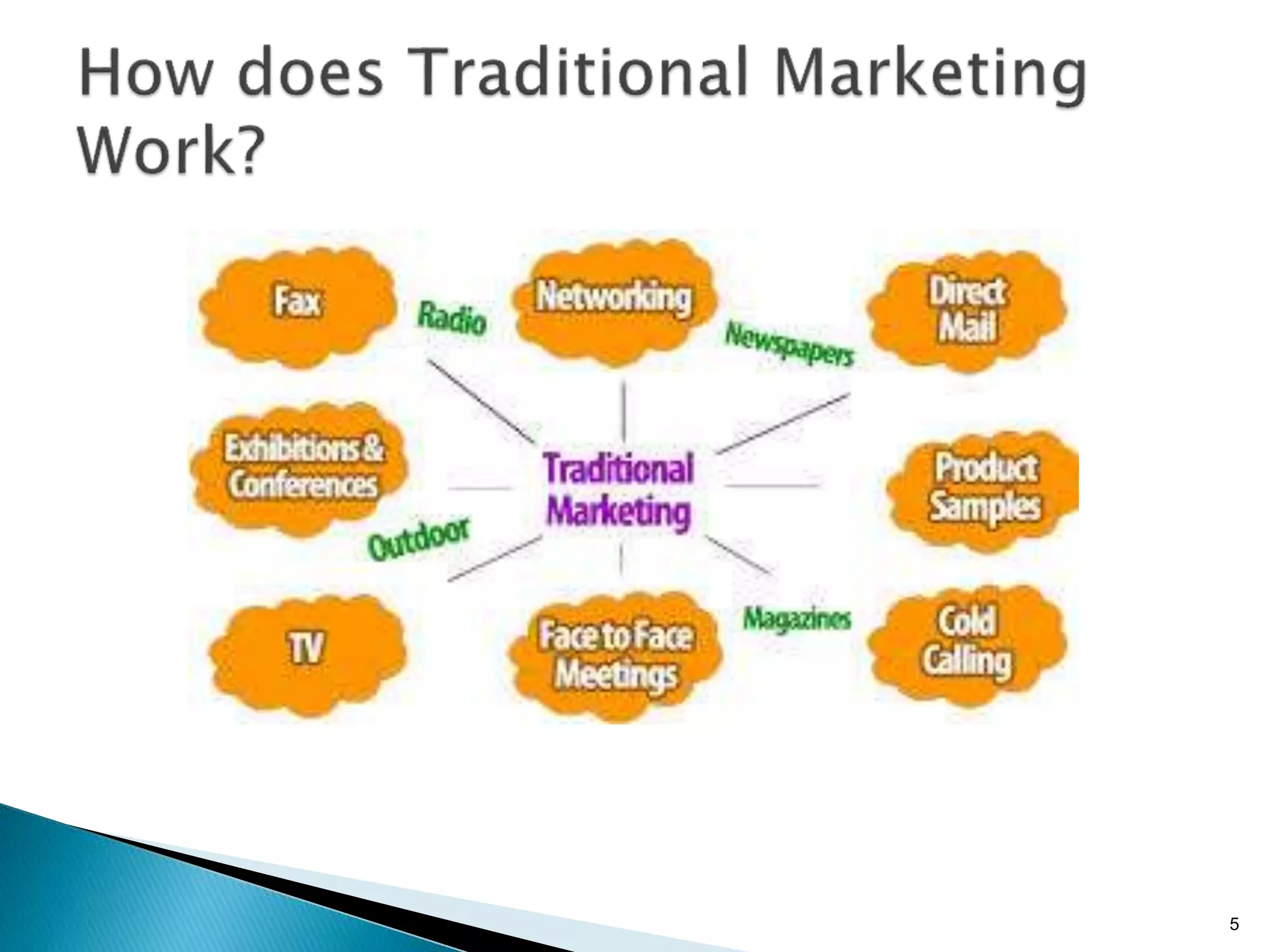
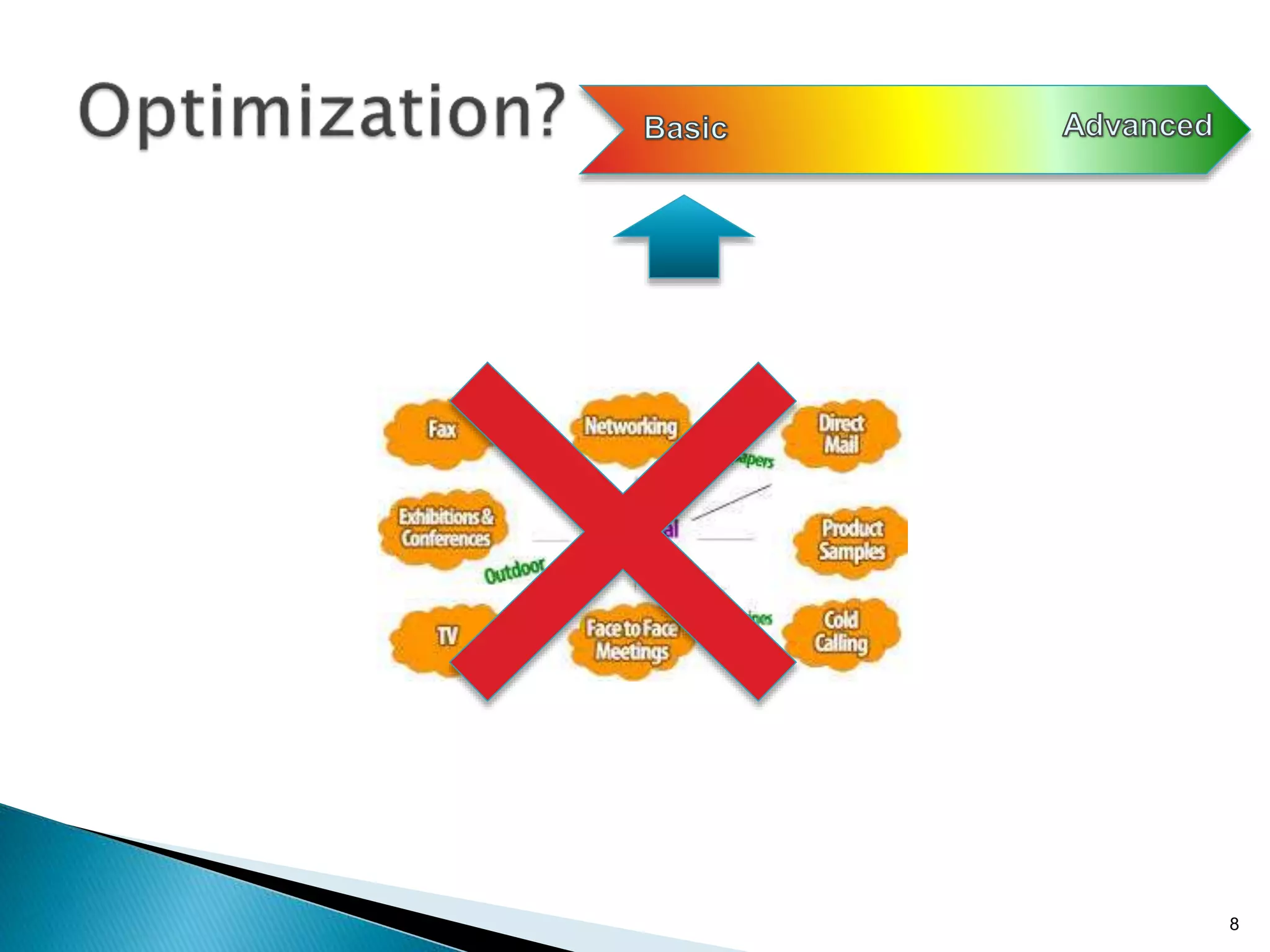
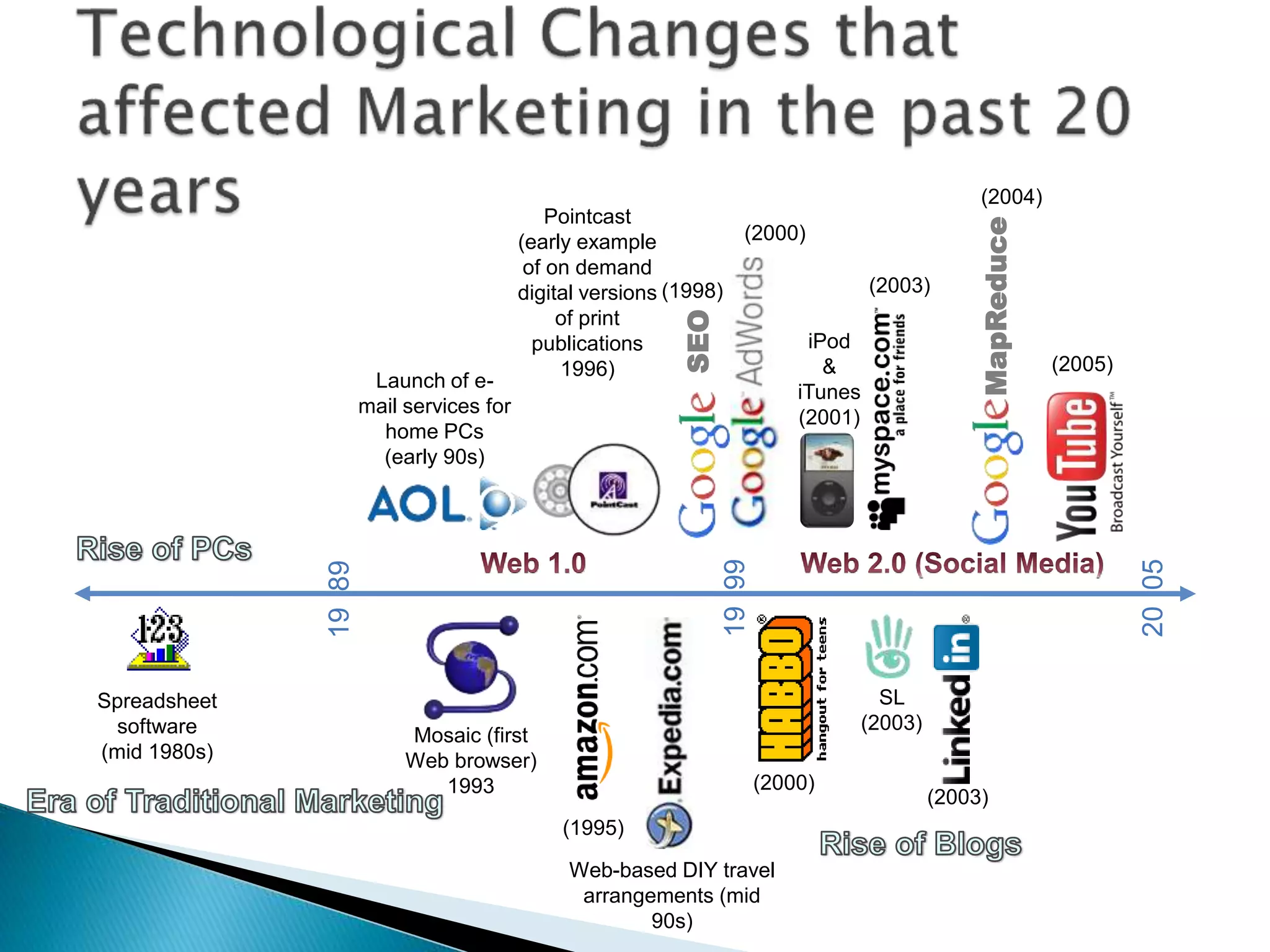
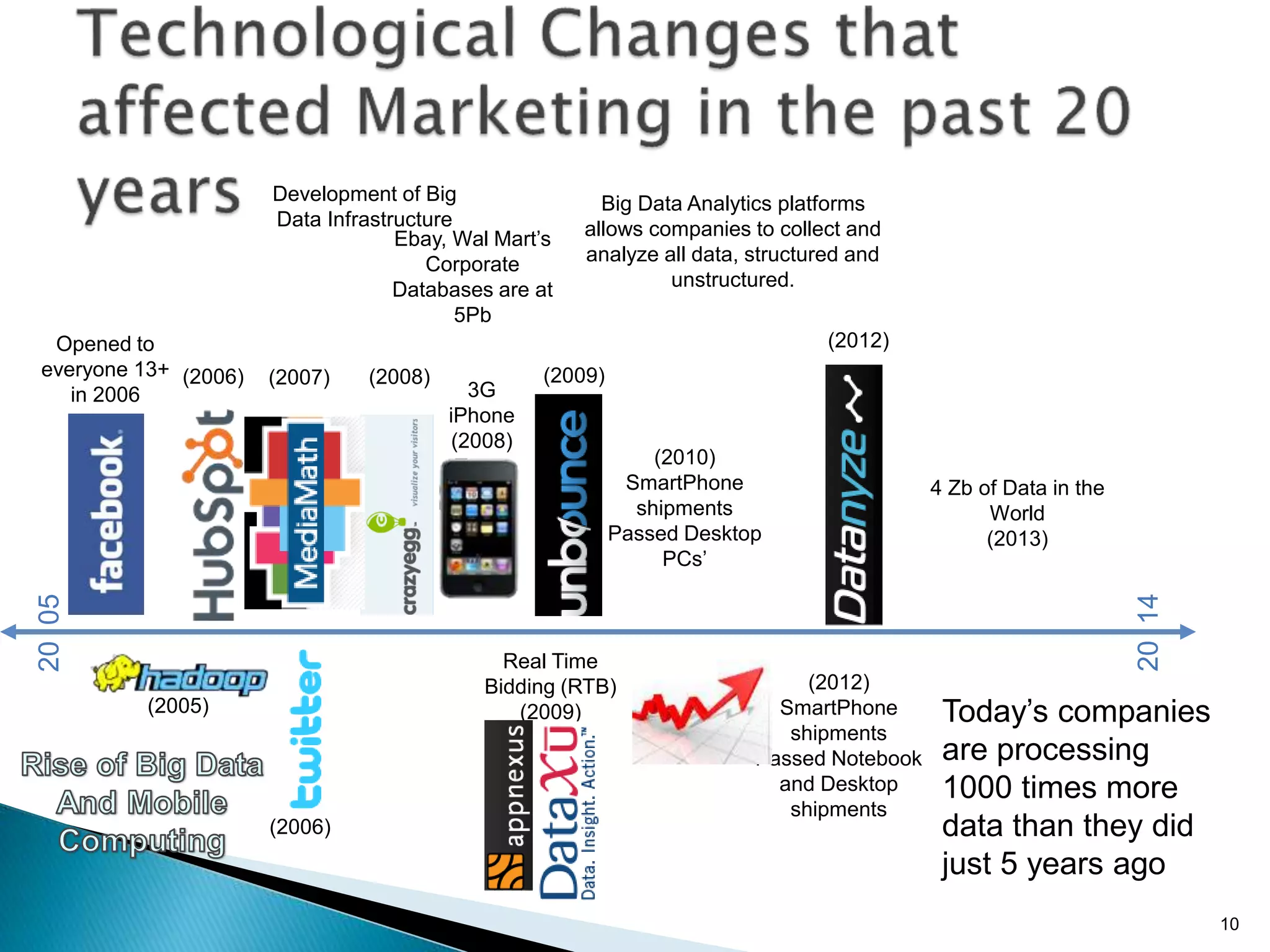
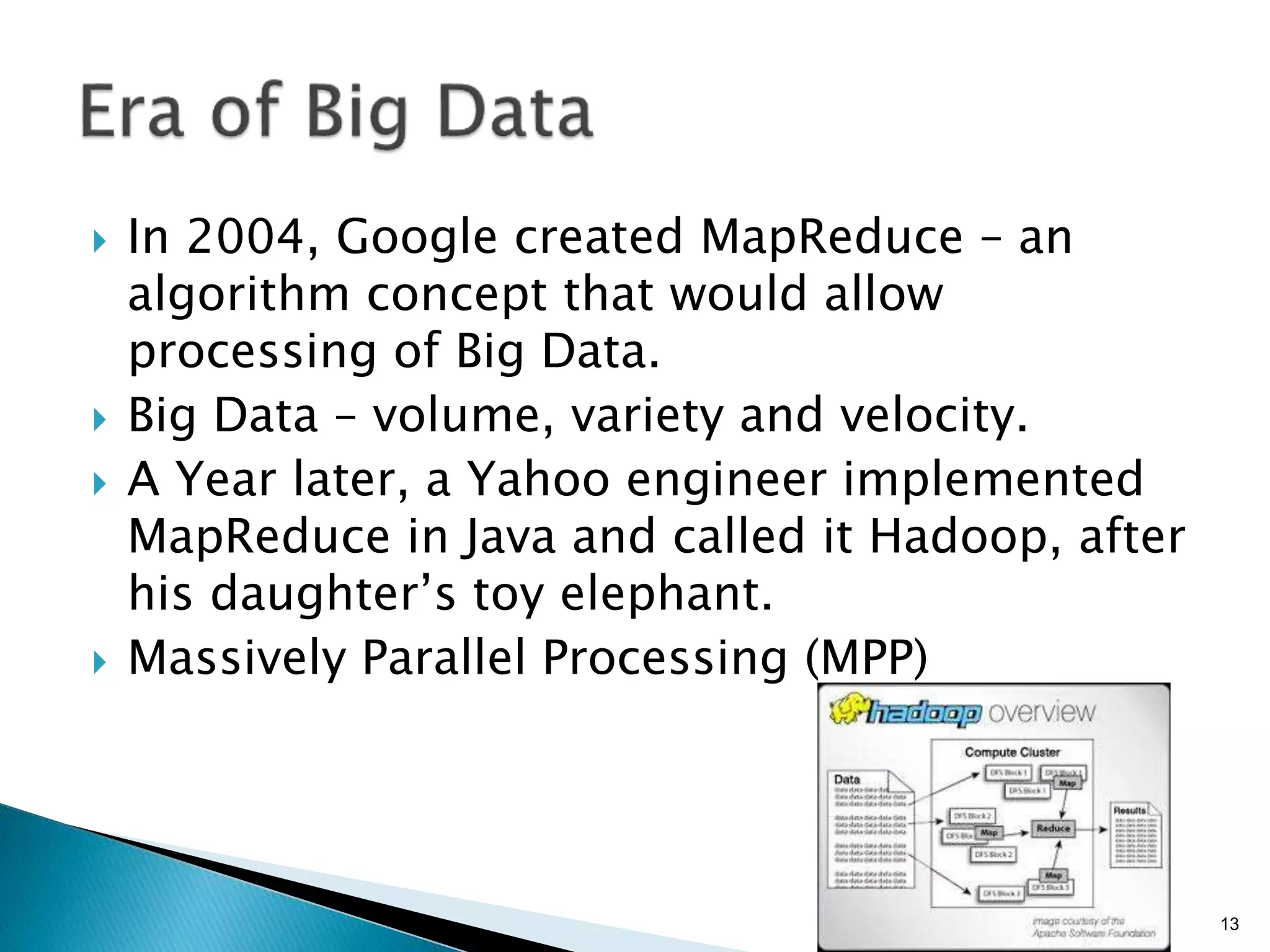
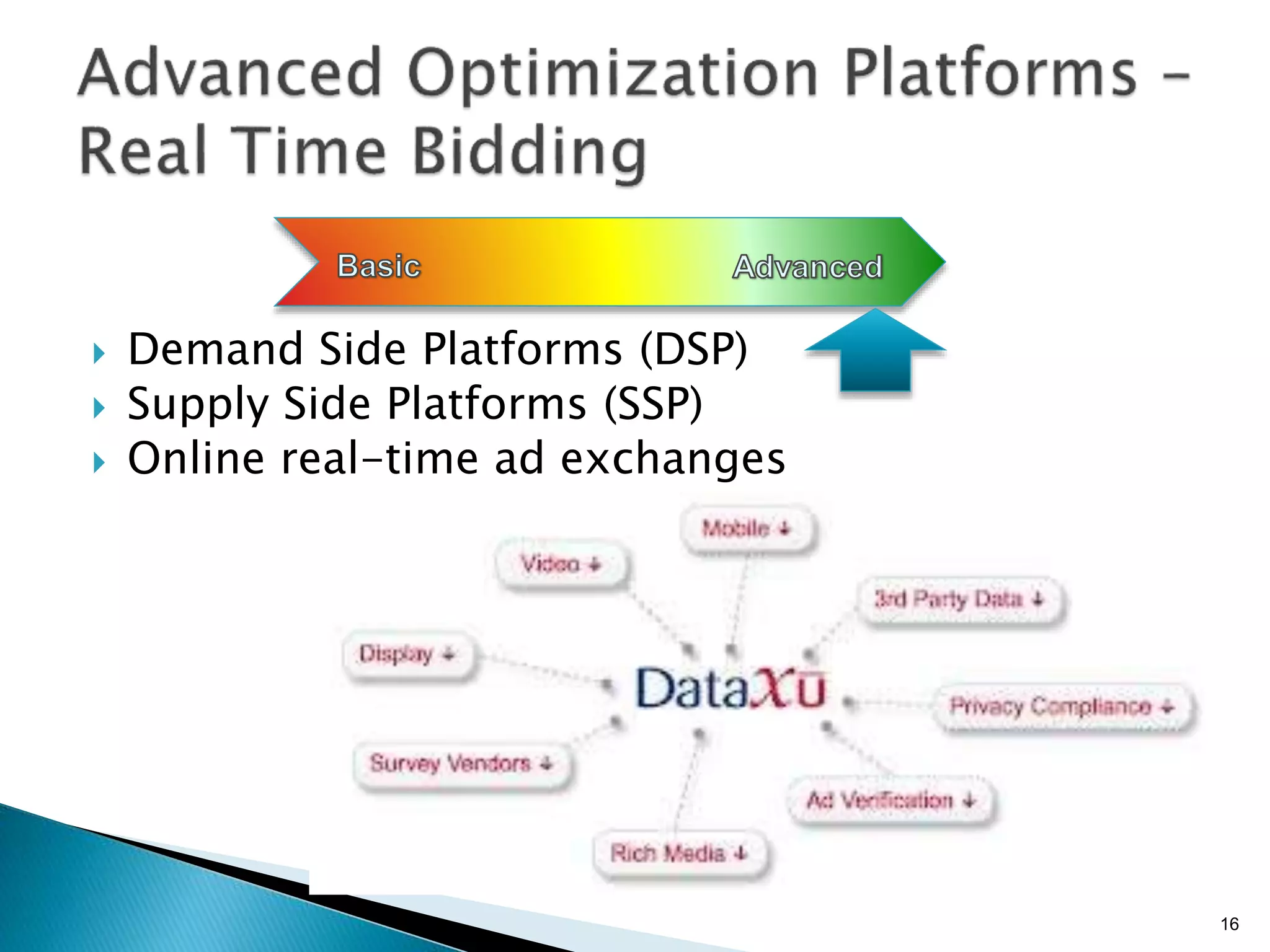
- Traditional marketing using non-digital methods like print ads, TV commercials, and brochures will become obsolete as data-driven digital marketing rises (Paragraph 4).
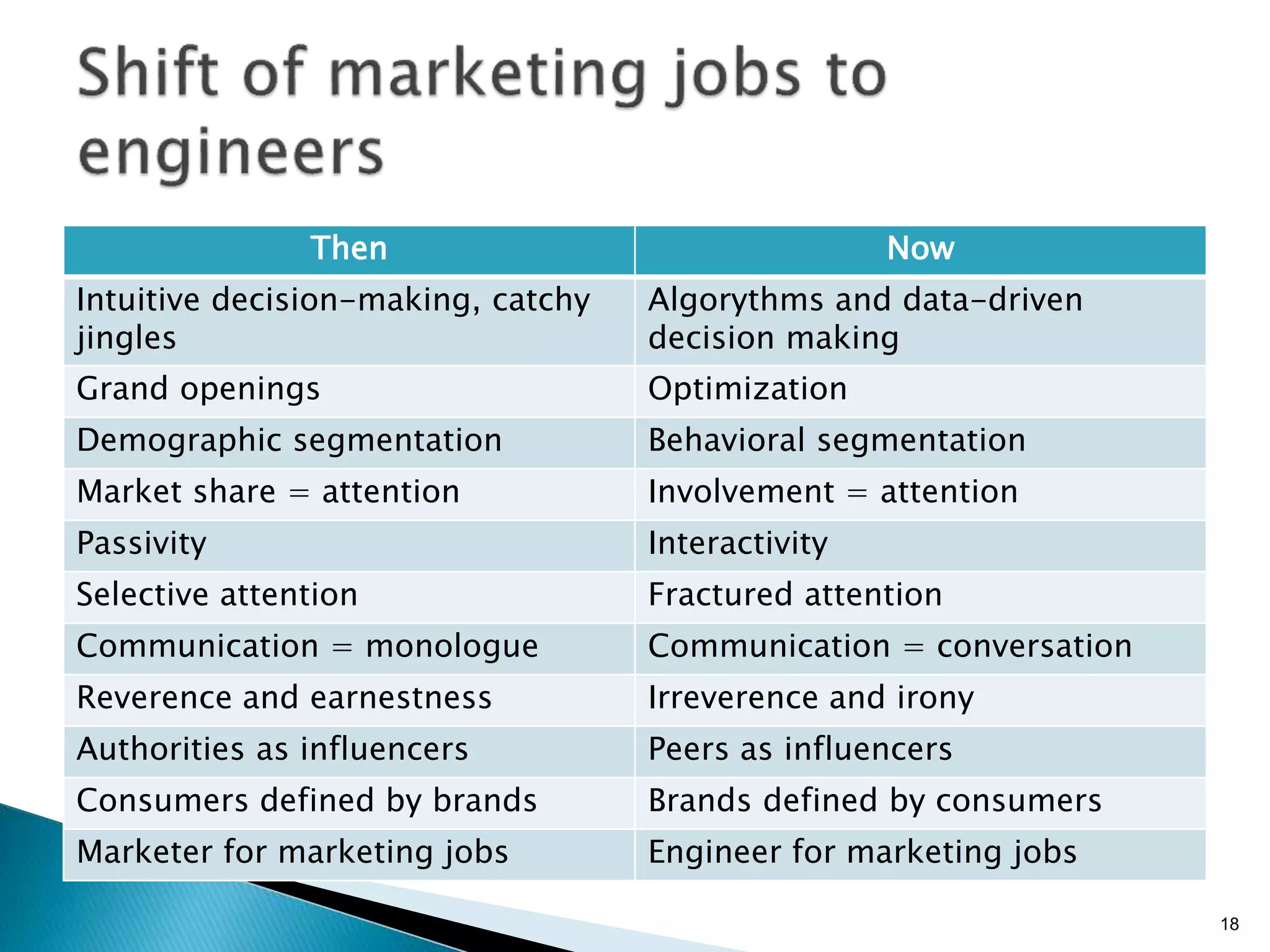
- As more data is created and collected, marketing will shift from focusing on brands to understanding individual customers using big data analytics (Paragraphs 8, 10, 14, 15).
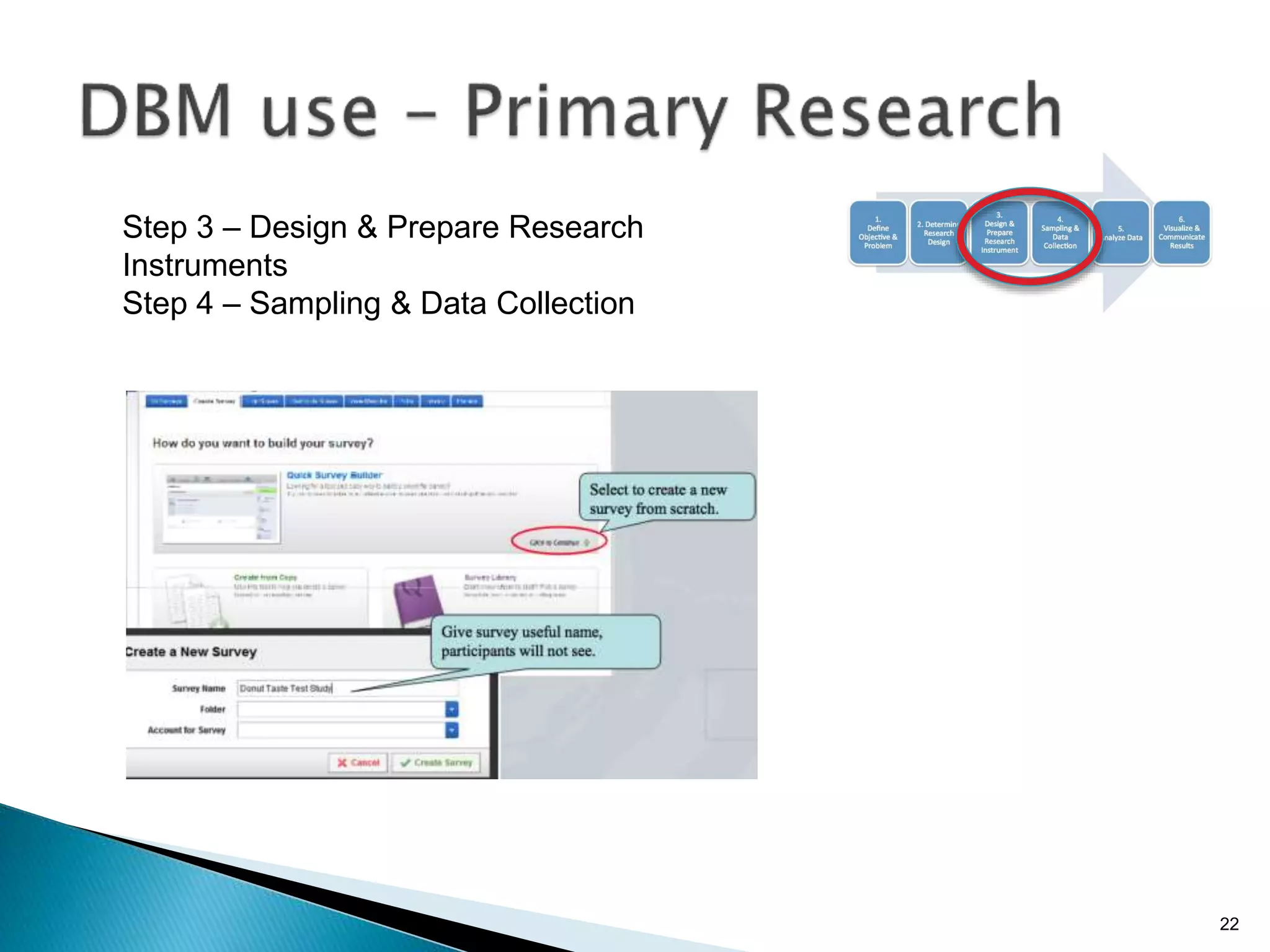
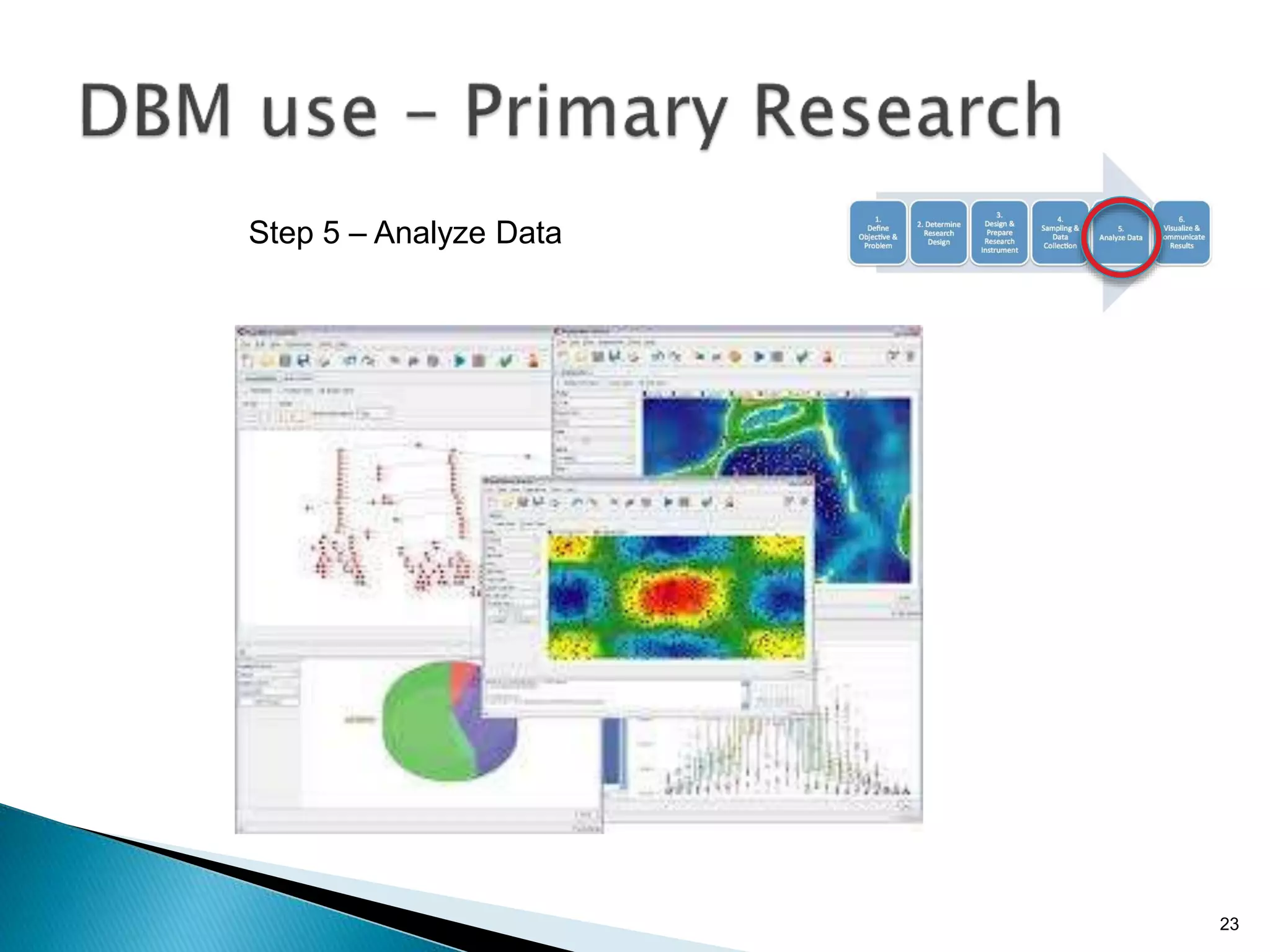
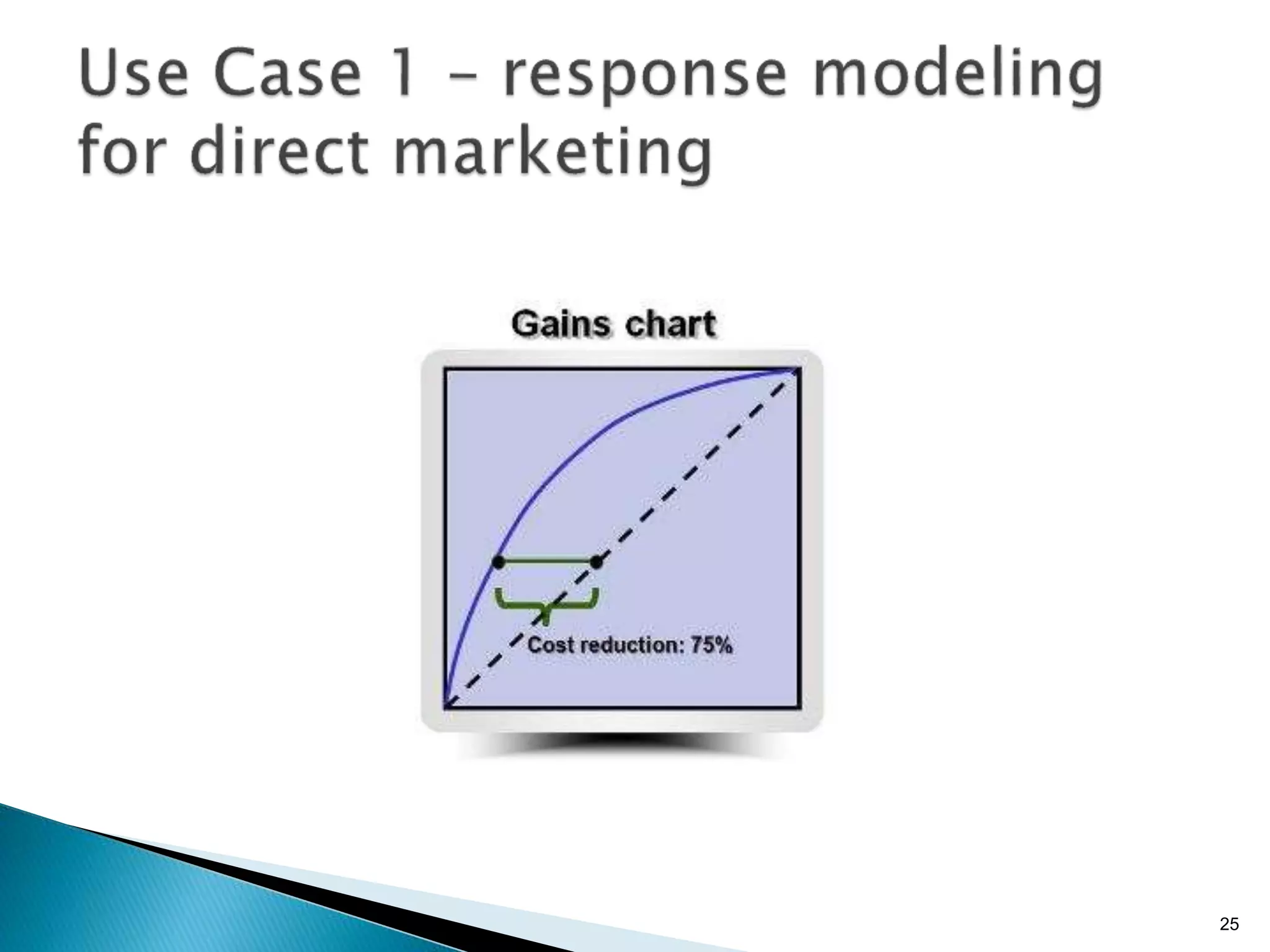
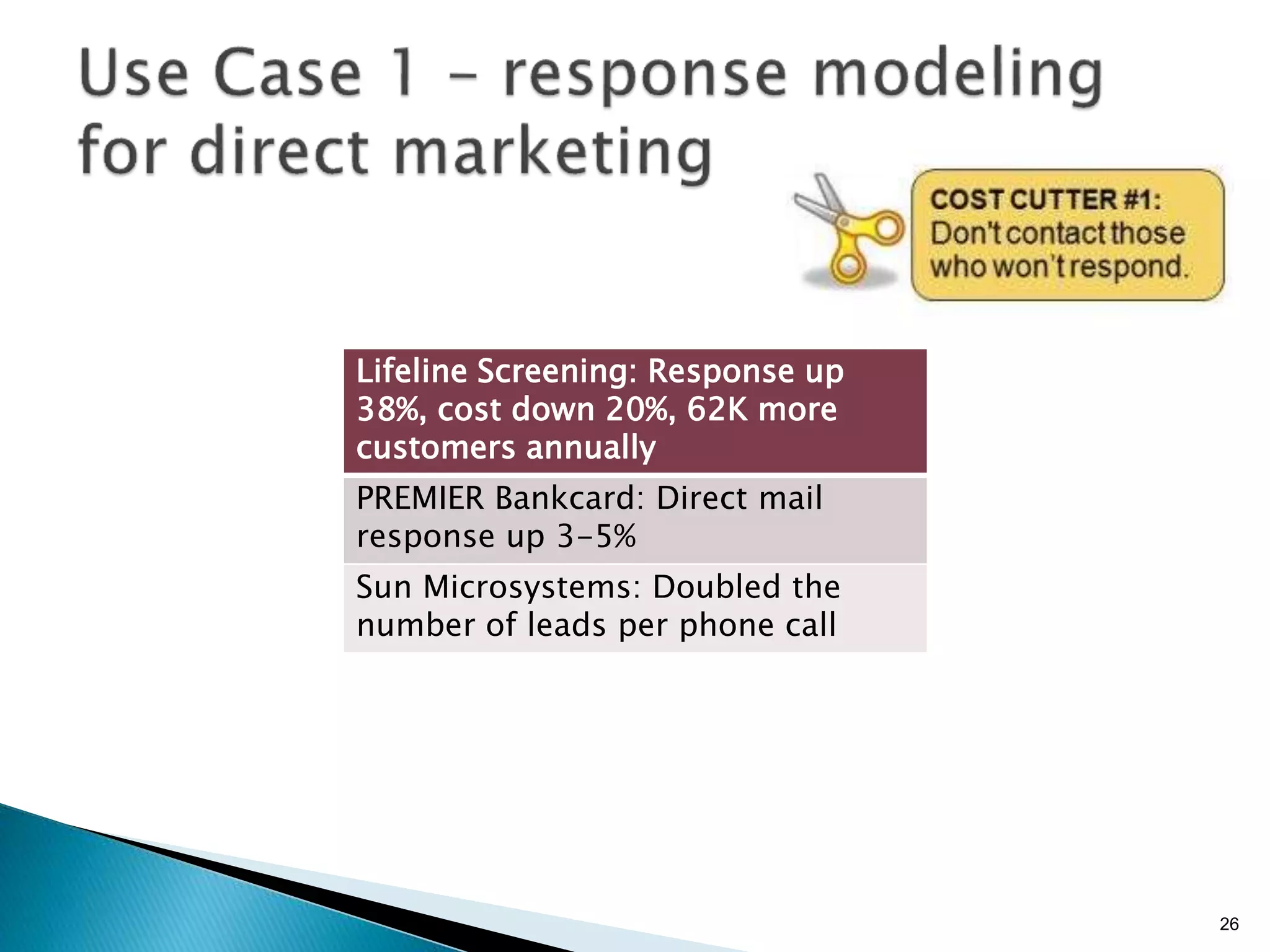
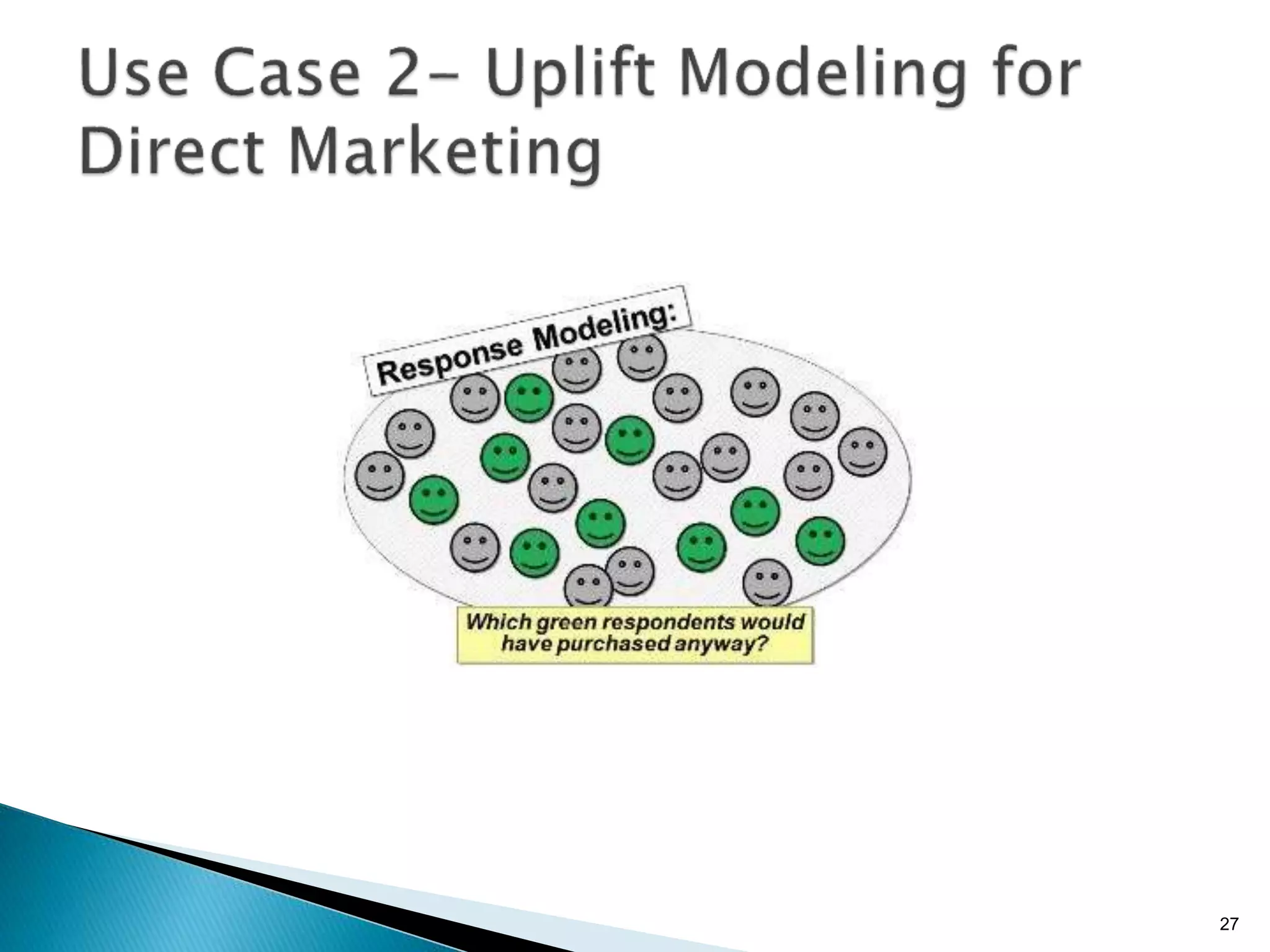
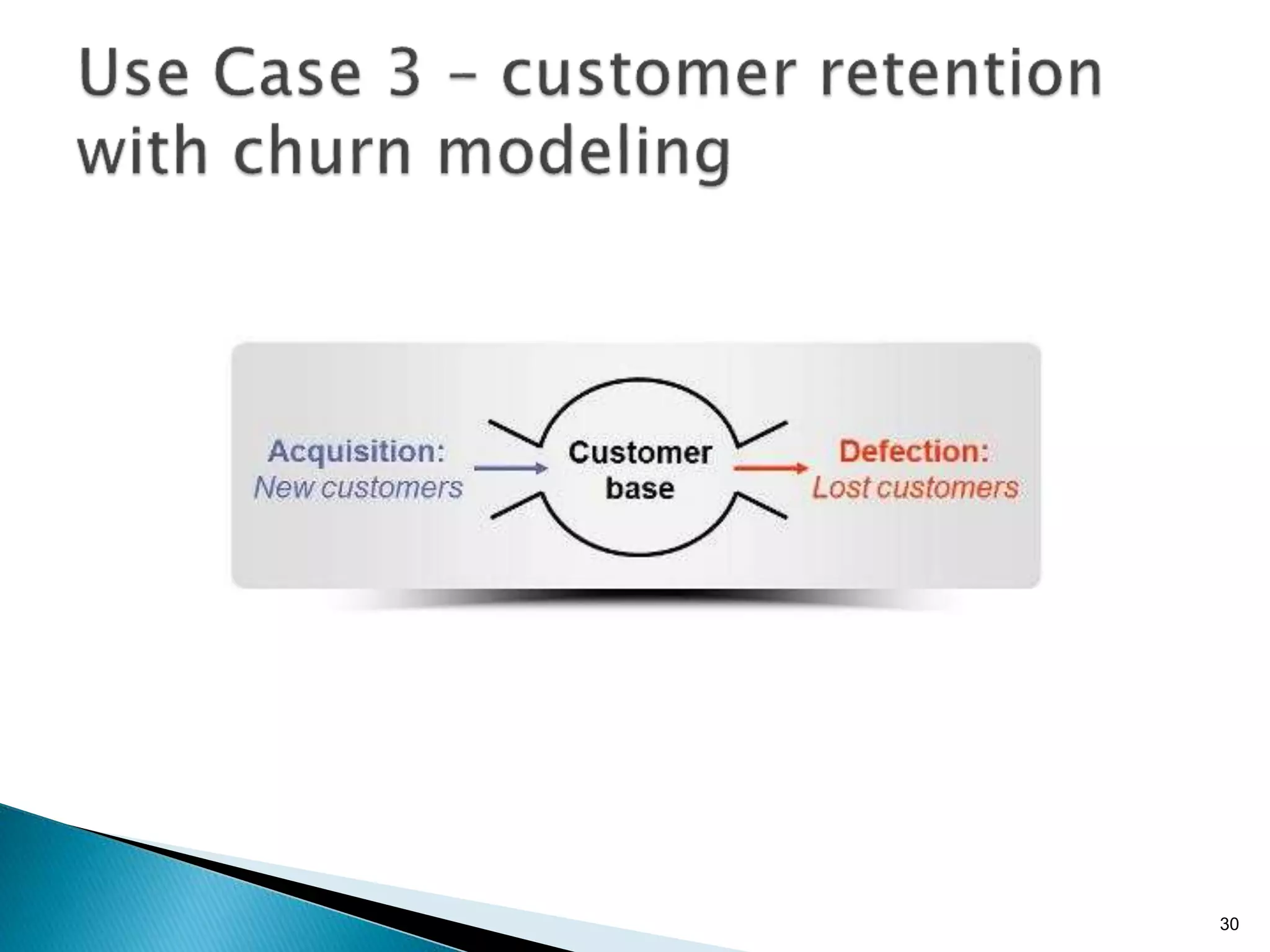
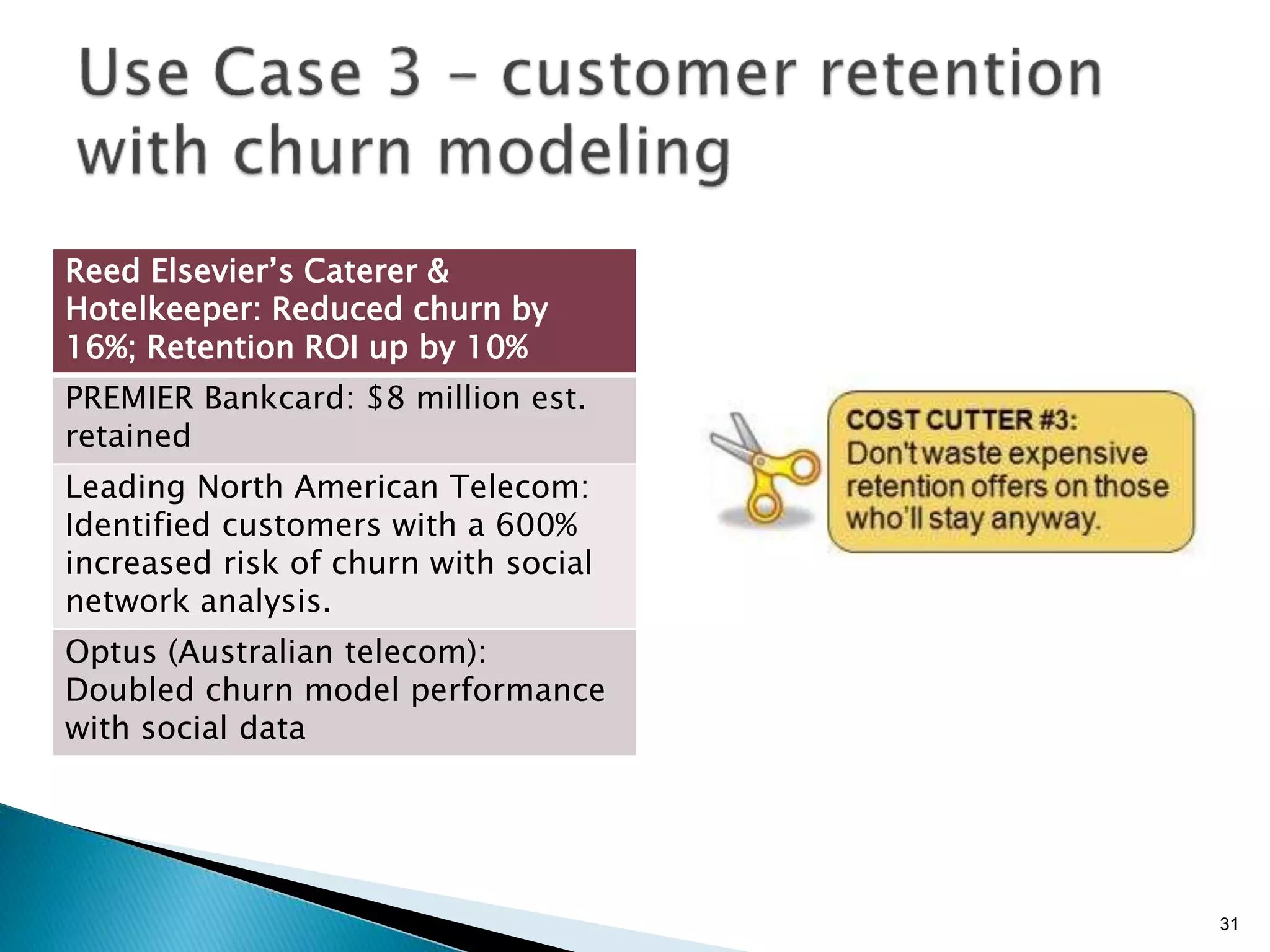
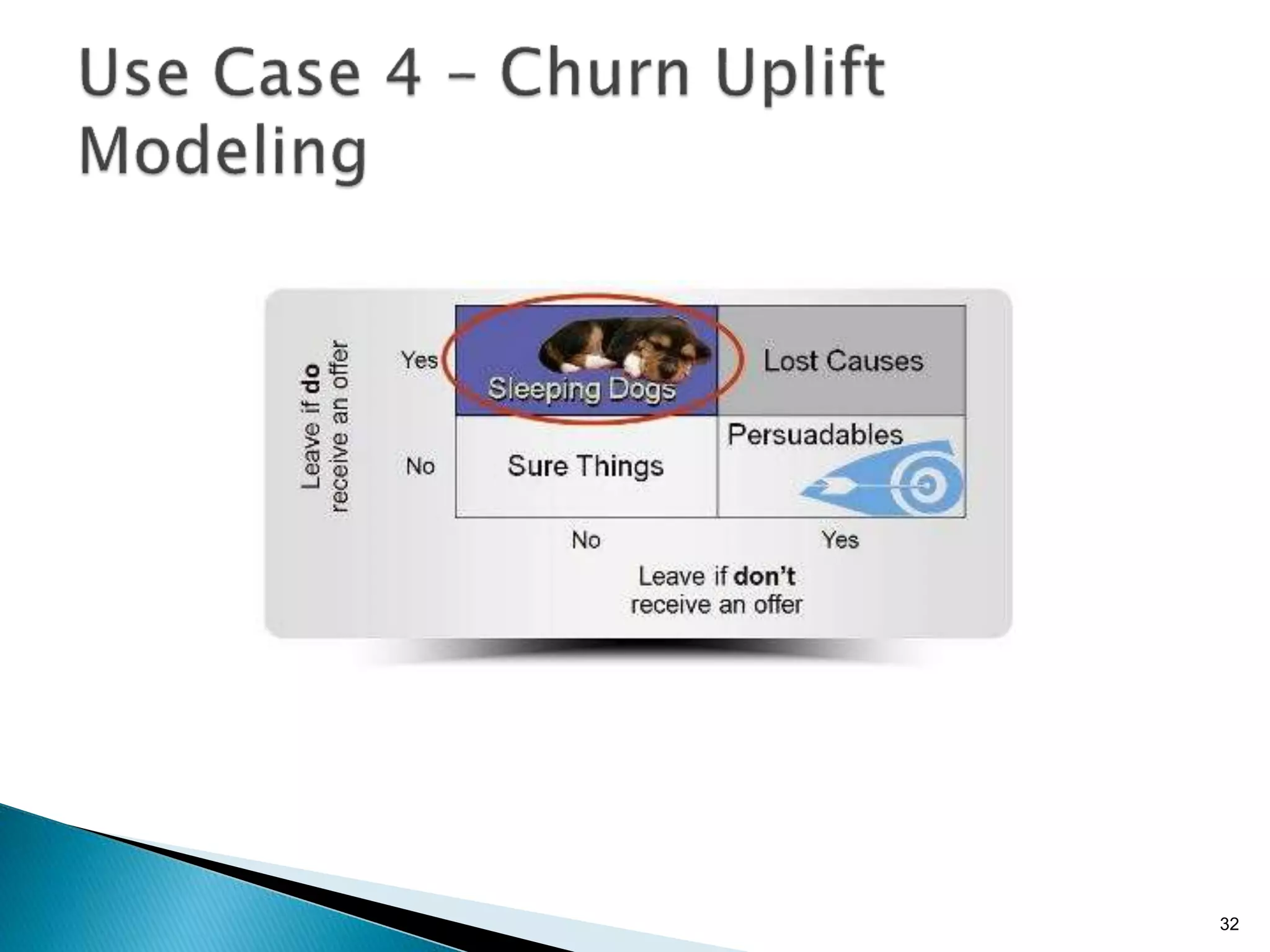
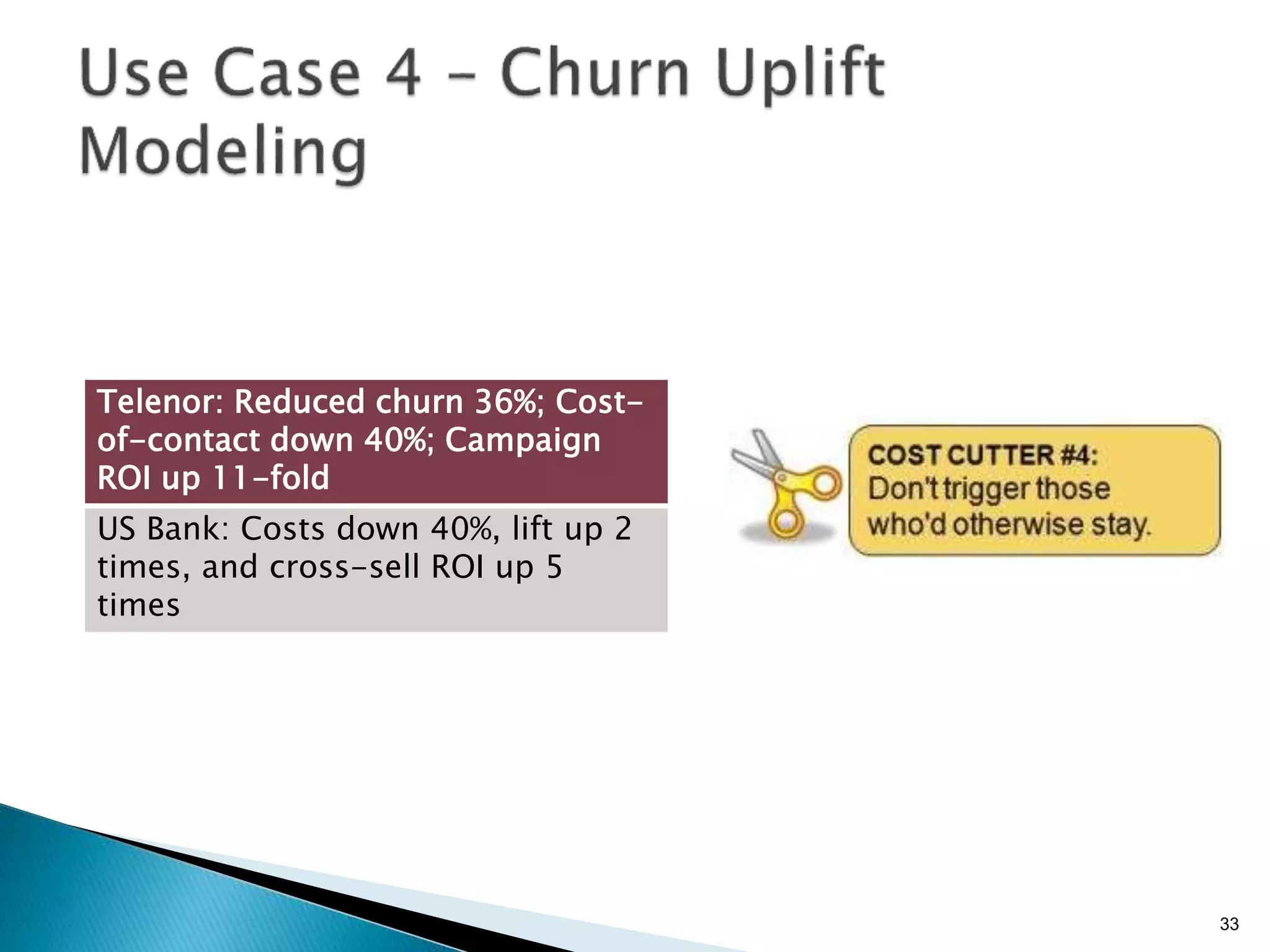
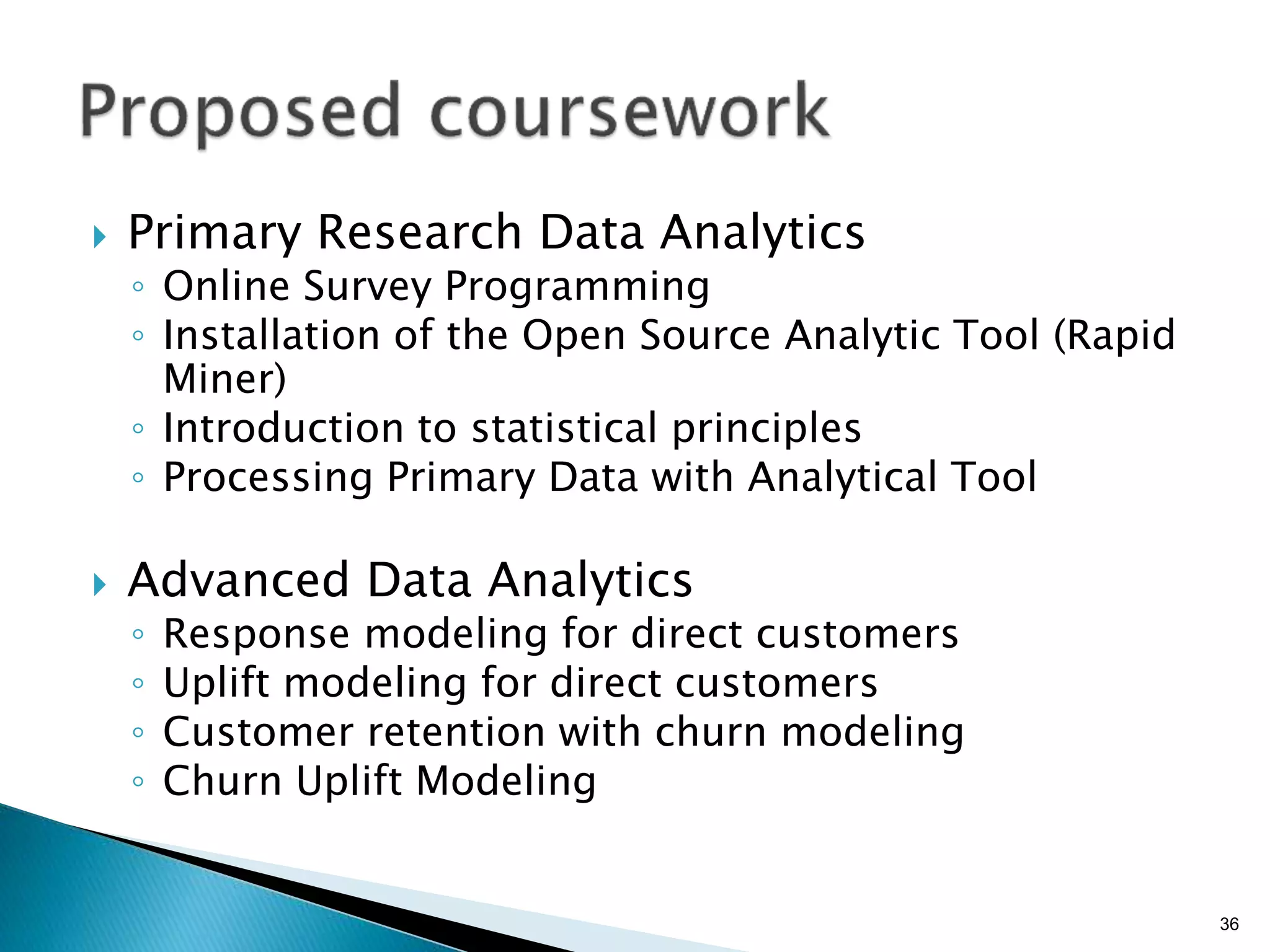
- By analyzing structured and unstructured data on customer behavior over time, data-based marketing allows companies to improve customer retention, response rates, and revenues through approaches like response modeling and churn analysis (Paragraphs 20, 23, 24).