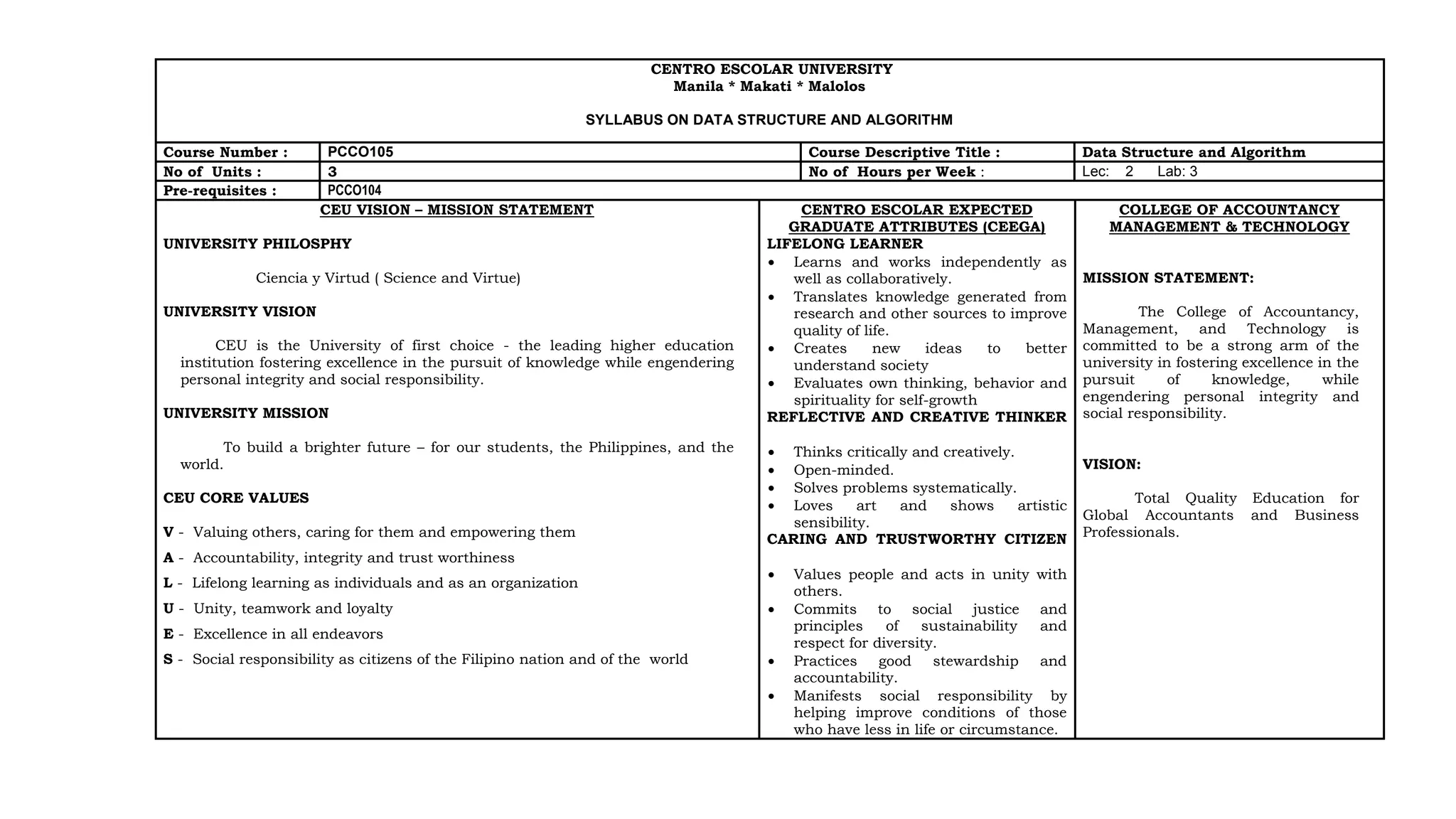
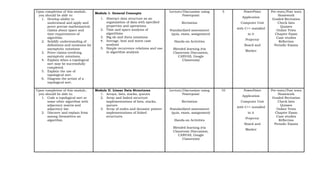
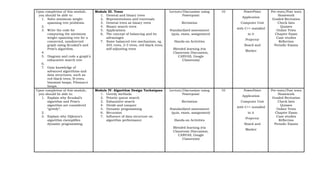
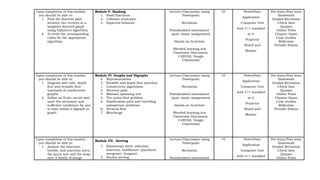
This document outlines a syllabus for a Data Structure and Algorithm course offered at Centro Escolar University. The syllabus details the course objectives, which include identifying data structures and algorithms, analyzing algorithm efficiency, and implementing data structures and algorithms. It also provides an overview of the topics that will be covered in each of the 9 modules, which include data structures like arrays, lists, trees and graphs, as well as algorithm design techniques like greedy methods and dynamic programming. Upon completing the course, students will submit a portfolio of activities demonstrating their mastery of data structures and algorithms.