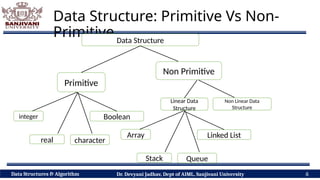
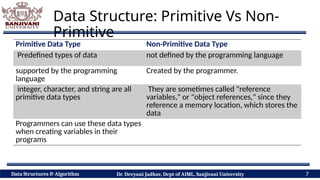
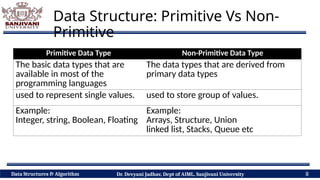
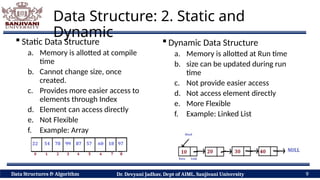
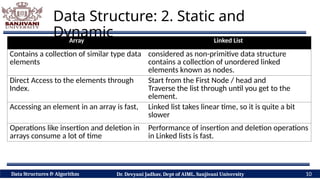
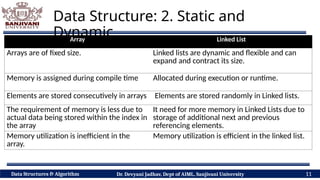
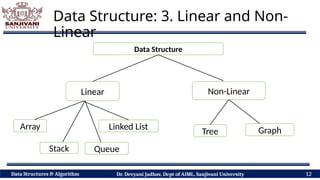
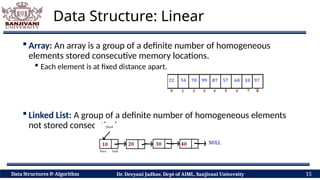
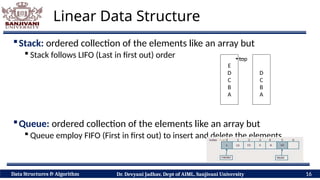
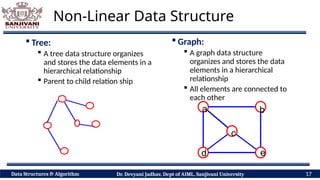
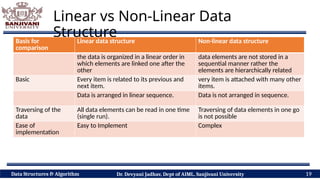
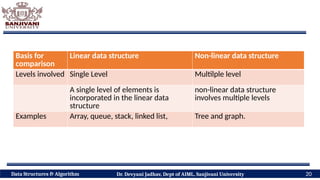
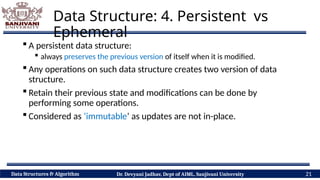
The document covers fundamental concepts of data structures and algorithms, detailing their types: primitive vs non-primitive, static vs dynamic, linear vs non-linear, and persistent vs ephemeral. It also outlines the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of each category, emphasizing their efficient organization and management of data. The course aims to equip students with the understanding necessary to distinguish between these data structures.