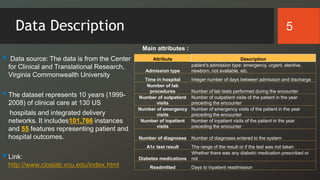
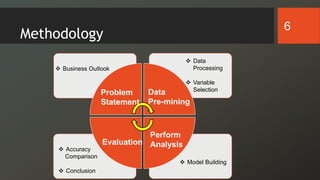
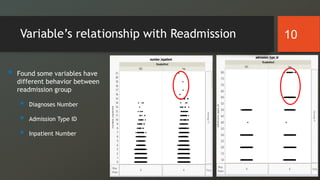
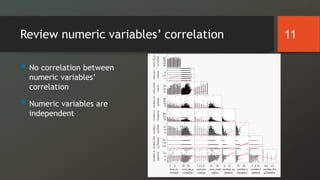
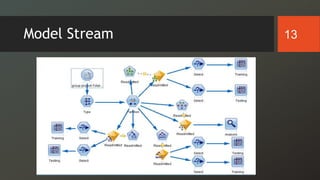
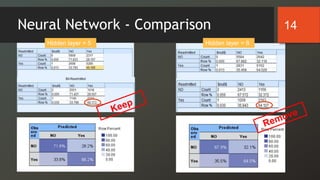
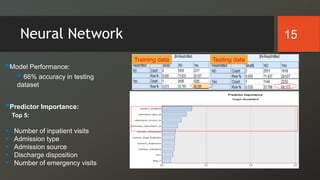
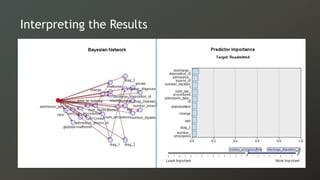
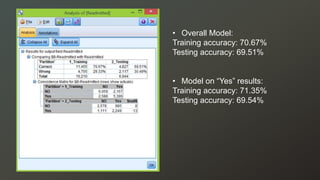
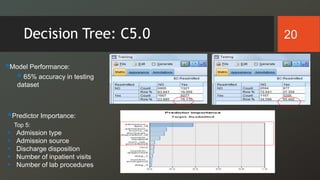
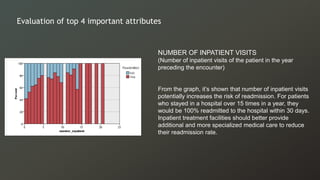
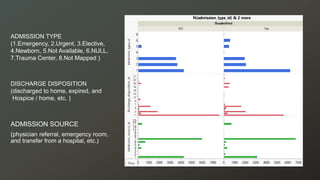
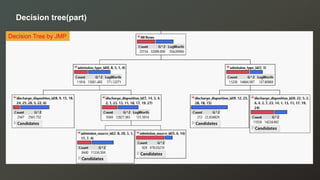
The document discusses a study on predicting diabetes readmissions using various data mining methodologies, analyzing a dataset of over 101,000 instances from U.S. hospitals. It highlights the importance of identifying key factors, including admission type and number of inpatient visits, that contribute to readmissions within 30 days of discharge. The study concludes that effective prediction can help hospitals reduce readmission rates and improve patient care by focusing on critical variables rather than the entire dataset.