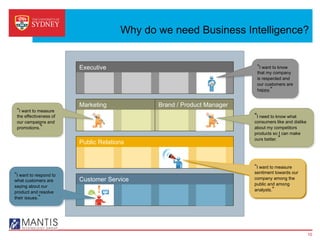
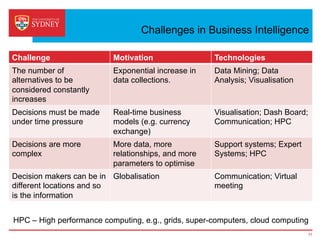
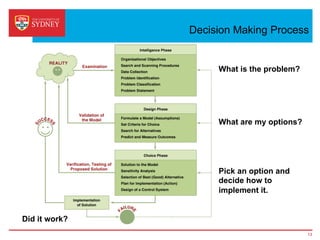
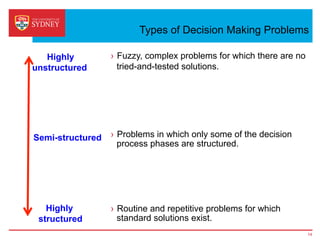
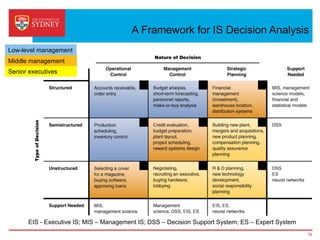
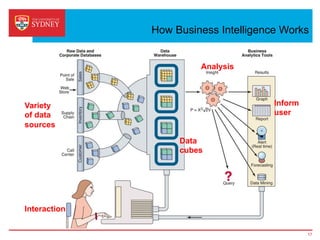
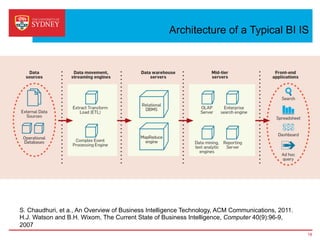
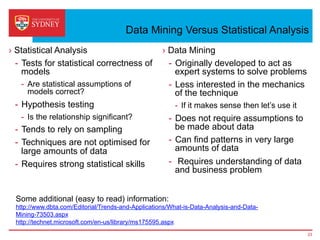
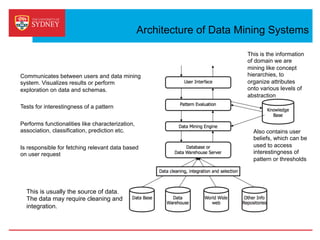
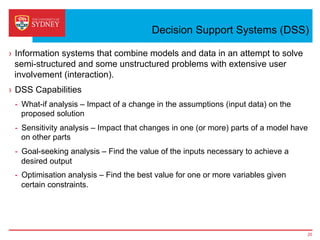
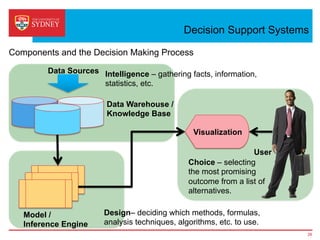
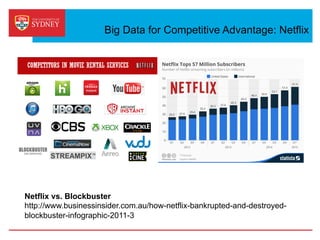
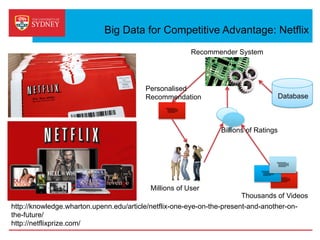
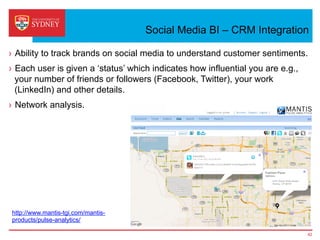
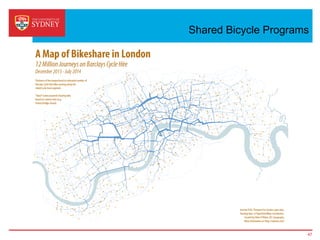
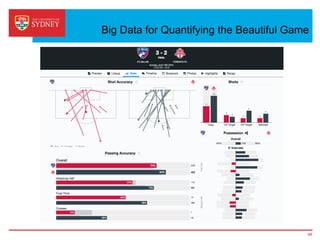
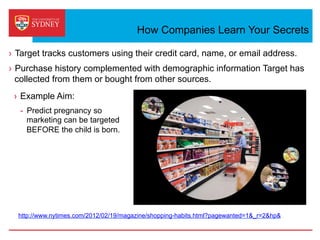
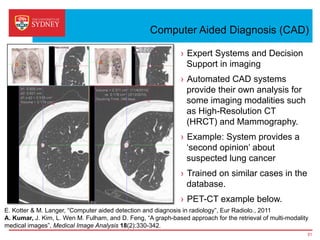
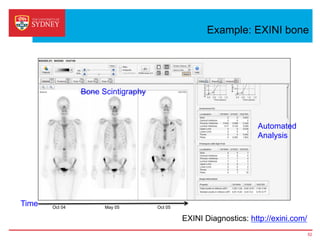
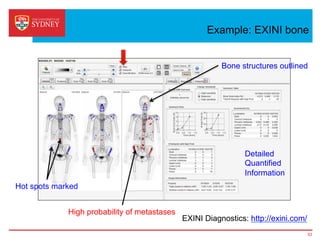
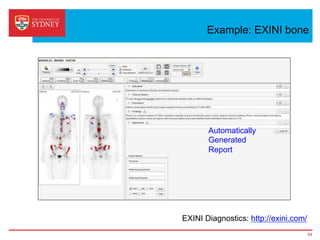
Business intelligence and analytics systems use data from various sources to provide useful information and insights. These systems include tools for online analytical processing, data mining, visualization, and decision support. They help organizations make better decisions by analyzing large amounts of structured and unstructured data. Netflix is an example of a company that has gained a competitive advantage through business intelligence by using customer viewing data to provide personalized recommendations.