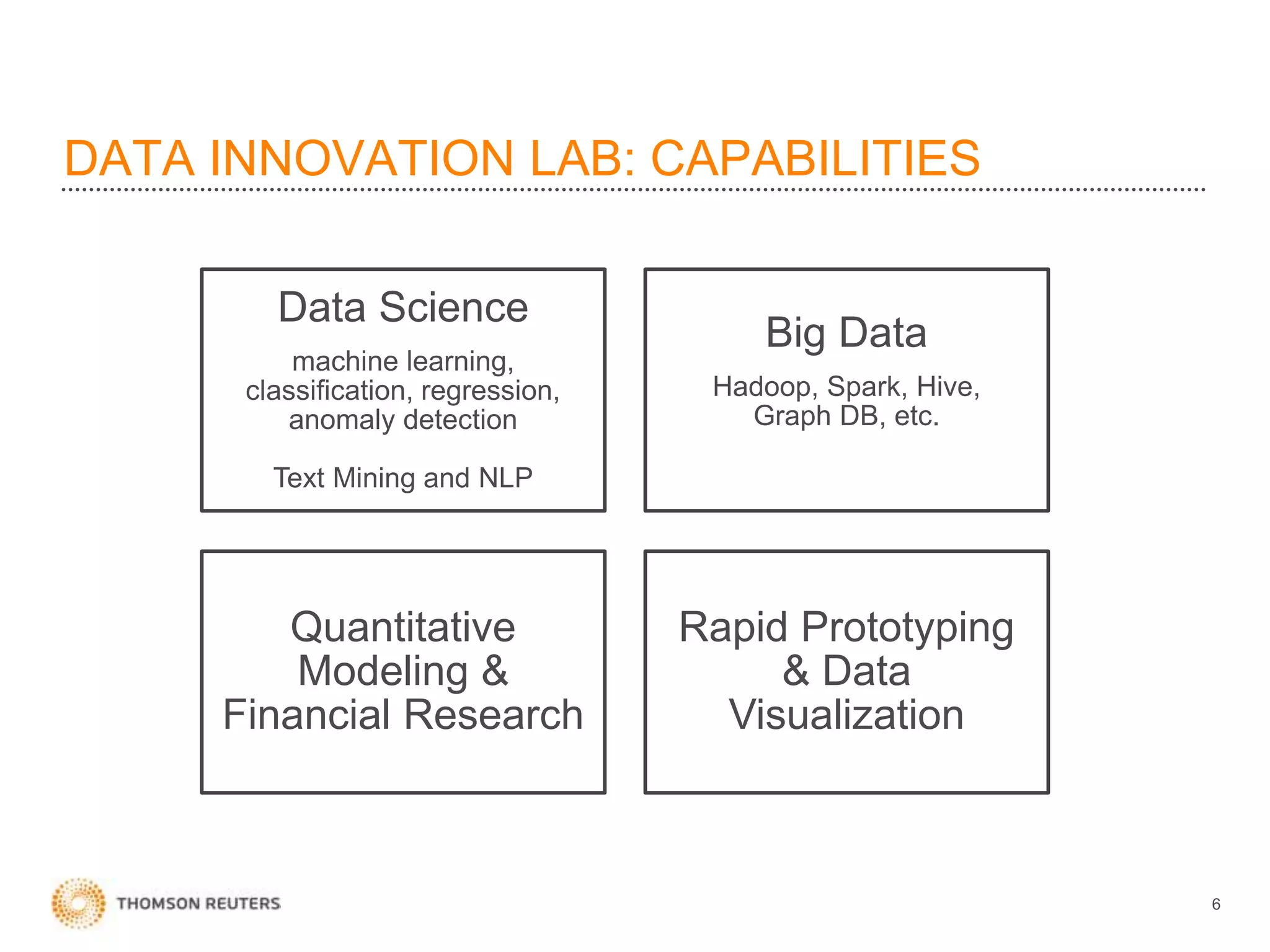
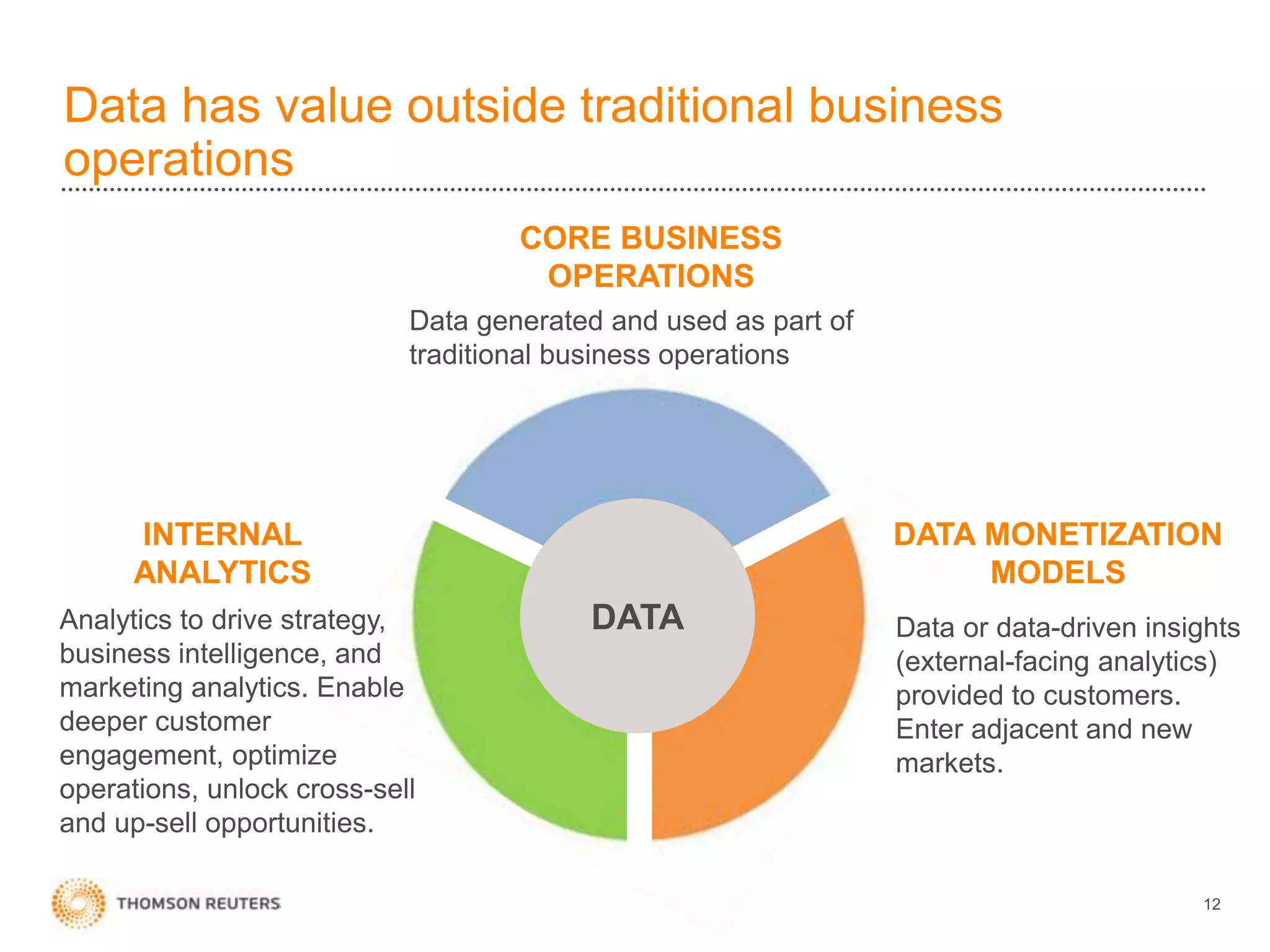
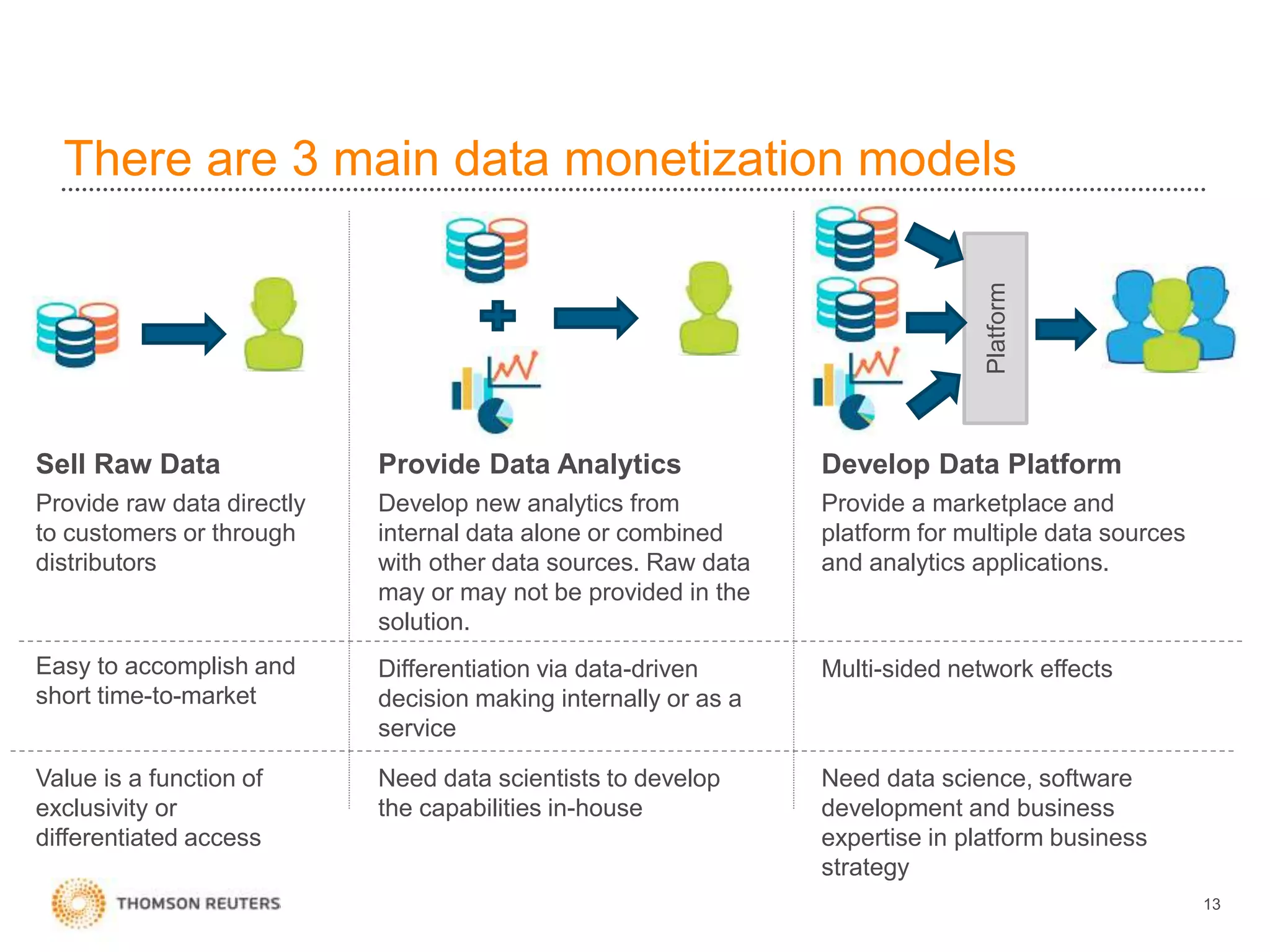
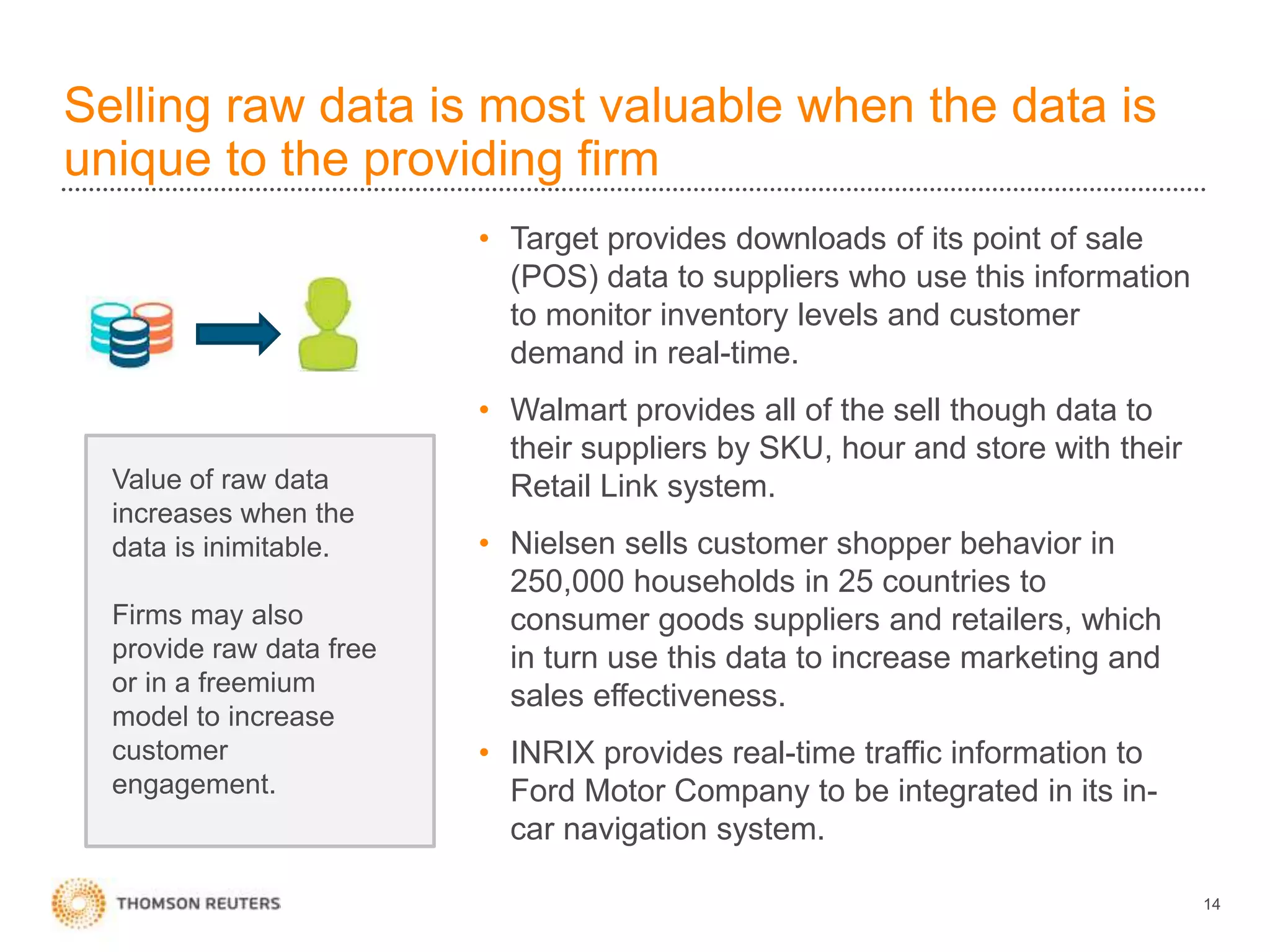
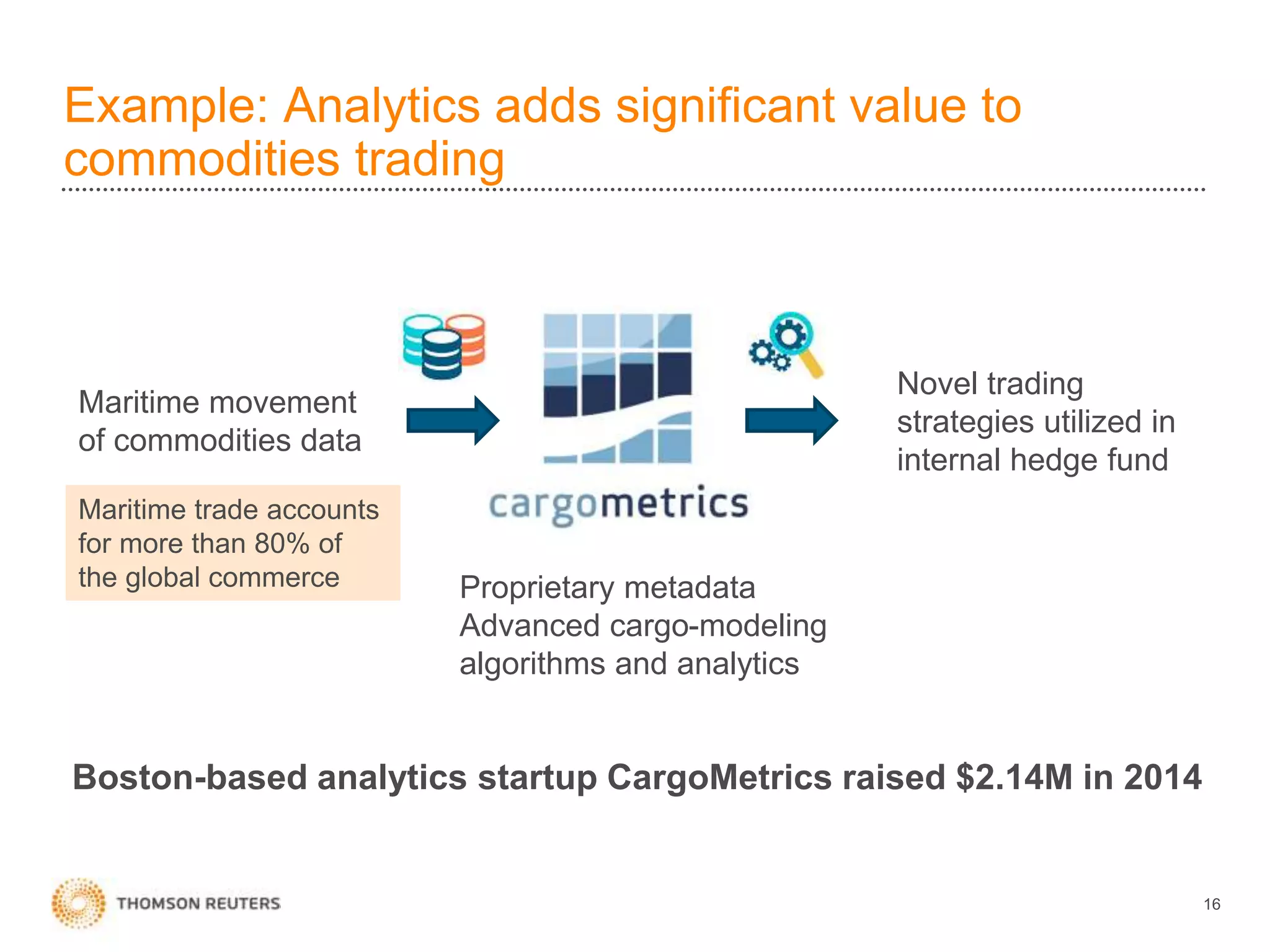
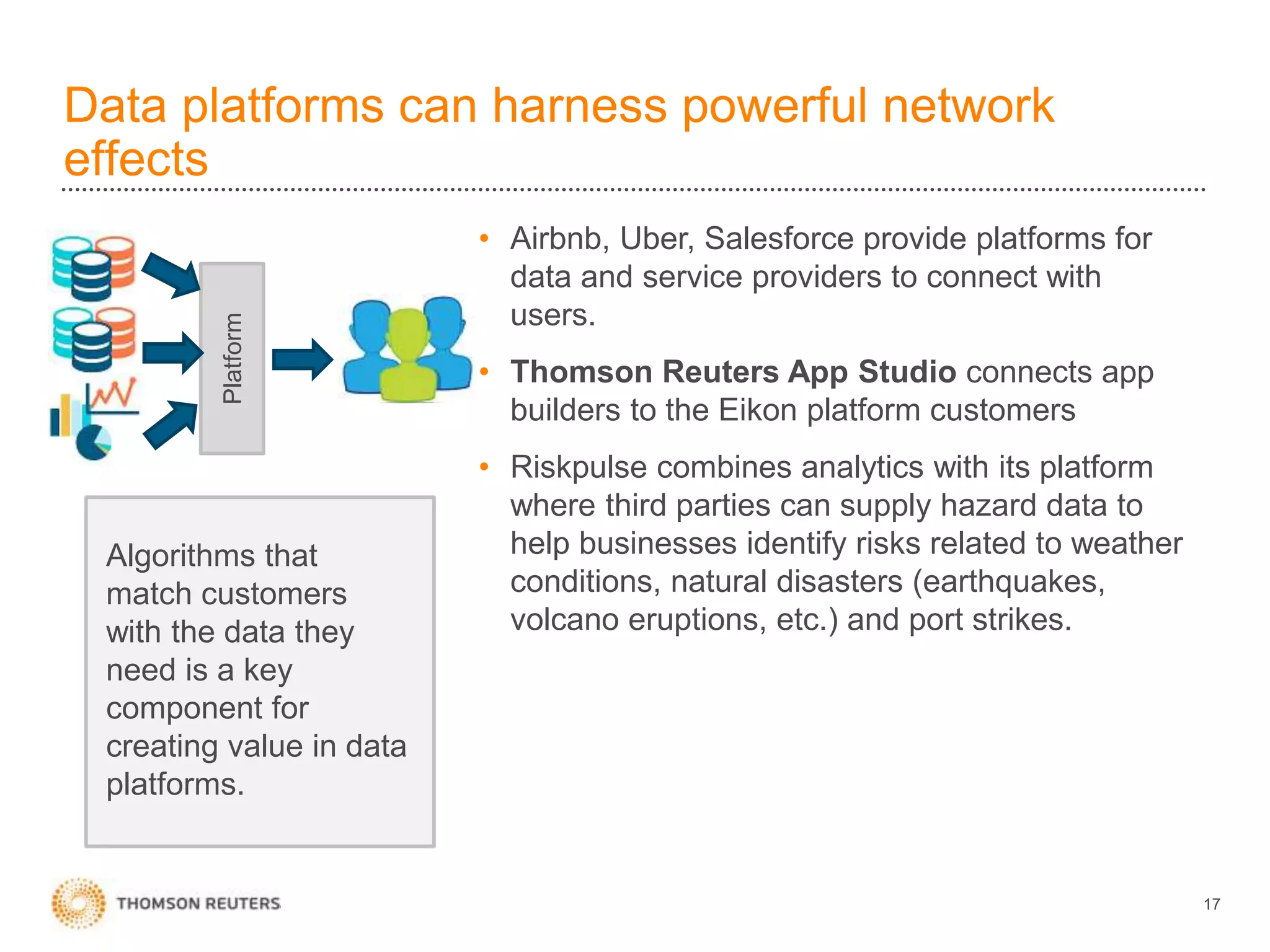
The document discusses building data science capabilities at Thomson Reuters. It introduces the Data Innovation Lab, which works on agile data science projects using lean sprints. The lab focuses on delivering insights to customers through proof-of-concepts and analytical models. It also discusses challenges in data monetization like finding reliable data sources and establishing rights to externalize data. Recent projects demonstrated include linking disparate data using PermIDs, predicting patent litigation risk through machine learning, and visualizing relationships between food insecurity and political instability.