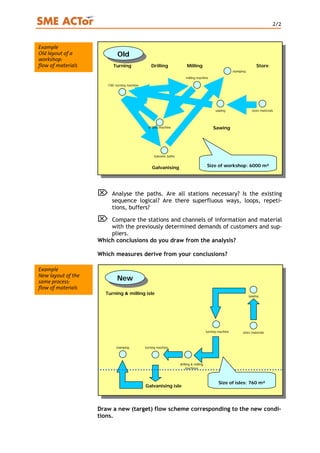
1) A flow analysis maps the channels of information and materials within a company to identify issues like double work, unnecessary steps, and error sources to optimize processes.
2) It involves creating layout maps of workspaces, drawing the pathways of information and materials between workstations, and analyzing the maps to see if all steps are necessary and sequences are logical.
3) The analysis conclusions are used to identify improvement measures like eliminating redundant steps or buffers.