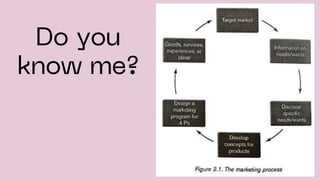
This document discusses customer value, relationship marketing, and customer satisfaction. It defines customer value as the unique benefits received by customers, including quality, price, and service. Companies can create value by offering low prices, high-quality products, or excellent service. Relationship marketing aims to develop close links with customers through trust and promises. It includes experiential, permission, and one-to-one marketing. Delivering customer satisfaction exceeds expectations and leads to loyal, happy customers.