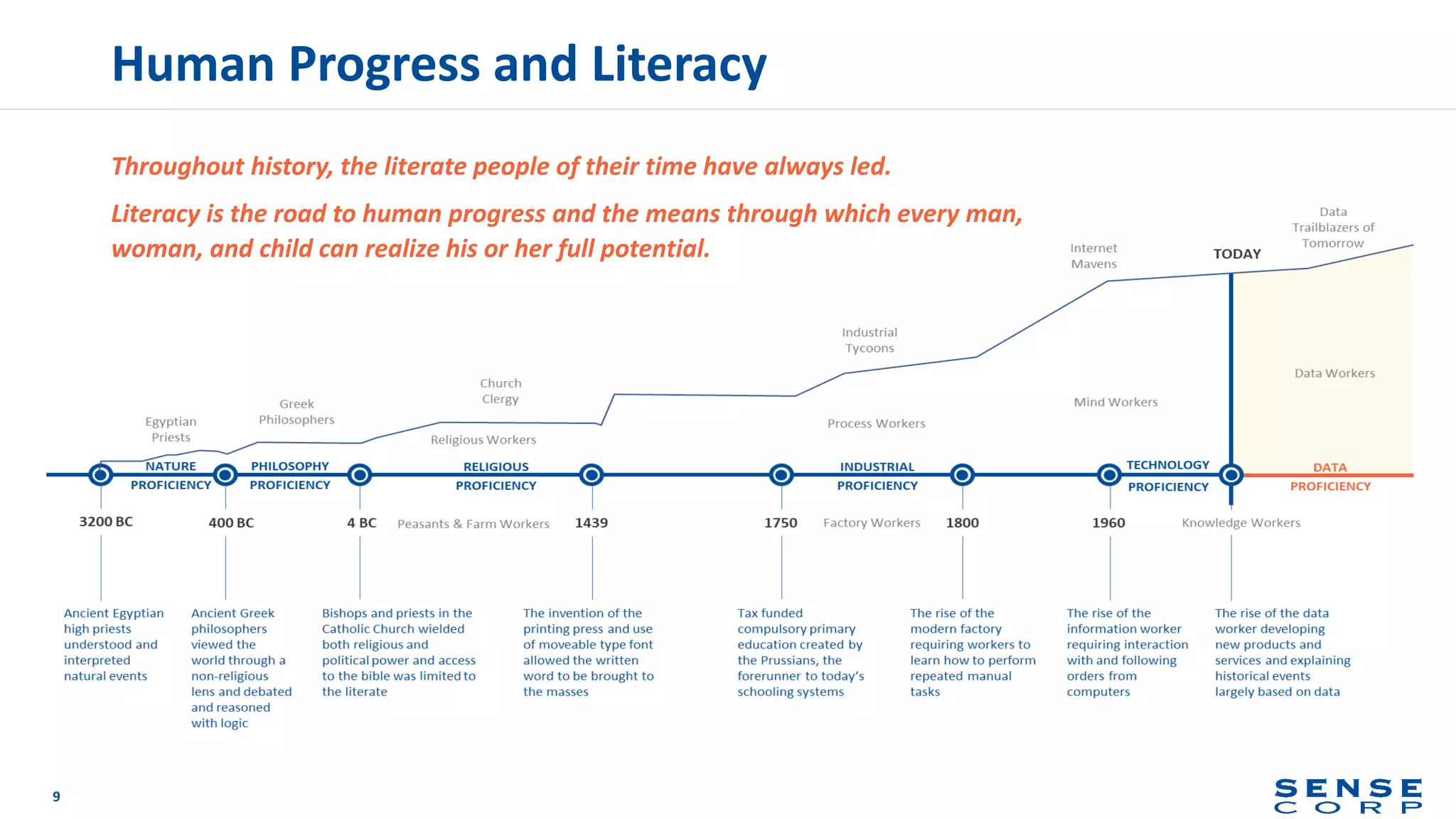
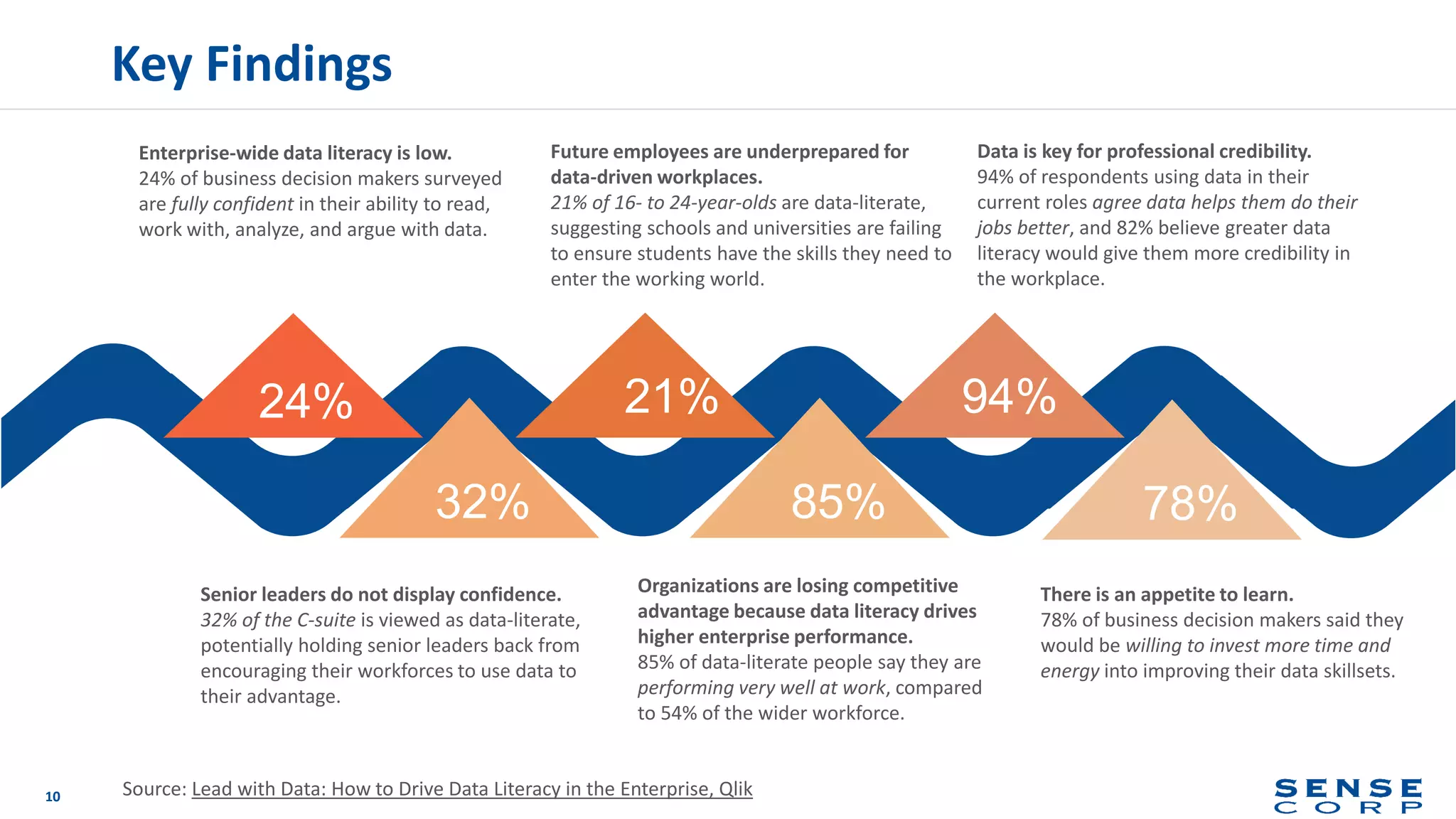
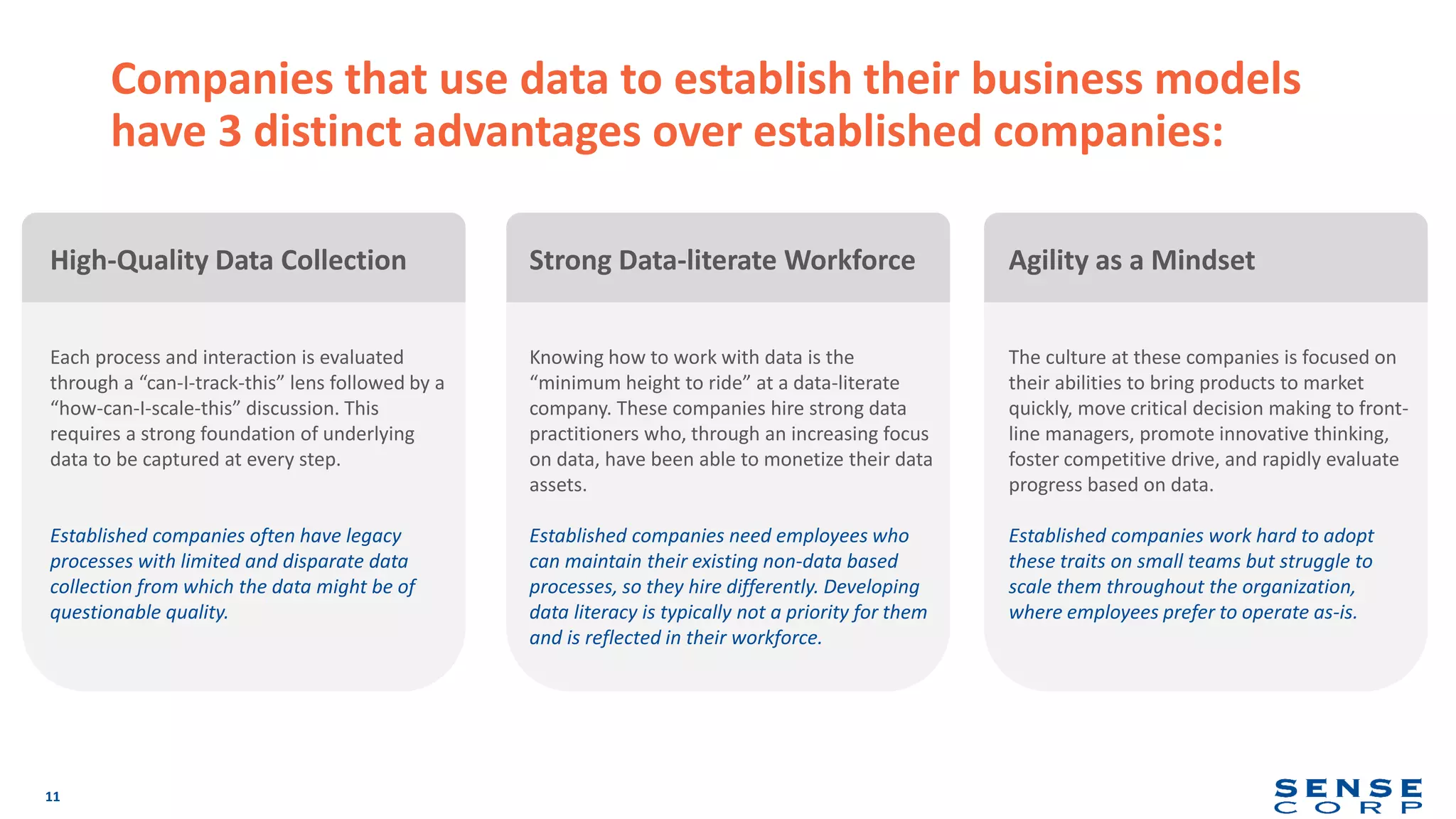
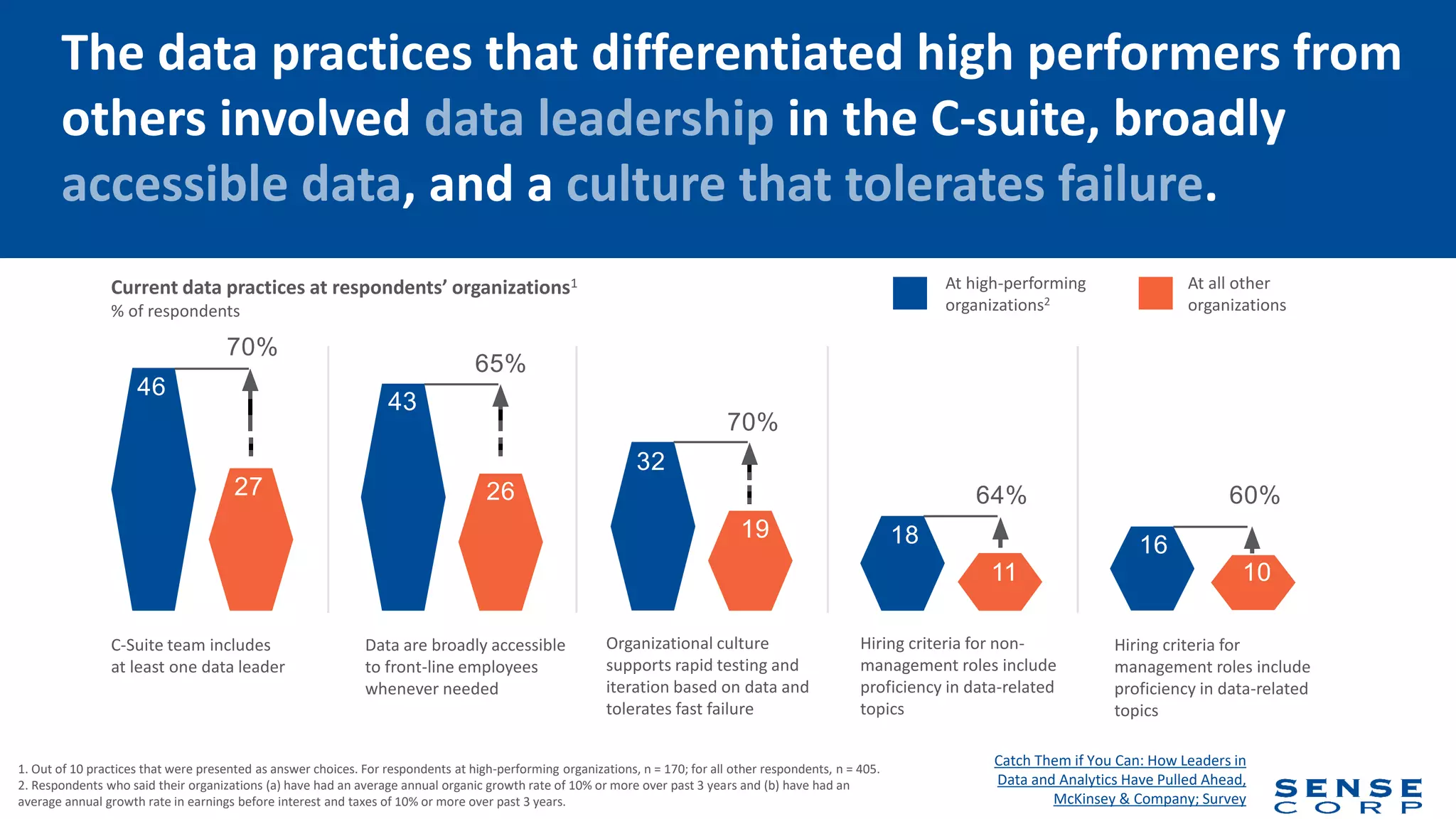
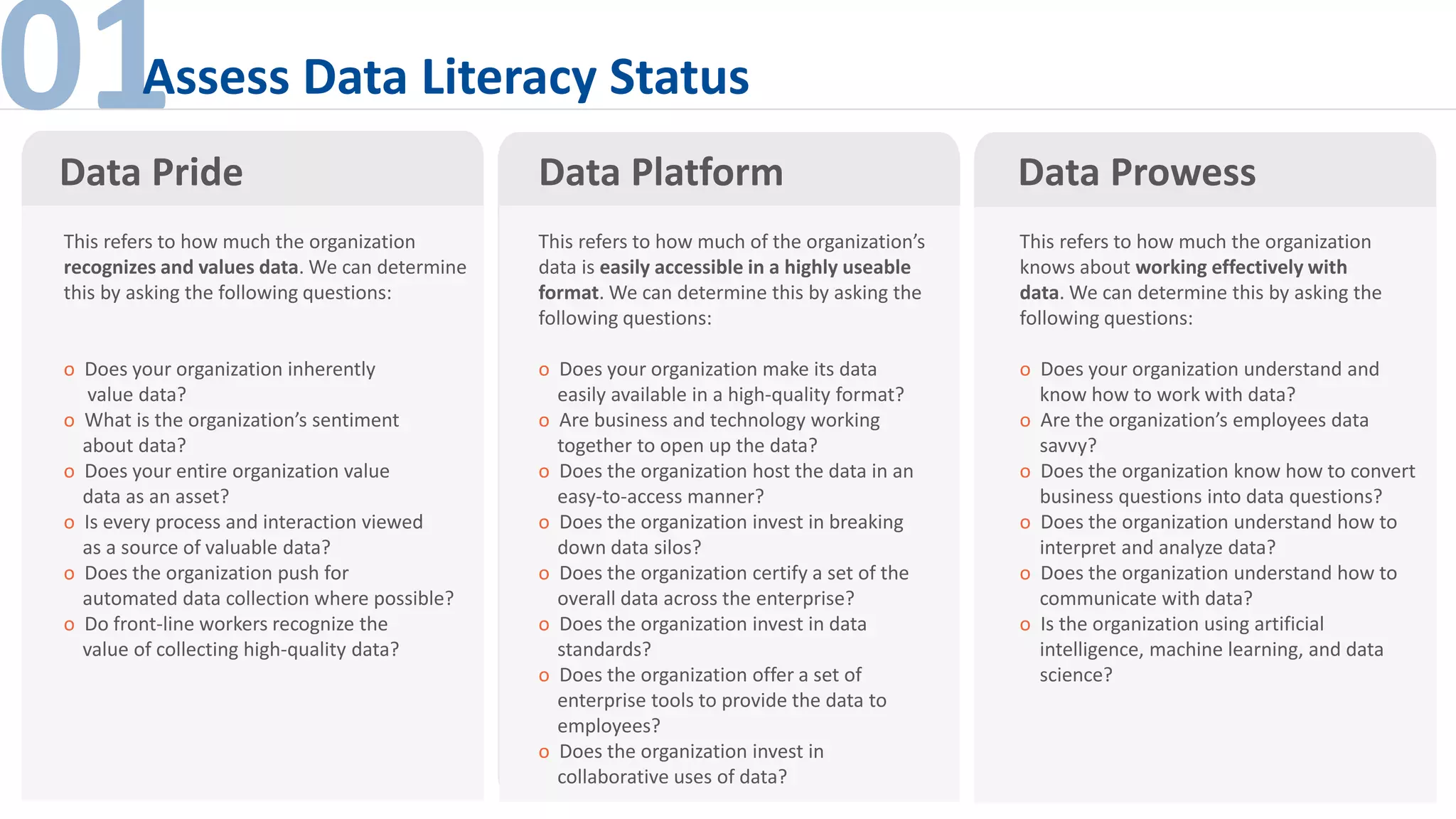
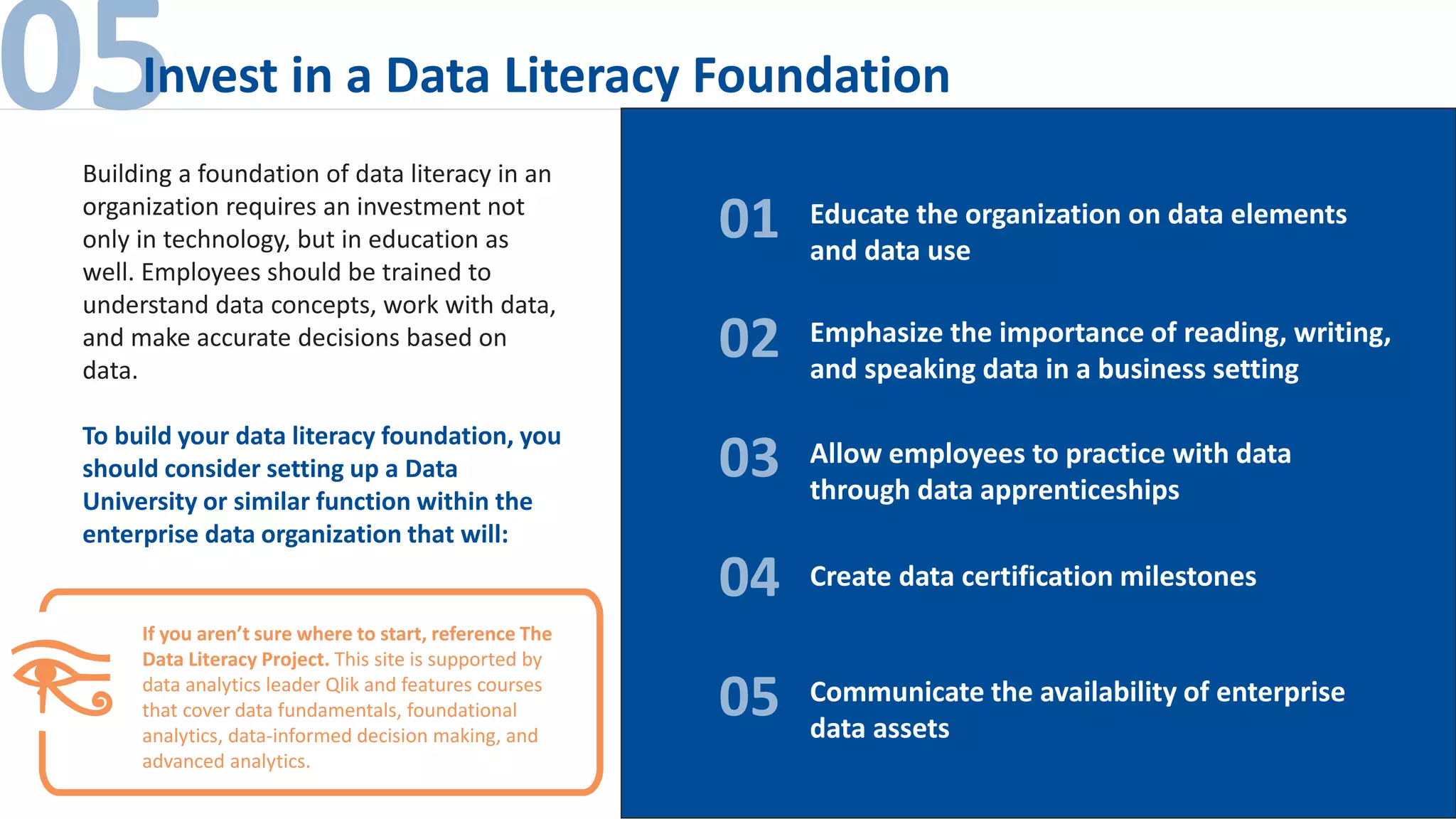
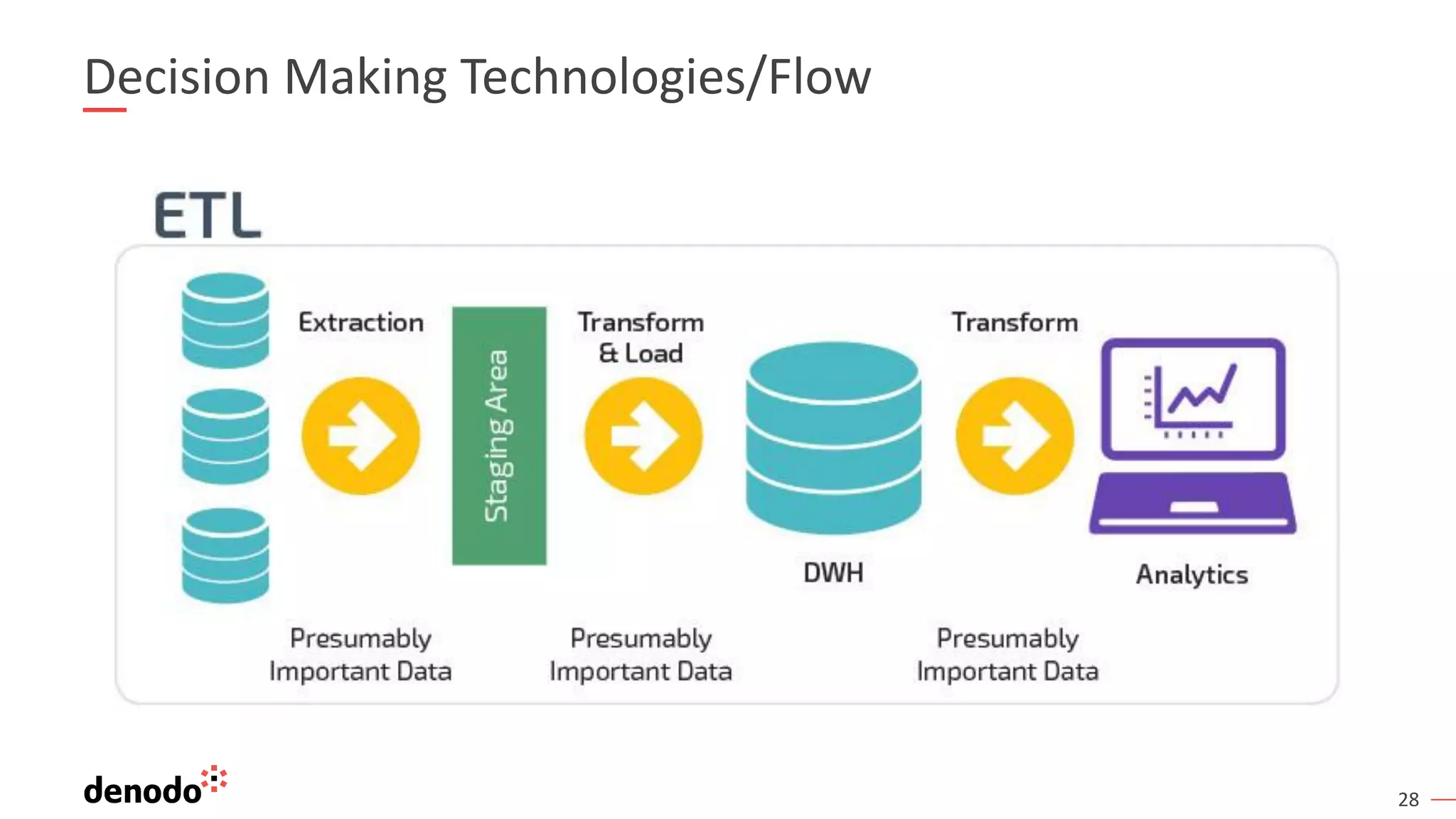
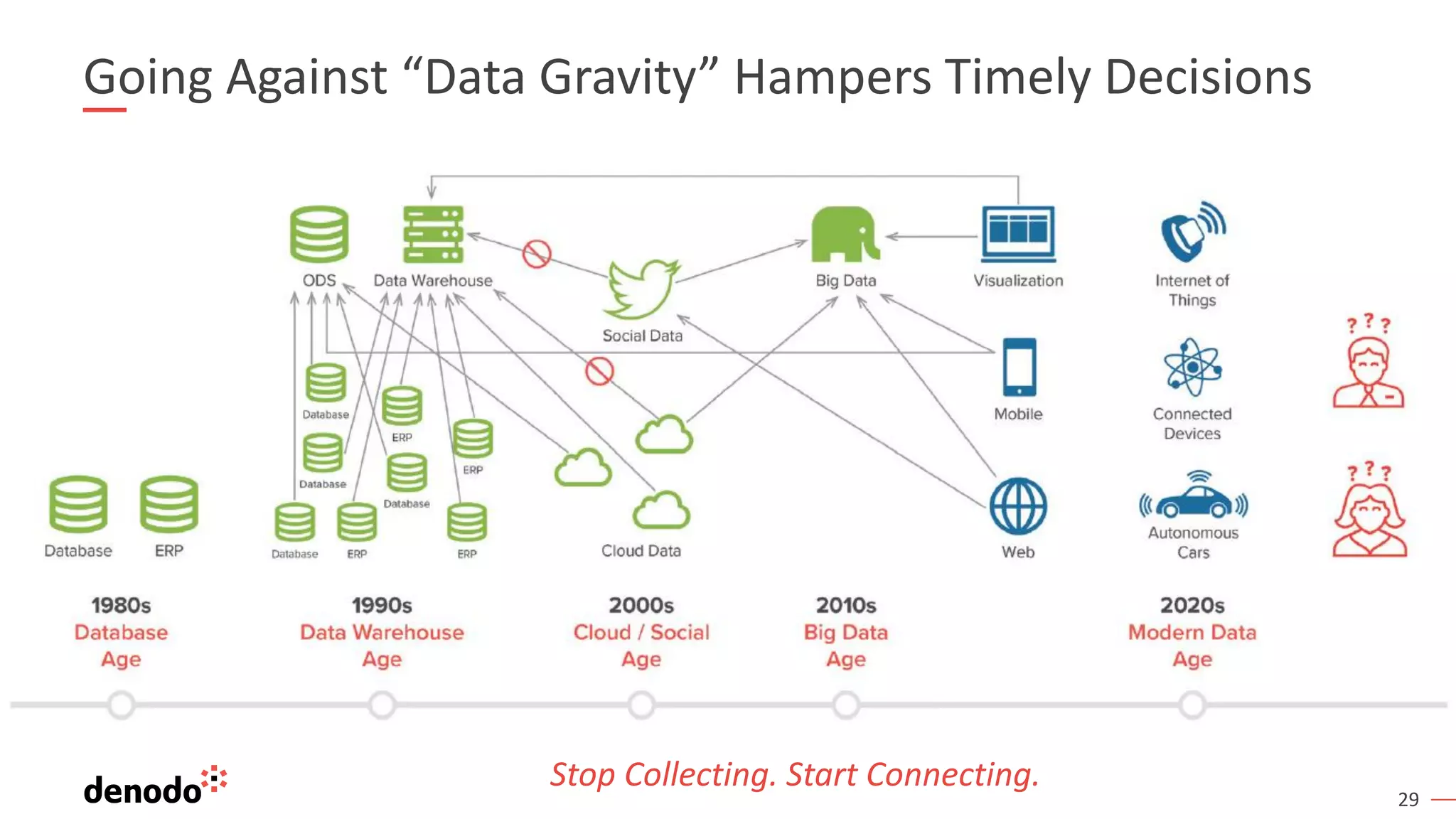
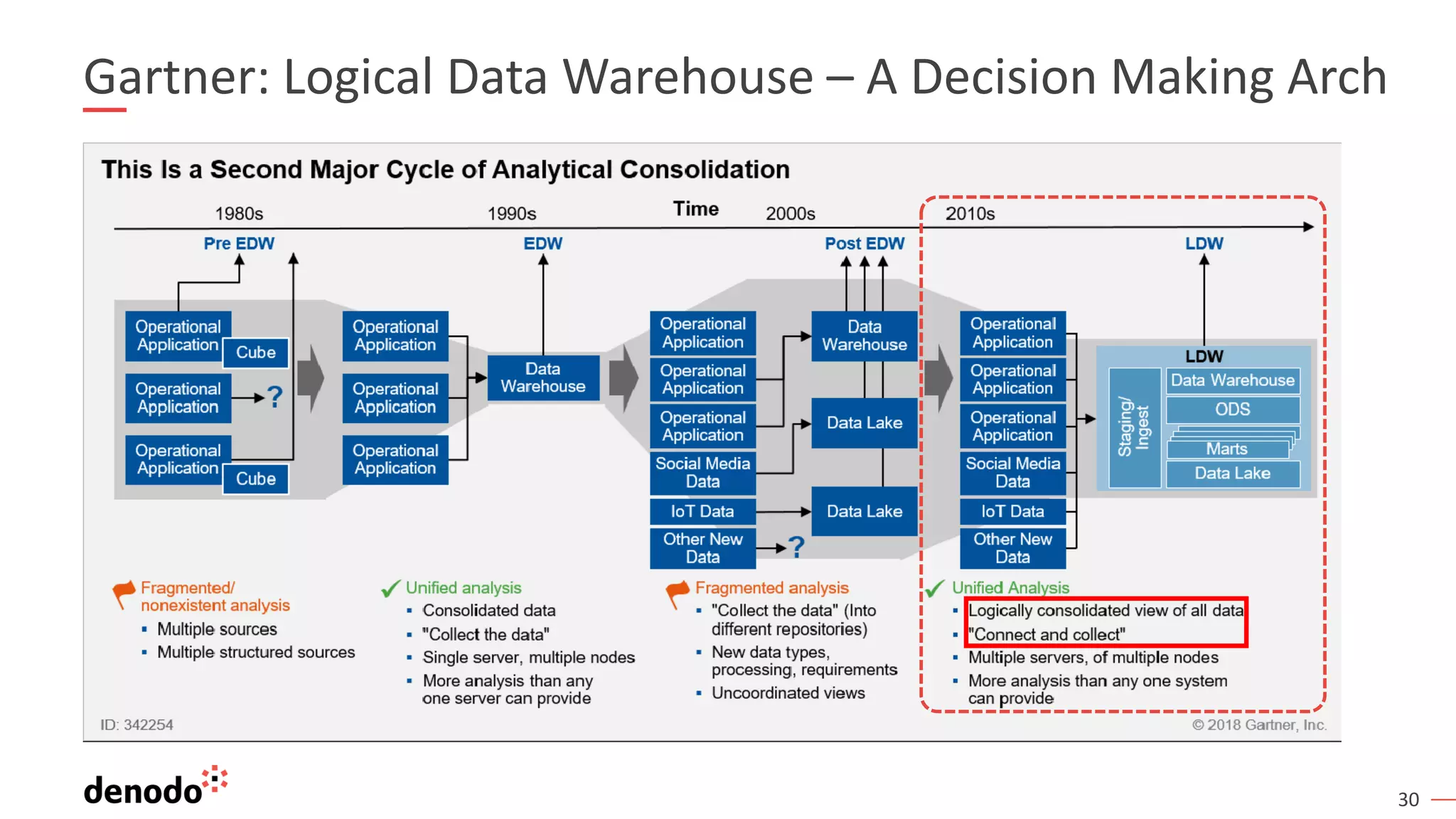
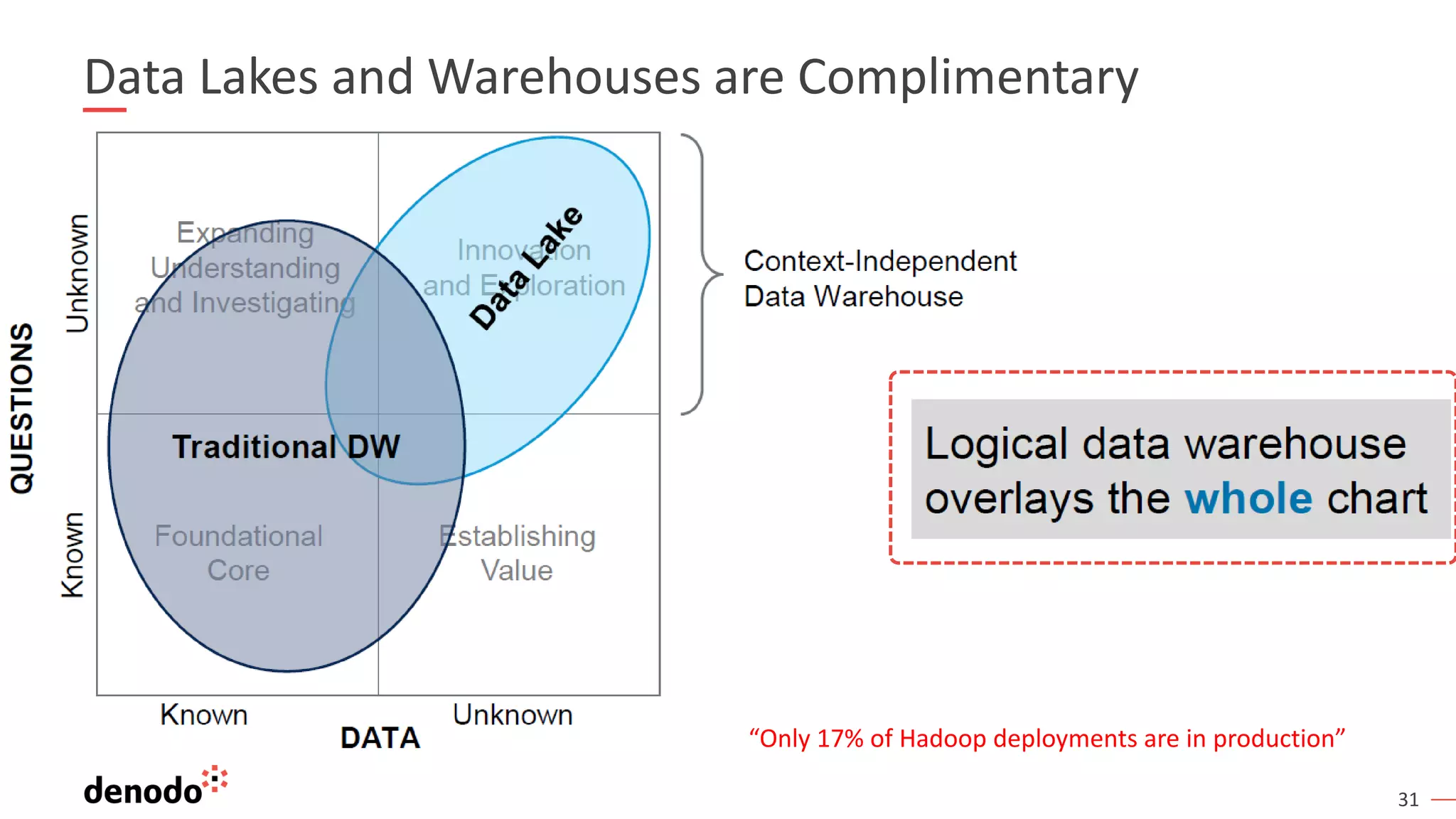
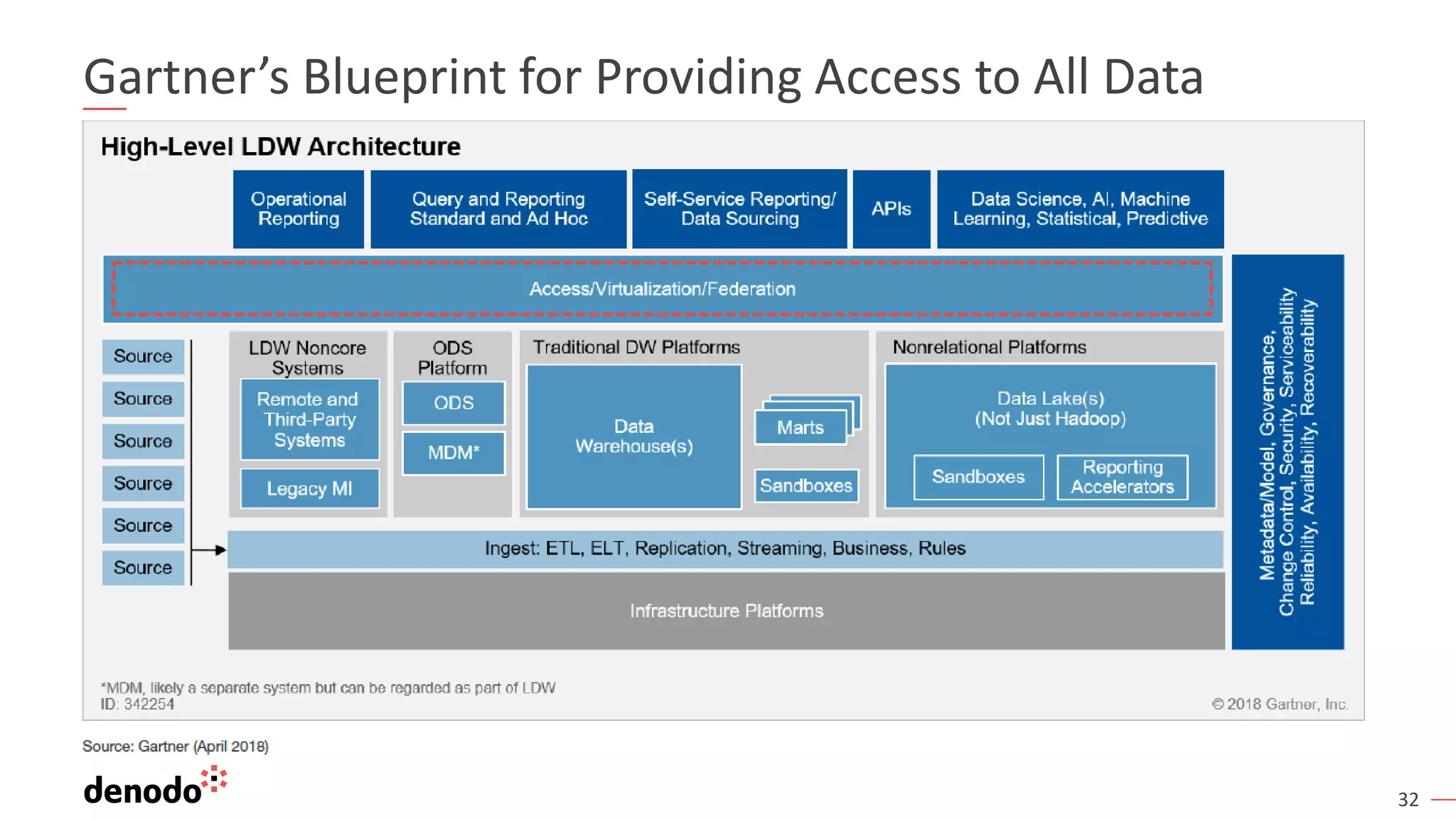
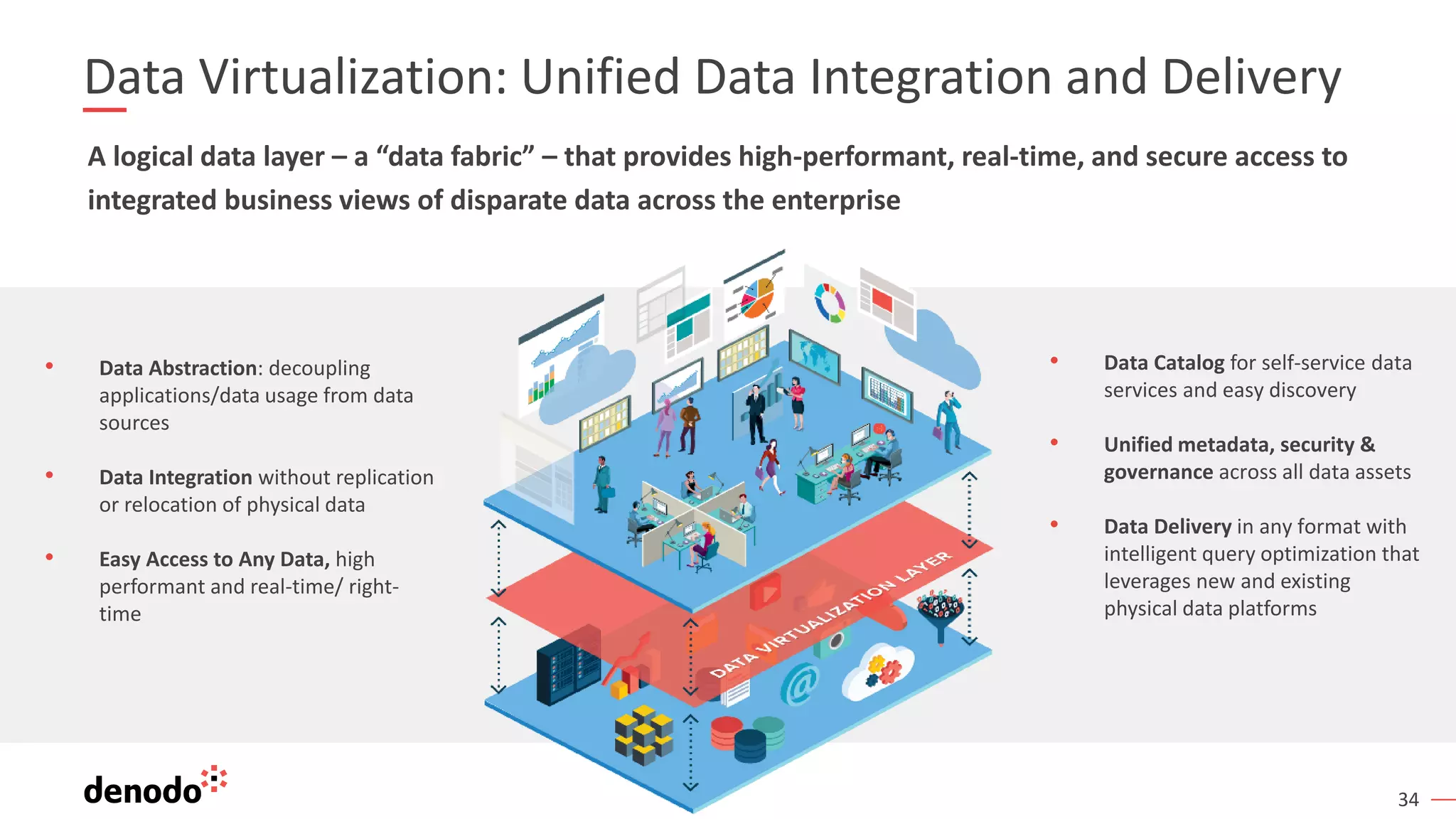
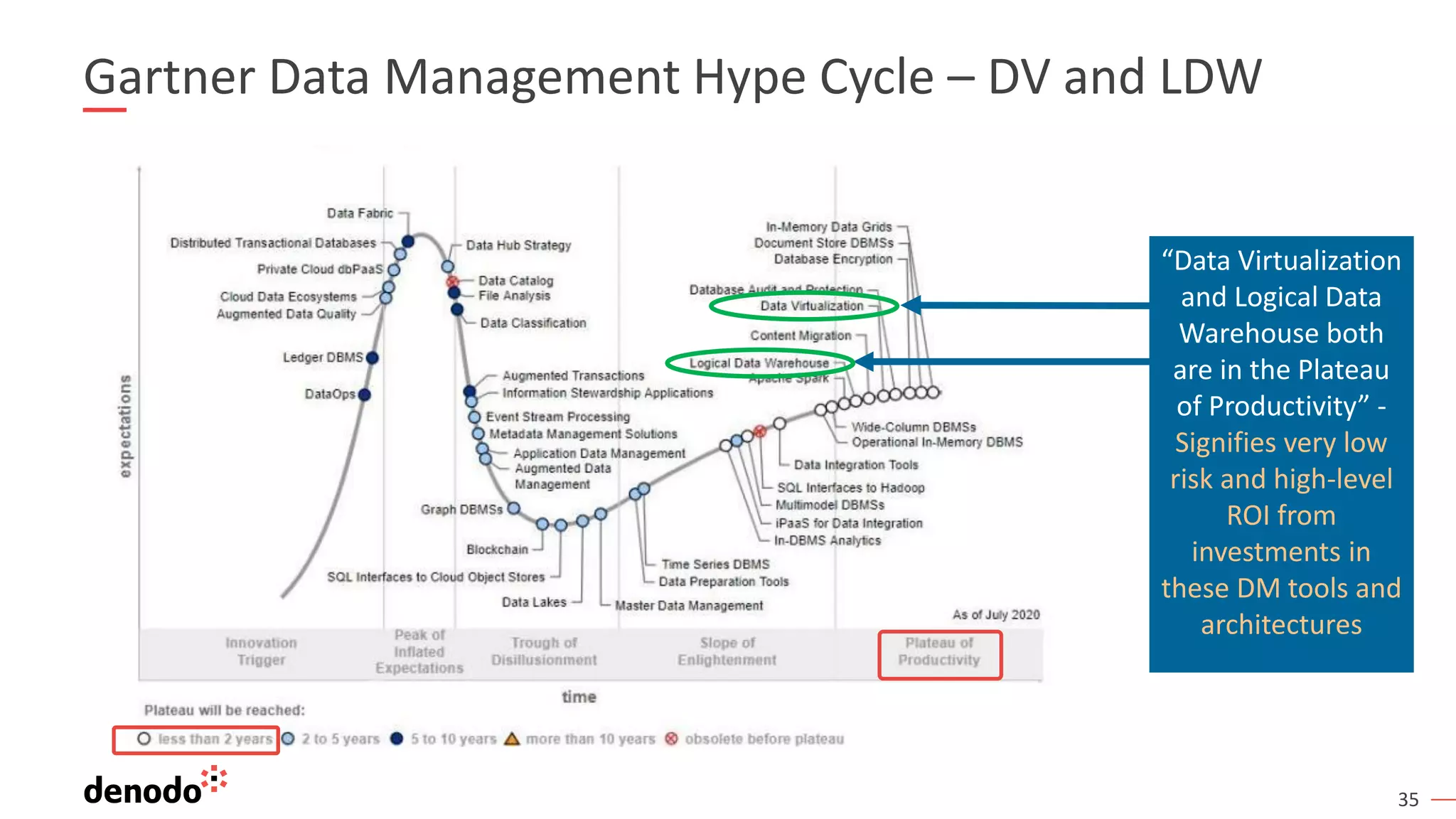
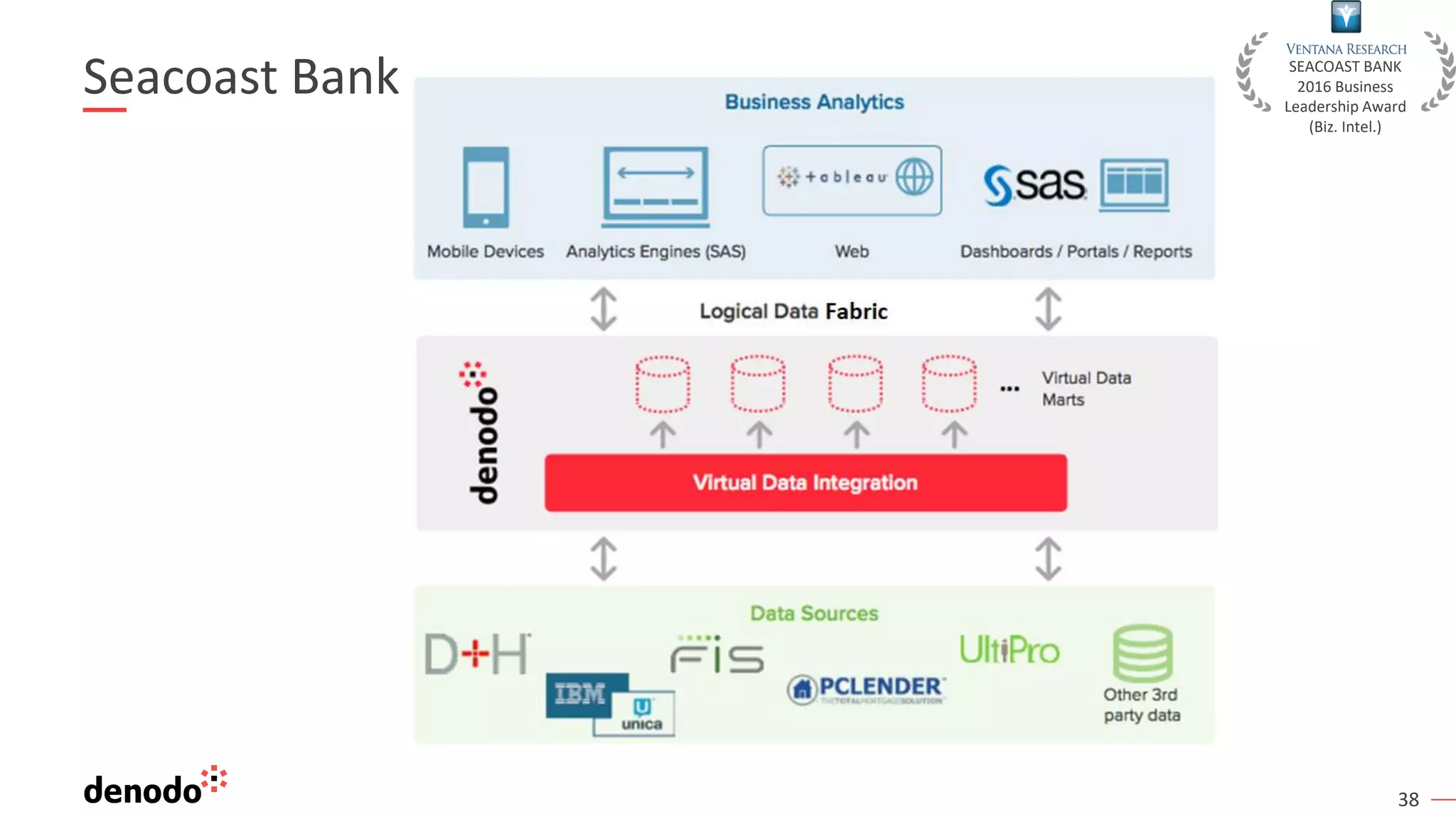
The document outlines the importance of data literacy in organizations, emphasizing the need for a data-literate workforce to drive performance and competitive advantage. It presents a 10-step framework to develop data literacy, including assessing current status, securing executive support, and integrating data into daily activities. Additionally, it highlights the role of data virtualization as a key technology to support accessibility and effective data practices within enterprises.