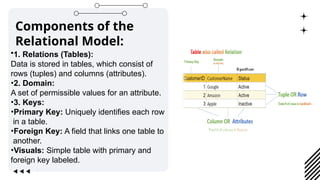
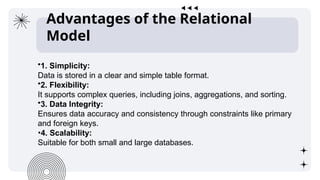
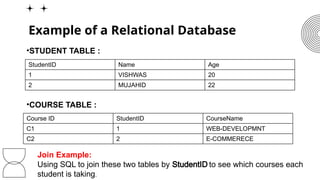
The document discusses data models, focusing on the relational data model, which organizes data into tables for efficient management and retrieval. It outlines key components like tables, rows, columns, and keys, along with the advantages of simplicity, flexibility, data integrity, and scalability. Additionally, it provides examples of relational databases and mentions future trends such as cloud databases and the integration of relational databases with big data tools.