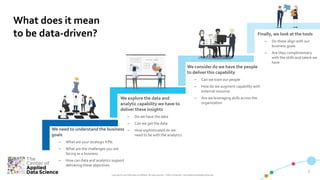
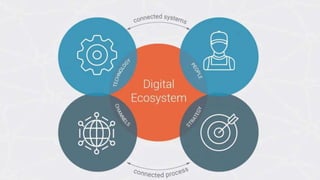
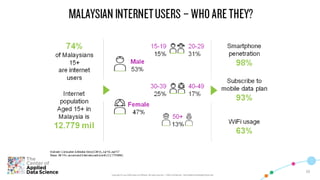
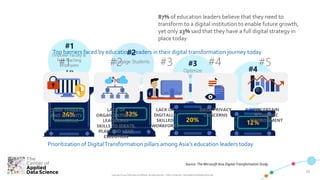
The document discusses key aspects of transforming a learning institution into a data-driven university (DDU). It outlines that a DDU aims to utilize data analytics to make higher education smarter and optimize management processes. Some key success factors for a DDU include developing industry-ready talent with skills in analytics, digital, and business and achieving operational excellence through analytics to build competitive resilience. The document also provides parameters that define a digital ecosystem and discusses barriers to digital transformation in education.