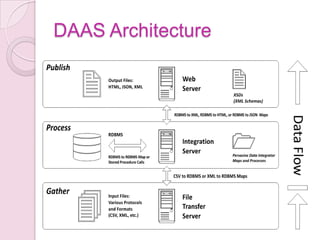
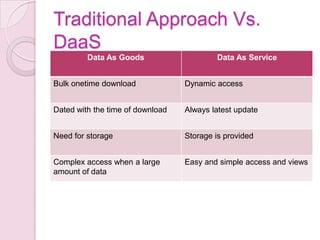
This document discusses Data as a Service (DaaS) in cloud computing. It defines DaaS and explains that it allows users to access data stored in the cloud from any location. The document outlines the components, architecture, pricing models, benefits and drawbacks of DaaS. It provides examples of companies that offer DaaS like Google, Windows Azure, and Amazon.