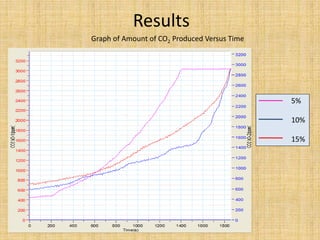
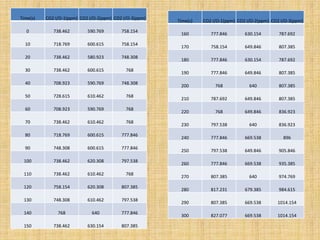
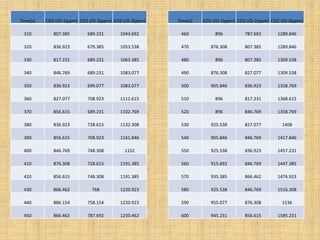
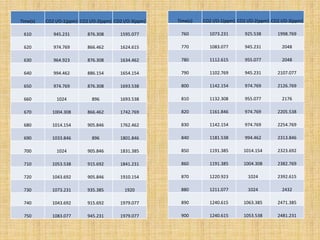
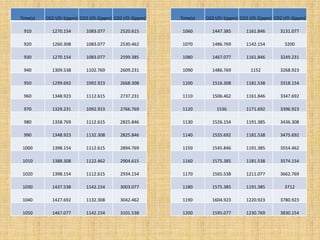
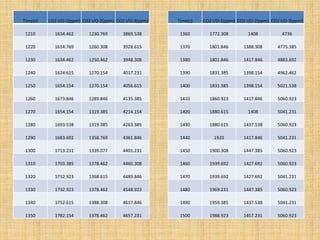
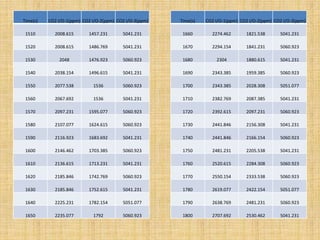
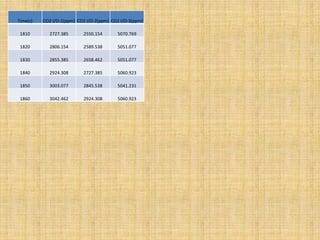
Anaerobic respiration occurs when oxygen is limited or absent. During anaerobic respiration in plant cells, glucose is partially broken down into ethanol and carbon dioxide, rather than being fully oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. The experiment measured the production of carbon dioxide gas over time from yeast fermenting different concentrations of glucose solutions (5%, 10%, 15%). Higher glucose concentrations produced more carbon dioxide, with the 15% solution producing the most.