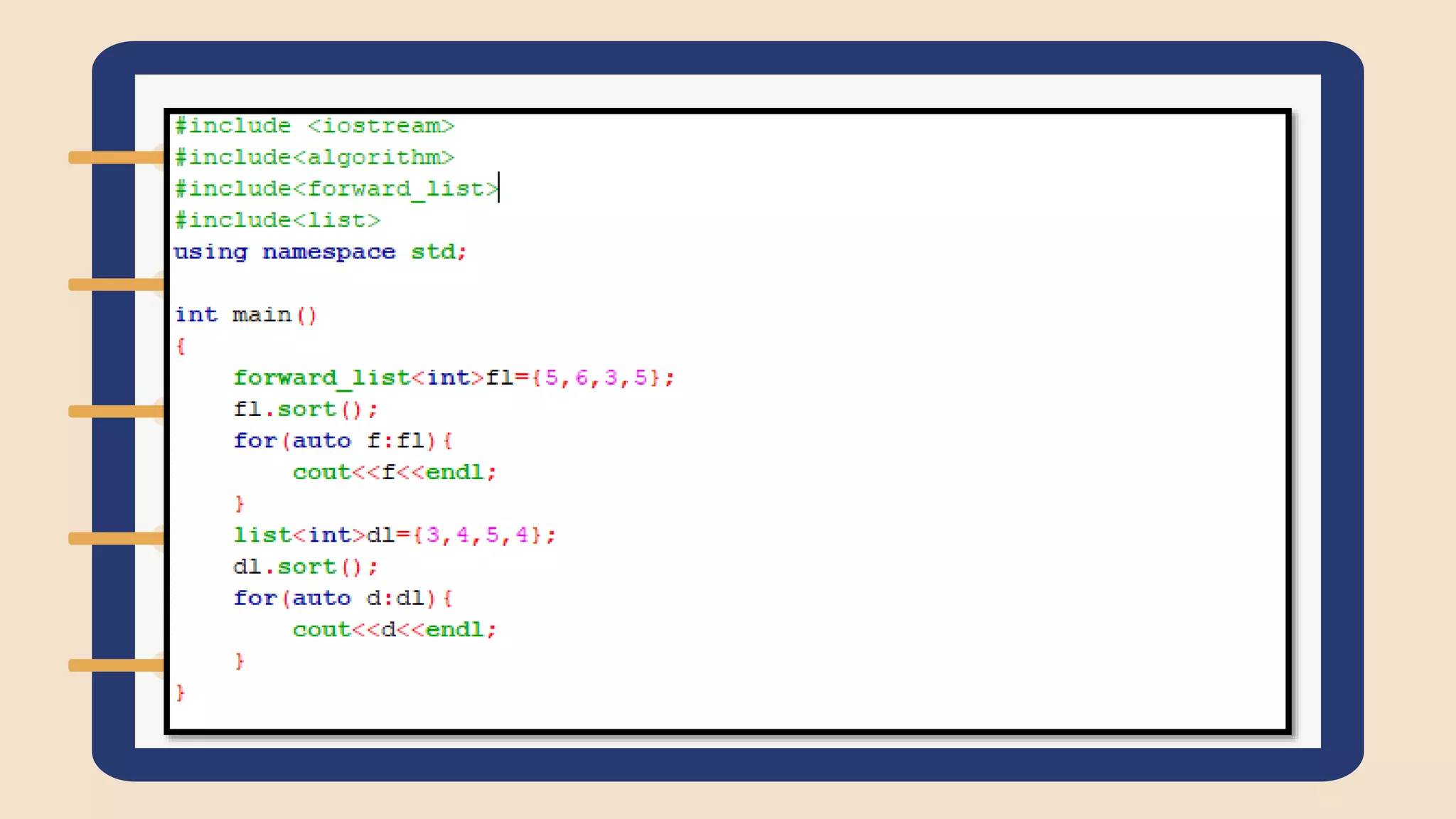
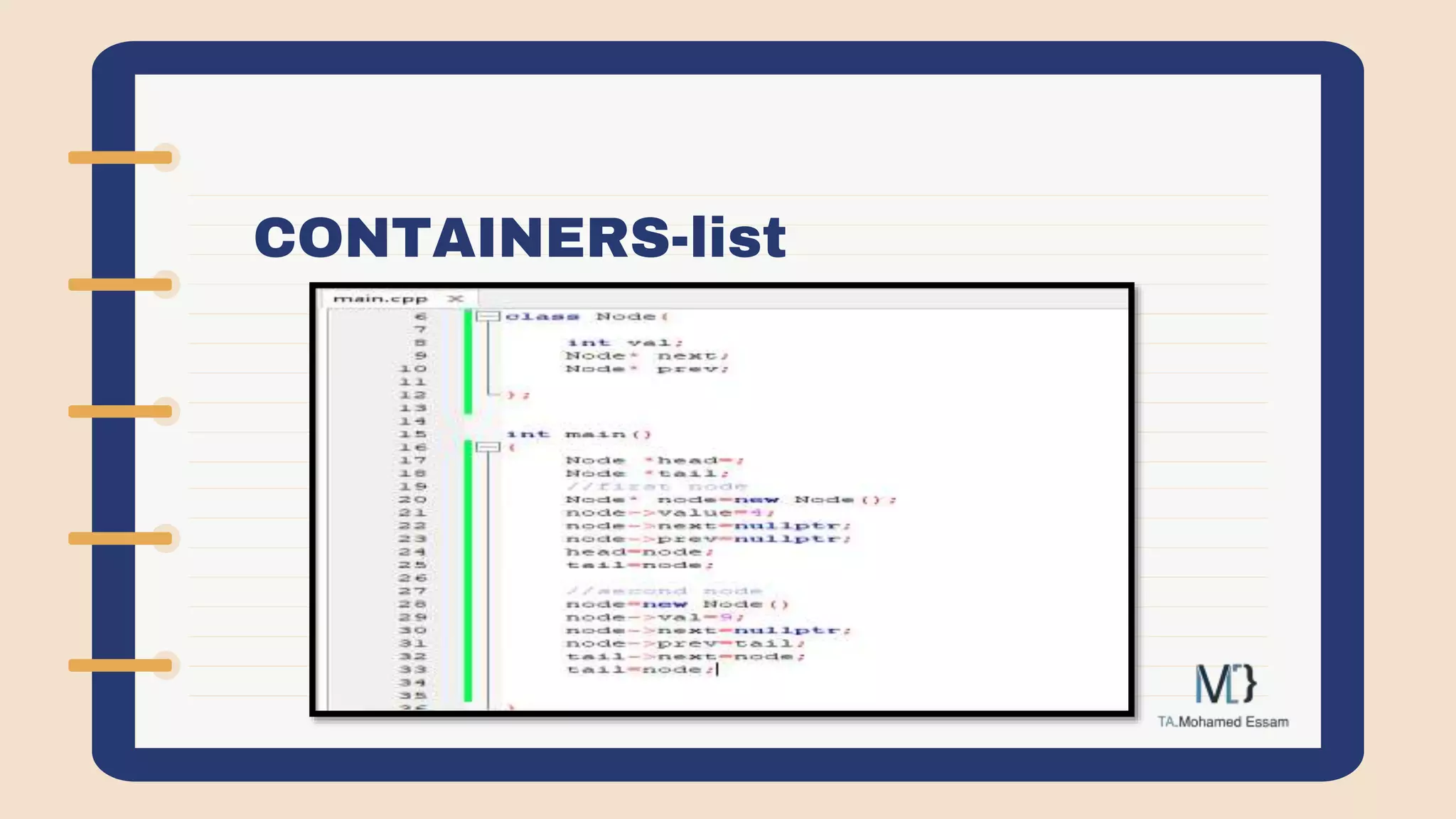
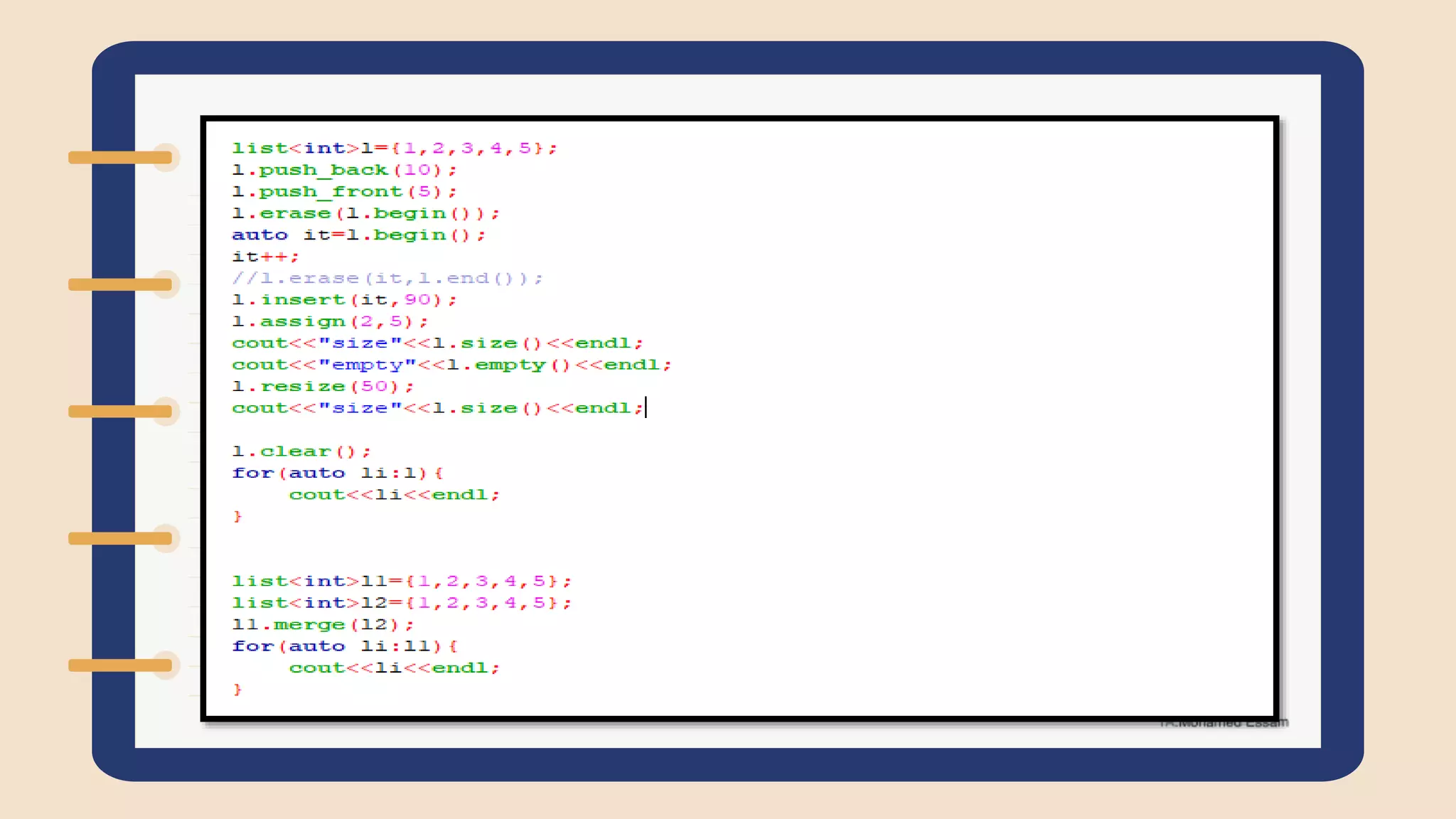
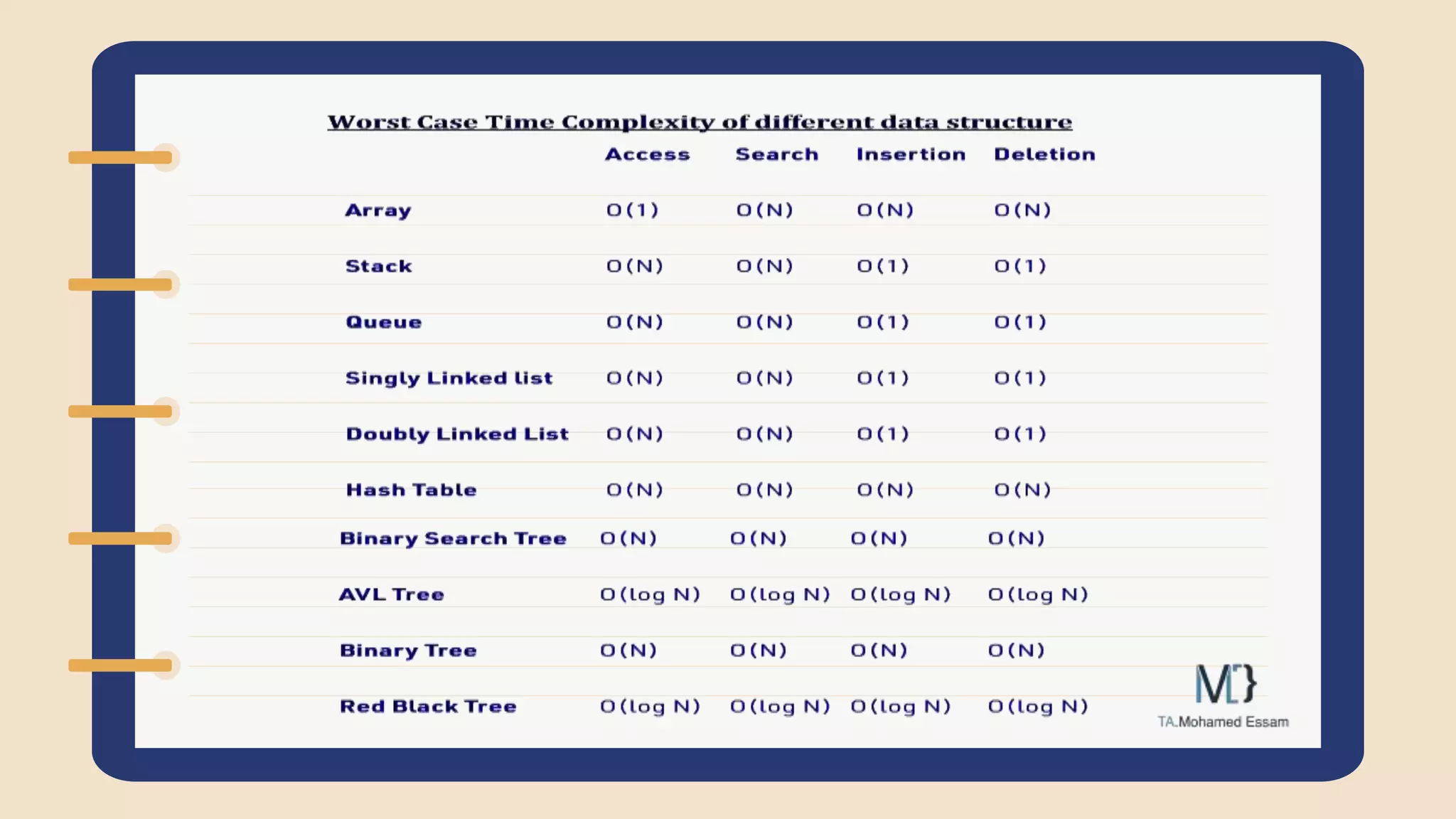
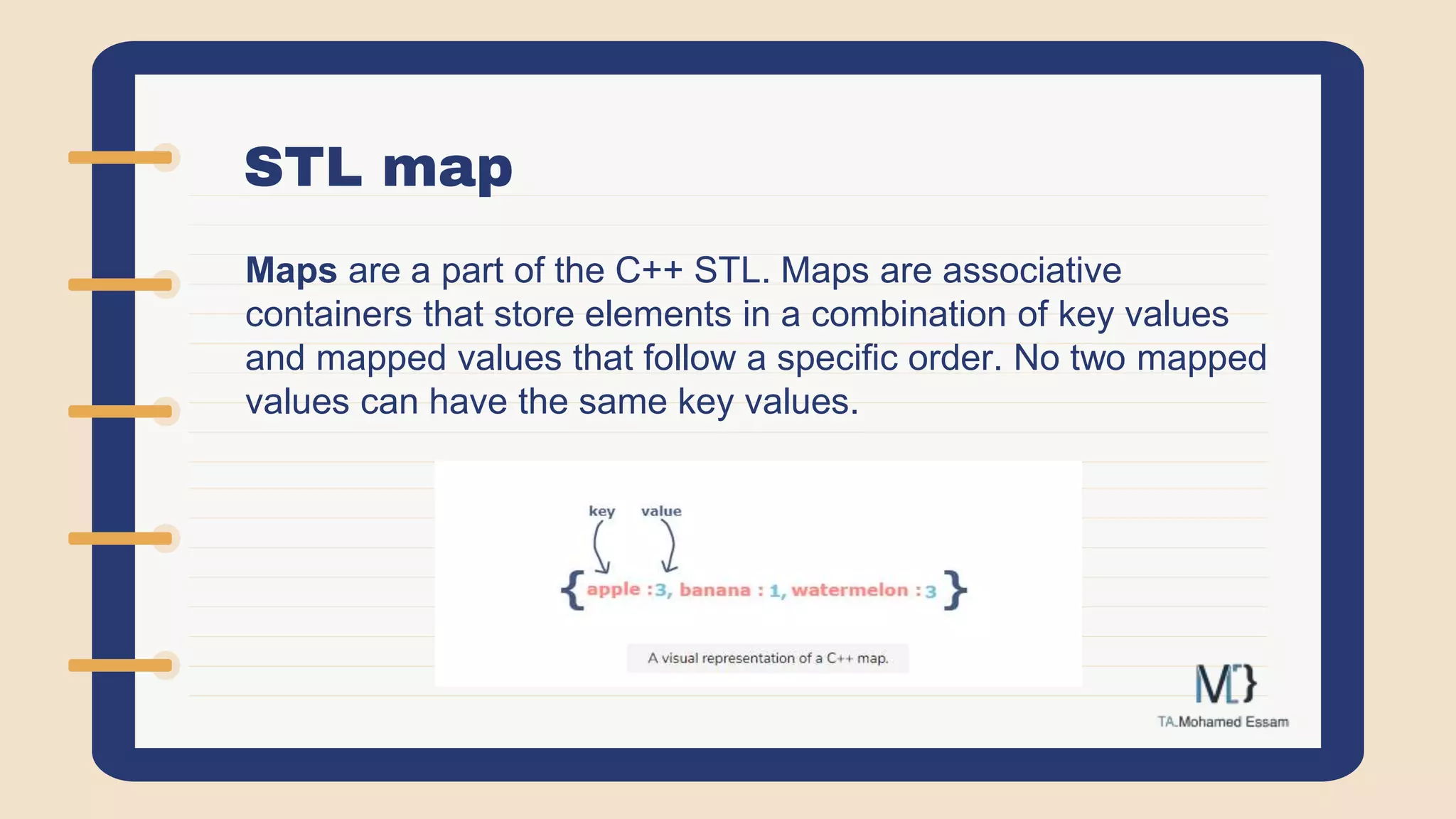
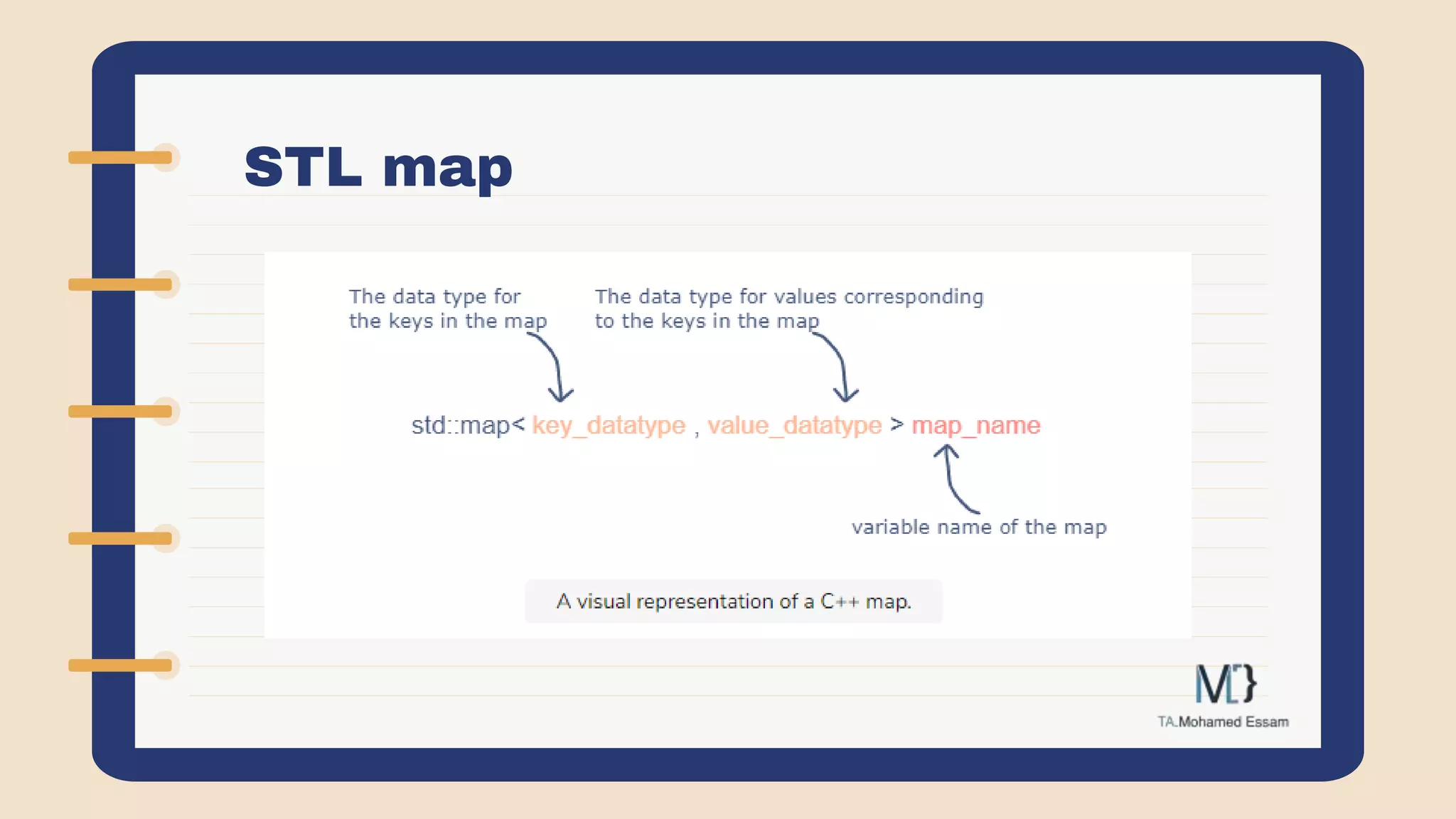
The document discusses the Standard Template Library (STL) in C++. It describes how STL helps store and manipulate objects and makes programs more reusable and robust. It then discusses some of the main components of STL, including containers like vectors, deques, lists, stacks, and maps that implement common data structures, as well as algorithms for processing container elements and iterators for traversing container elements.






![Elements of the STL
- Containers
- Collections of objects or primitive types
- [Array, vector, deque, stack, set, map, etc]
- Algorithms
- Functions for processing sequences of elements from containers
- [find, max, count, accumulate, sort, etc]
- Iterators
- Generate sequence of element from containers
- [forward, reverse, by value, by reference, constant, etc.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastrucurewithstl2-221006155759-26f0a375/75/Data-Strucure-with-STL-9-2048.jpg)