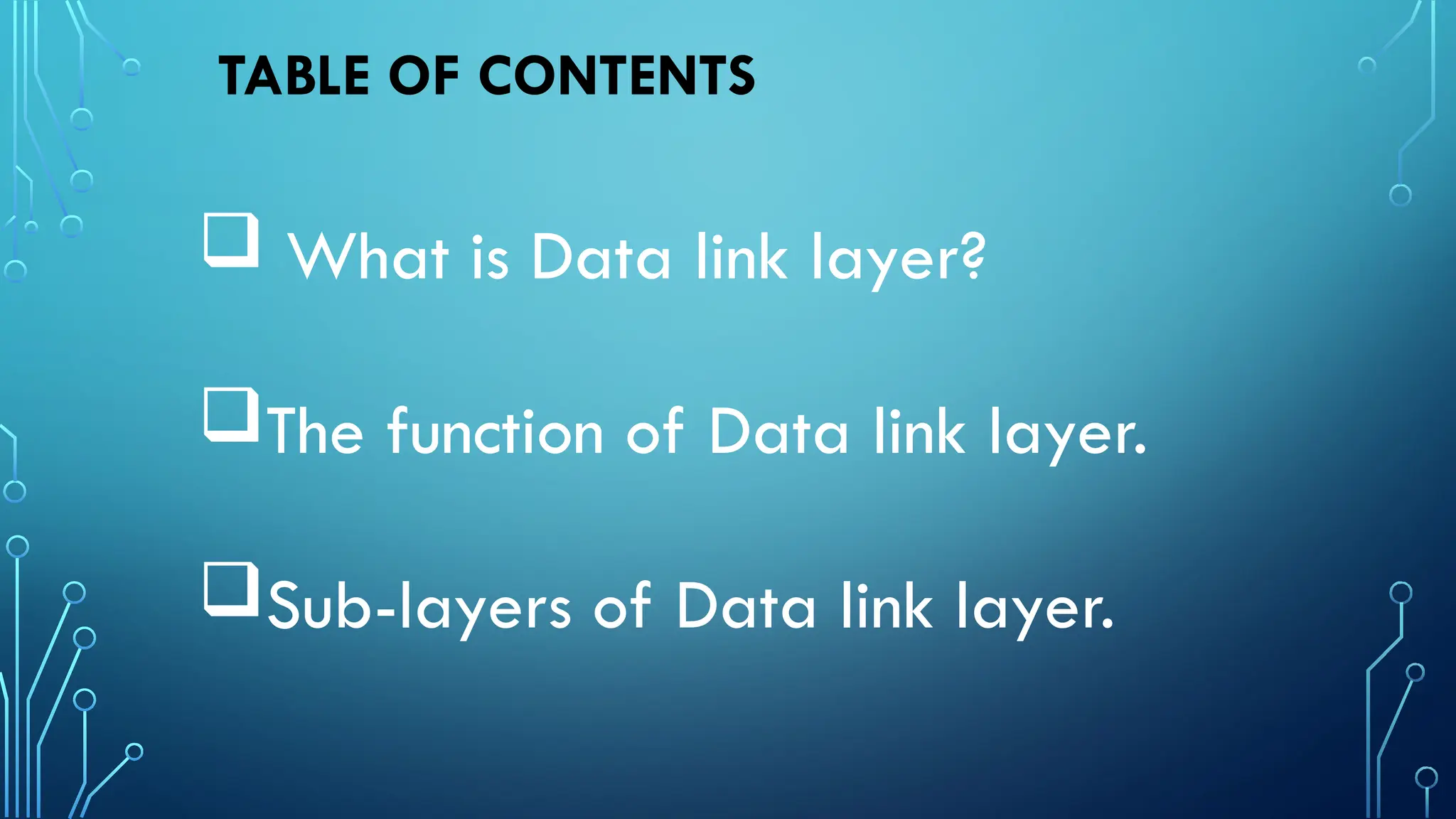
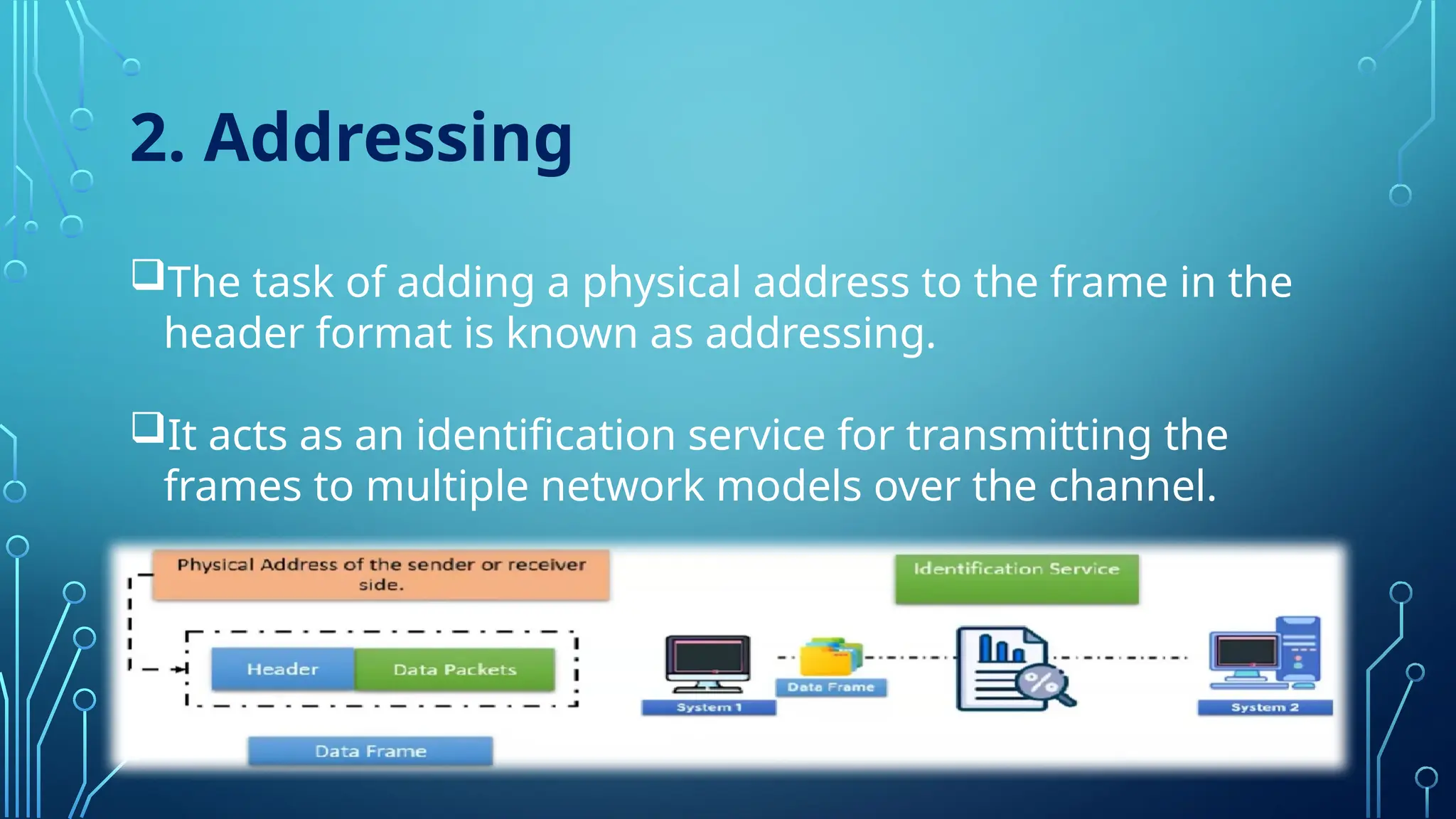
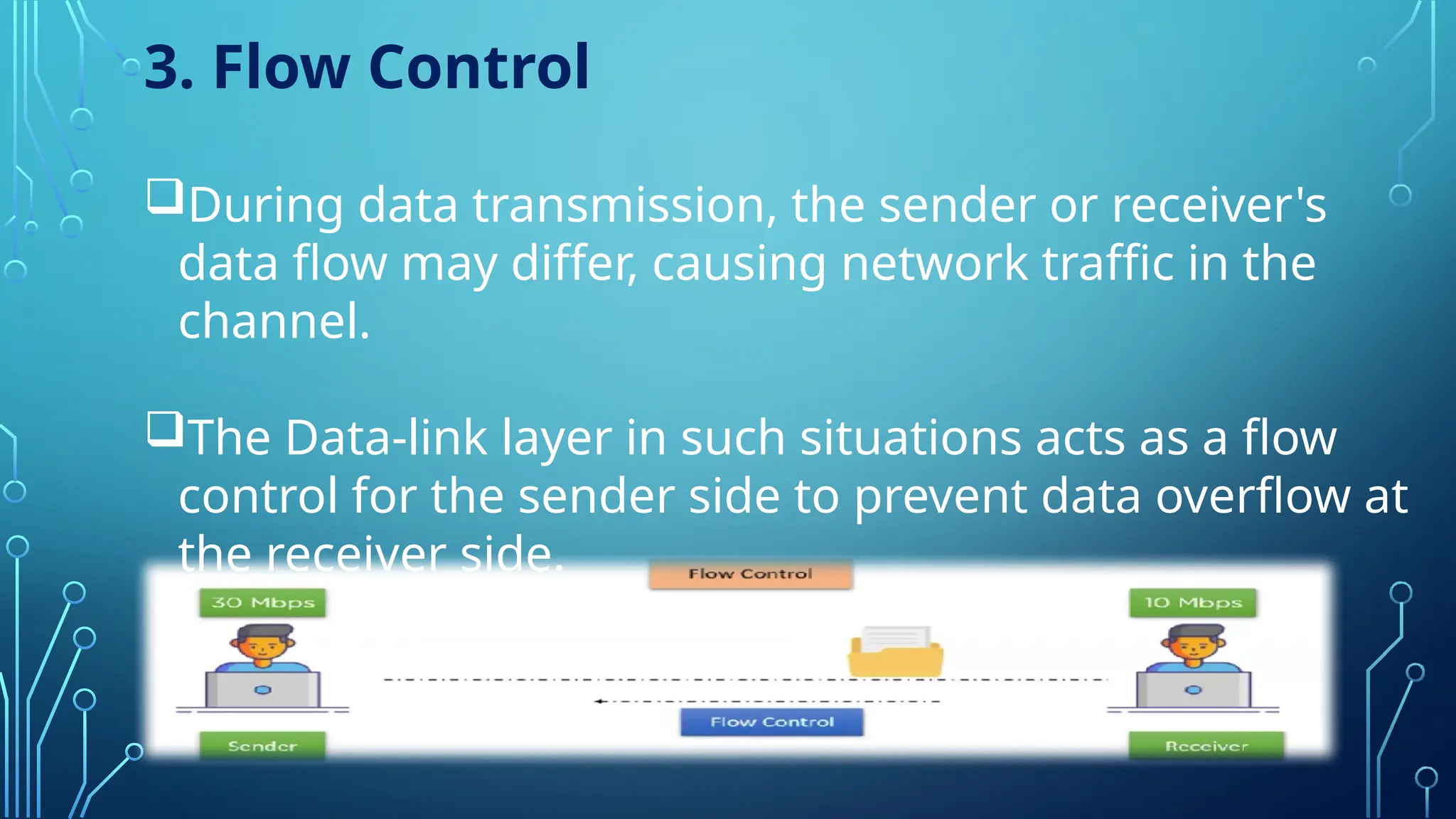
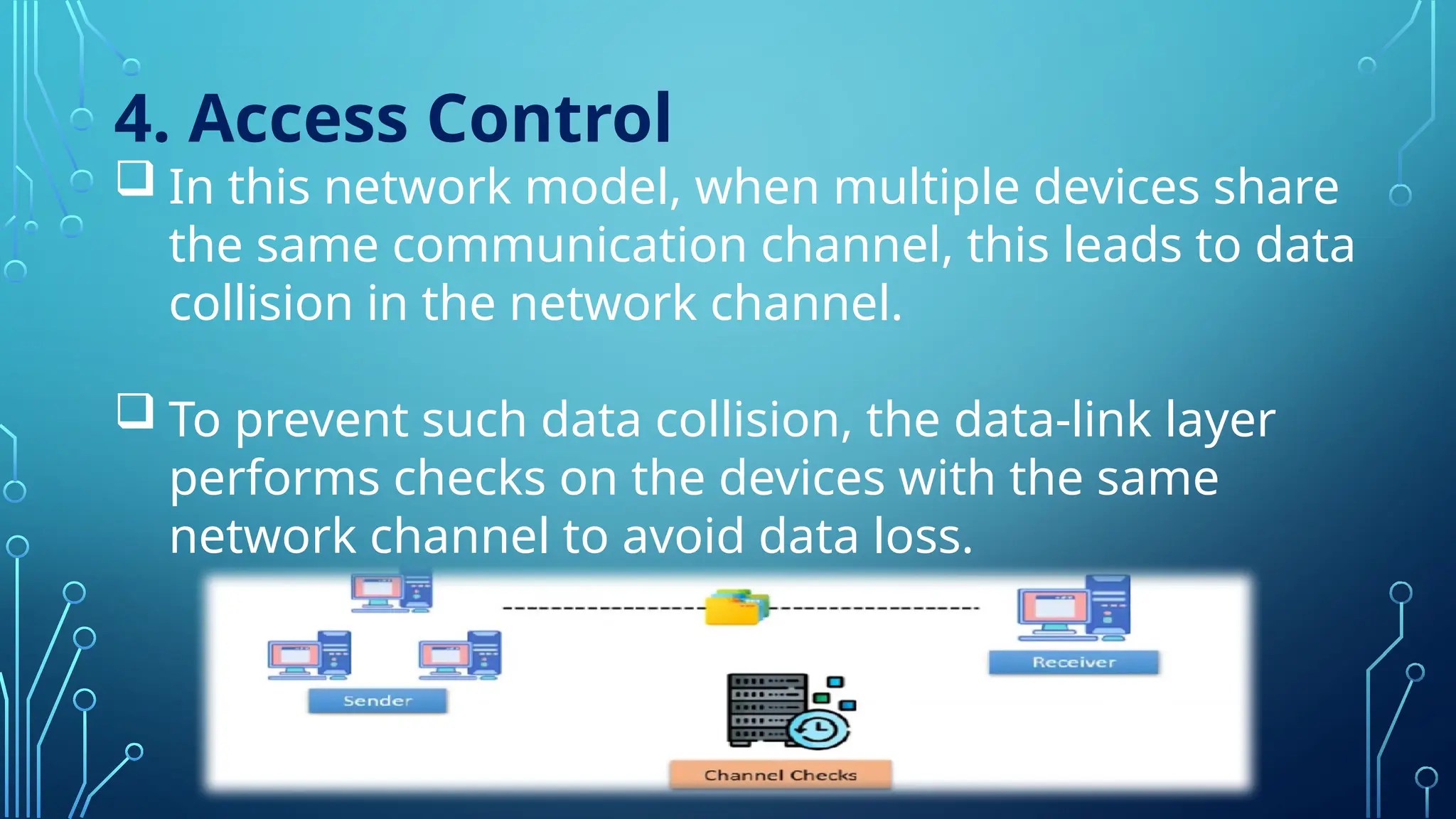
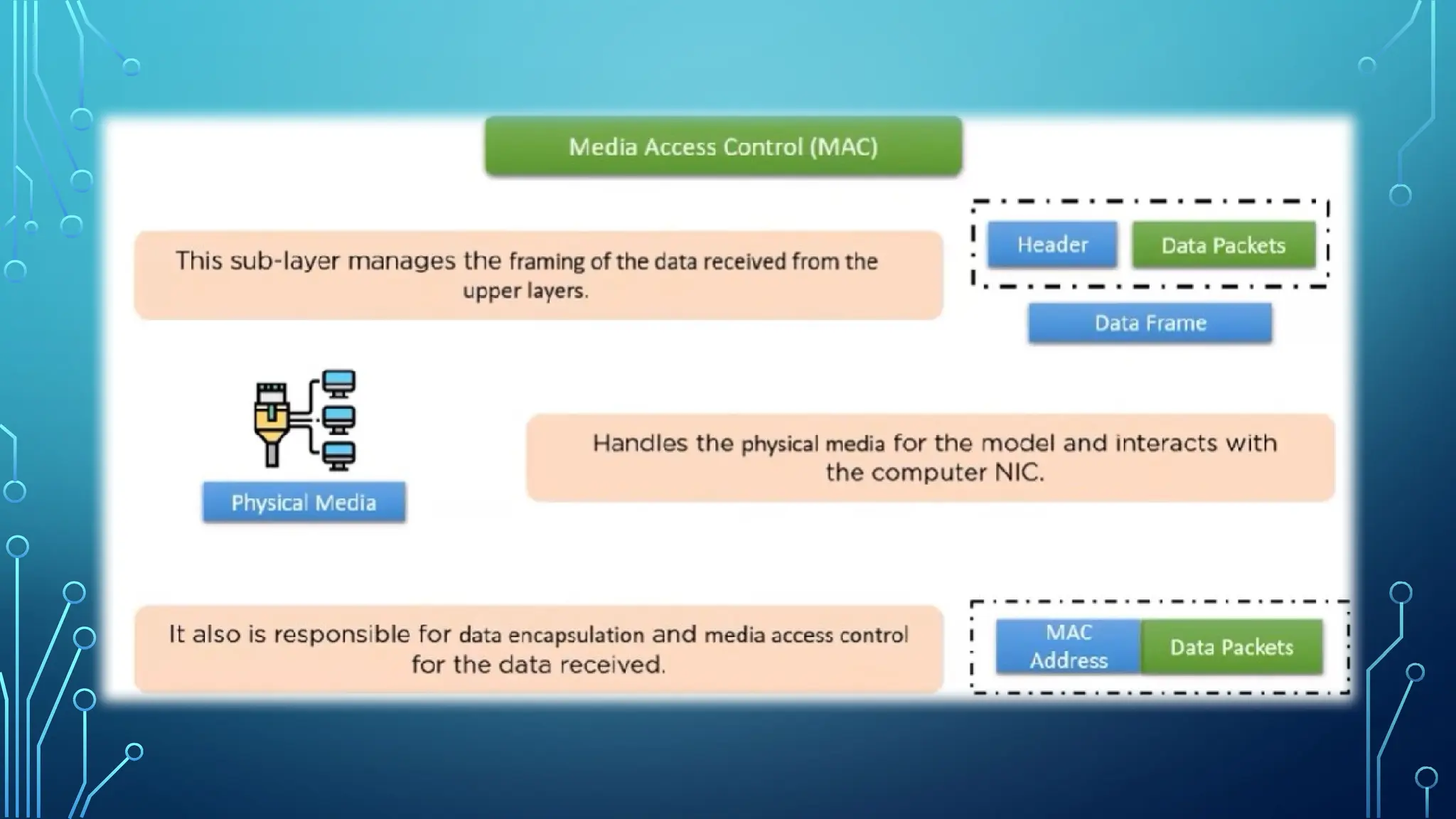
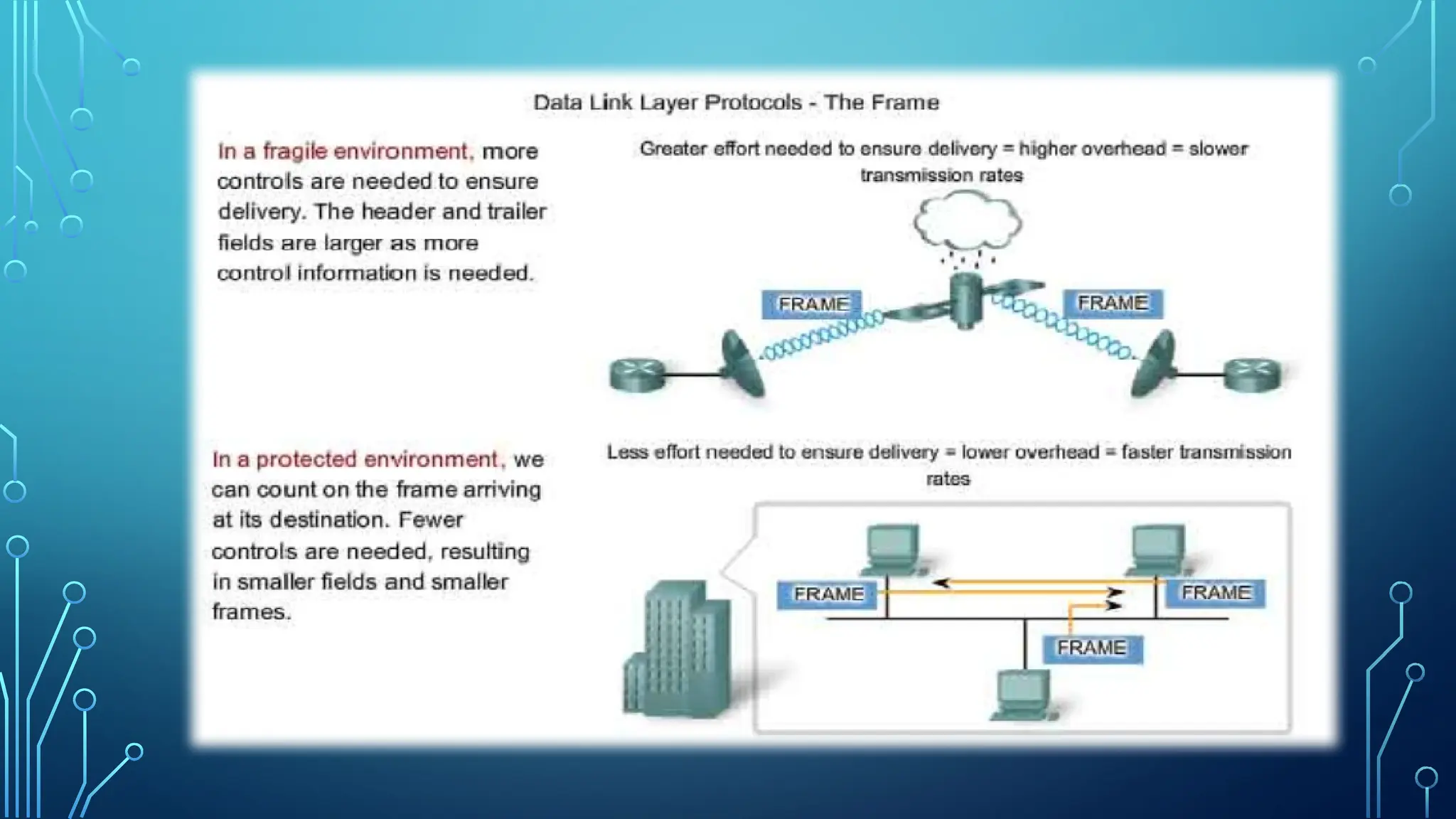
The data link layer is the second layer of the OSI model, responsible for node-to-node data delivery and ensuring error-free transmission. It performs functions such as framing, addressing, flow control, access control, and error control, which help manage data transmission over network channels. The layer consists of two sub-layers: Logical Link Control (LLC), which manages communication and error handling, and Media Access Control (MAC), which deals with data framing and control.