Cyber warfare involves politically motivated attacks on a nation's computer and information systems, replacing traditional military tactics with cyber tactics such as sabotage and espionage. Strategies for cyber warfare include offensive methods like psychological operations and technical weapons, as well as defensive measures emphasizing inter-agency cooperation and ongoing preparatory work. Key examples of cyber warfare include the Stuxnet attack on Iran's nuclear program and the 2007 cyberattacks against Estonia, highlighting the complexities of attribution and legality in this new domain of conflict.















![REFERENCES
Code wars: America's cyber threat [Video file]. (2011). Retrieved February 10, 2017, from
http://fod.infobase.com/PortalPlaylists.aspx?wID=96757&xtid=47288
Davis, J. (2007, August 21). Hackers take down the most wired country in Europe. Retrieved
February 10, 2017, from https://www.wired.com/2007/08/ff-estonia/
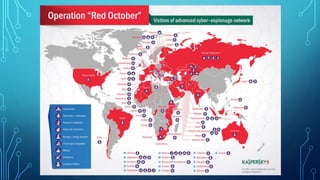
Lee, D. (2013, January 14). 'Red October' cyber-attack found by Russian researchers. Retrieved
February 10, 2017, from http://www.bbc.com/news/technology-21013087
Peterson, A. (2014, December 18). The Sony Pictures hack, explained. Retrieved February 10,
2017, from https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/theswitch/wp/2014/12/18/ the-sony
pictures-hack explained/?utm_term=.23be3932b130
Vacca, J. R. (Ed.). (2013). Computer and information security handbook (2nd ed.). Waltham, MA:
Steve Elliot.
What is cyberwarefare (cyber war)? (n.d.). Retrieved February 9, 2017, from
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/13600/cyberwarfare
Zetter, K. (2014, November 3). An unprecedented look at Stuxnet, the world's first digital weapon.
Retrieved February 10, 2017, from https://www.wired.com/2014/11/countdown-to-zero-day
stuxnet/
Live Free or Die Hard (2007)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cyberwarfare-jamiereecemoore-170425134824/85/Cyber-Warfare-Jamie-Reece-Moore-17-320.jpg)