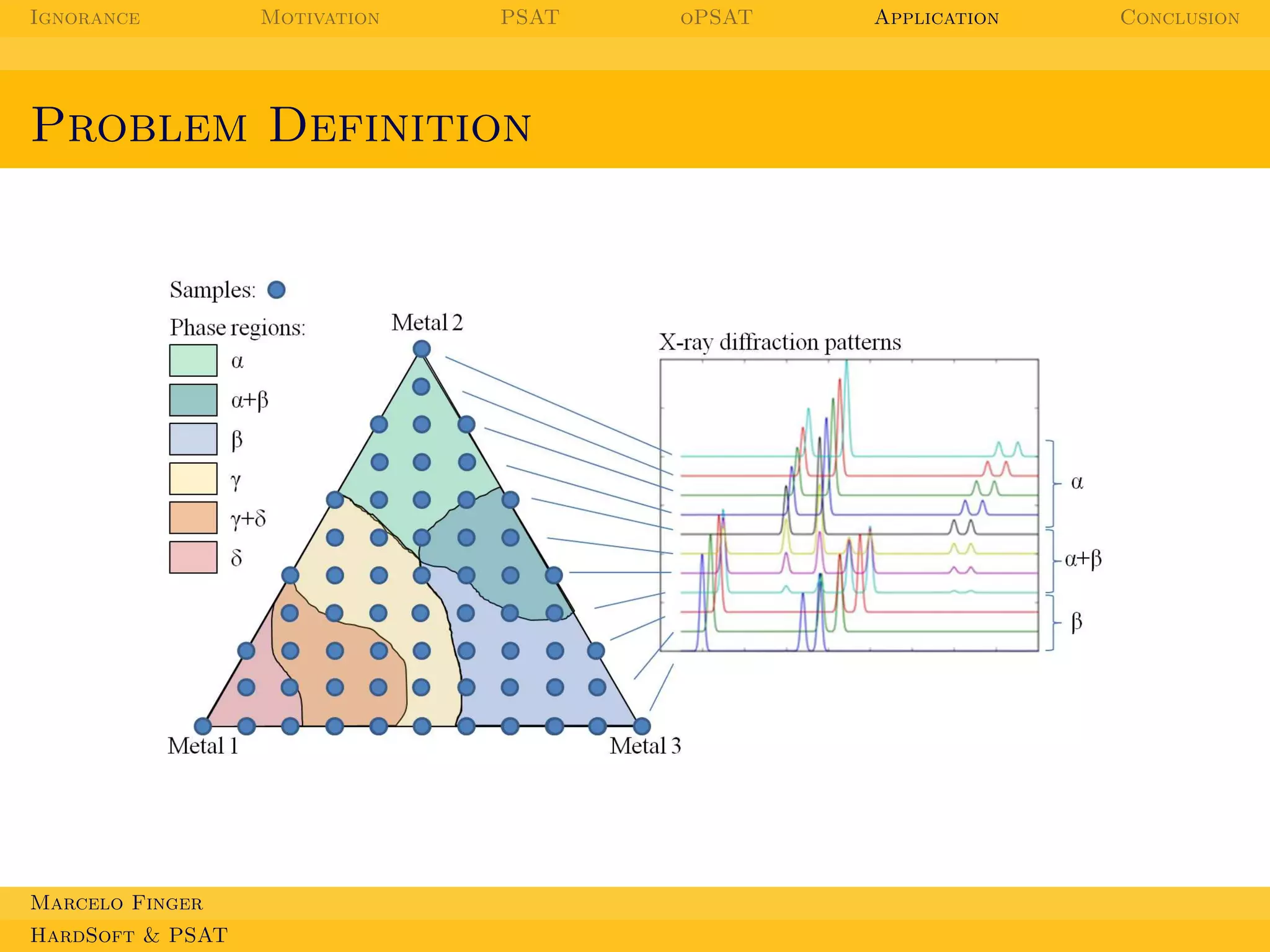
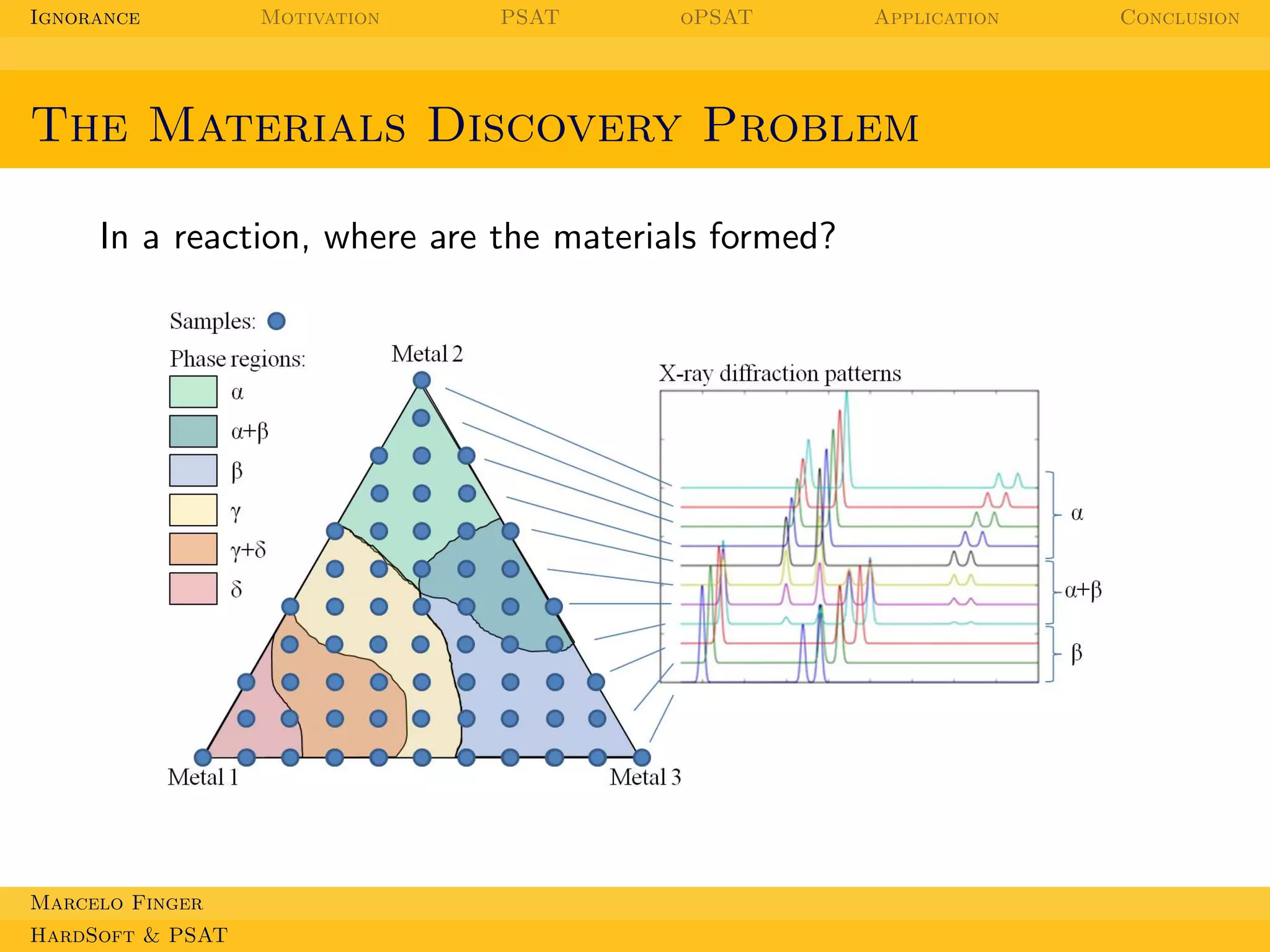
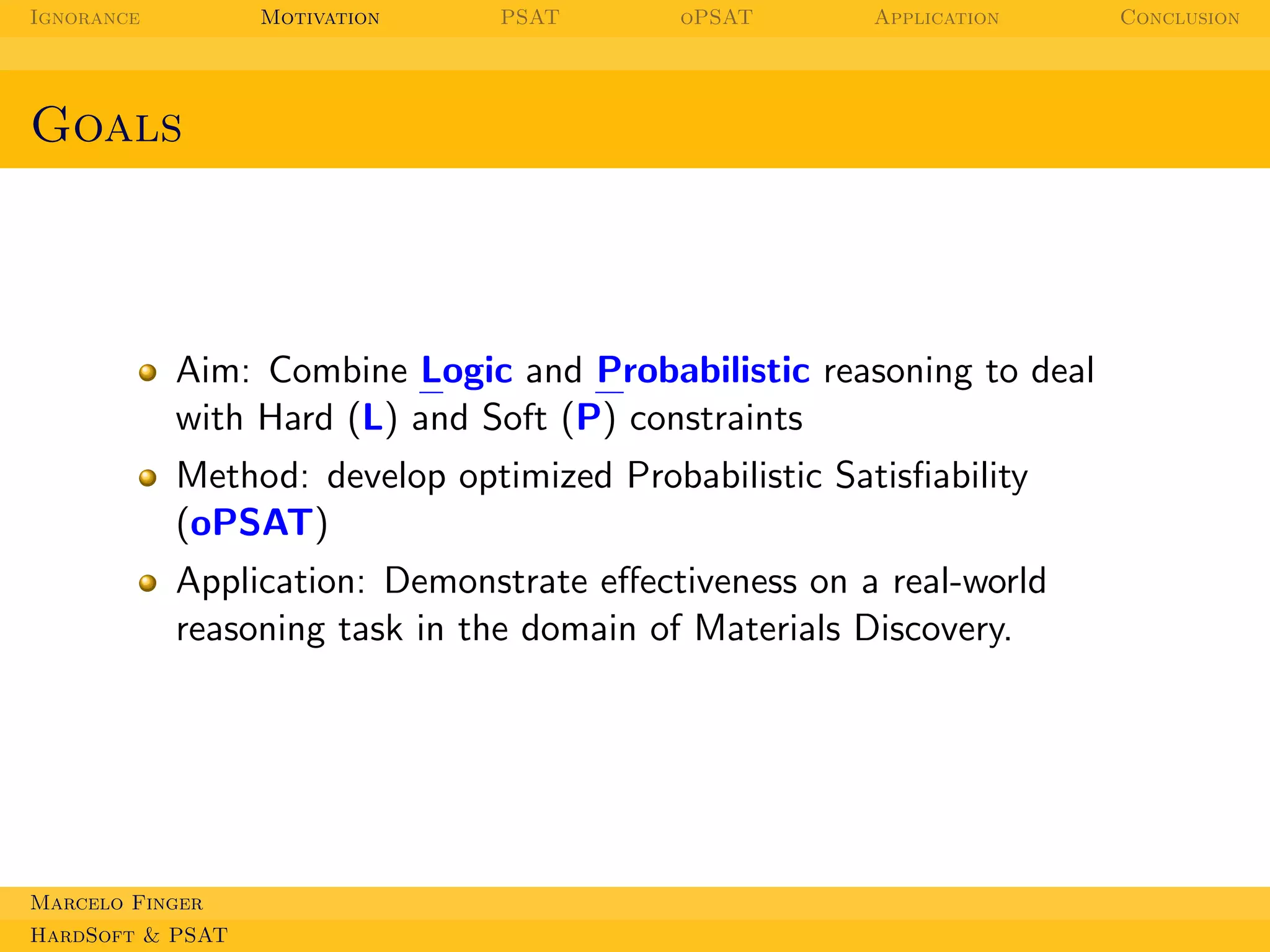
This document discusses applications of probabilistic logic to materials discovery. It begins by outlining the topics to be covered, which include probabilistic satisfiability (PSAT) and optimizing probability distributions with oPSAT. It then motivates this work by explaining how practical problems involve both hard and soft constraints. The goal is to combine logic and probabilistic reasoning to deal with these using oPSAT, demonstrating its effectiveness on materials discovery. PSAT is introduced as a way to combine logic and probability that respects probabilistic axioms. The document provides examples of how PSAT could be applied to problems involving constraints, such as scheduling student course enrollment.













![Ignorance
Motivation
PSAT
oPSAT
Application
Combining Logic and Probability
Many proposals in the literature
Markov Logic Networks [Richardson & Domingos 2006]
Probabilistic Inductive Logic Prog [De Raedt et. al 2008]
Relational Models [Friedman et al 1999], etc
Marcelo Finger
HardSoft & PSAT
Conclusion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curitiba2013-materials-slides-131114122612-phpapp01/75/Applications-of-Probabilistic-Logic-to-Materials-Discovery-Solving-problems-with-hard-and-soft-constraints-25-2048.jpg)
![Ignorance
Motivation
PSAT
oPSAT
Application
Conclusion
Combining Logic and Probability
Many proposals in the literature
Markov Logic Networks [Richardson & Domingos 2006]
Probabilistic Inductive Logic Prog [De Raedt et. al 2008]
Relational Models [Friedman et al 1999], etc
Our choice: Probabilistic Satisfiability (PSAT)
Natural extension of Boolean Logic
Desirable properties, e.g. respects Kolmogorov axioms
Probabilistic reasoning free of independence presuppositions
Marcelo Finger
HardSoft & PSAT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curitiba2013-materials-slides-131114122612-phpapp01/75/Applications-of-Probabilistic-Logic-to-Materials-Discovery-Solving-problems-with-hard-and-soft-constraints-26-2048.jpg)
![Ignorance
Motivation
PSAT
oPSAT
Application
Conclusion
Combining Logic and Probability
Many proposals in the literature
Markov Logic Networks [Richardson & Domingos 2006]
Probabilistic Inductive Logic Prog [De Raedt et. al 2008]
Relational Models [Friedman et al 1999], etc
Our choice: Probabilistic Satisfiability (PSAT)
Natural extension of Boolean Logic
Desirable properties, e.g. respects Kolmogorov axioms
Probabilistic reasoning free of independence presuppositions
What is PSAT?
Marcelo Finger
HardSoft & PSAT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curitiba2013-materials-slides-131114122612-phpapp01/75/Applications-of-Probabilistic-Logic-to-Materials-Discovery-Solving-problems-with-hard-and-soft-constraints-27-2048.jpg)
![Ignorance
Motivation
PSAT
oPSAT
Application
A Brief History of PSAT
Proposed by [Boole 1854],
On the Laws of Thought
Rediscovered several times since Boole
De Finetti [1937, 1974], Good [1950], Smith [1961]
Studied by Hailperin [1965]
Nilsson [1986] (re)introduces PSAT to AI
PSAT is NP-complete [Georgakopoulos et. al 1988]
Nilsson [1993]: “complete impracticability” of PSAT
computation
Many other works; see Hansen & Jaumard [2000]
Marcelo Finger
HardSoft & PSAT
Conclusion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curitiba2013-materials-slides-131114122612-phpapp01/75/Applications-of-Probabilistic-Logic-to-Materials-Discovery-Solving-problems-with-hard-and-soft-constraints-30-2048.jpg)

![Ignorance
Motivation
PSAT
oPSAT
Application
Conclusion
The Setting
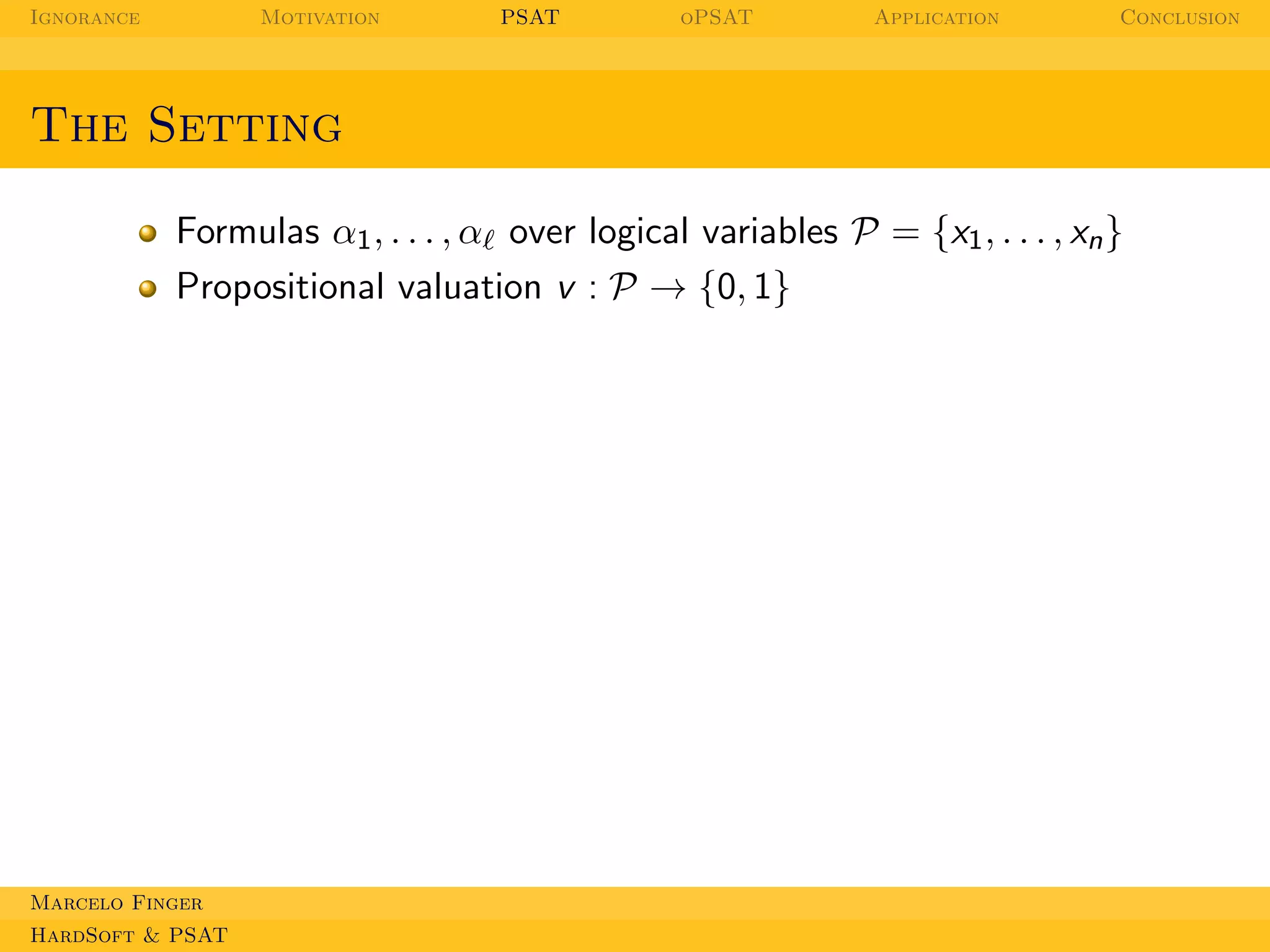
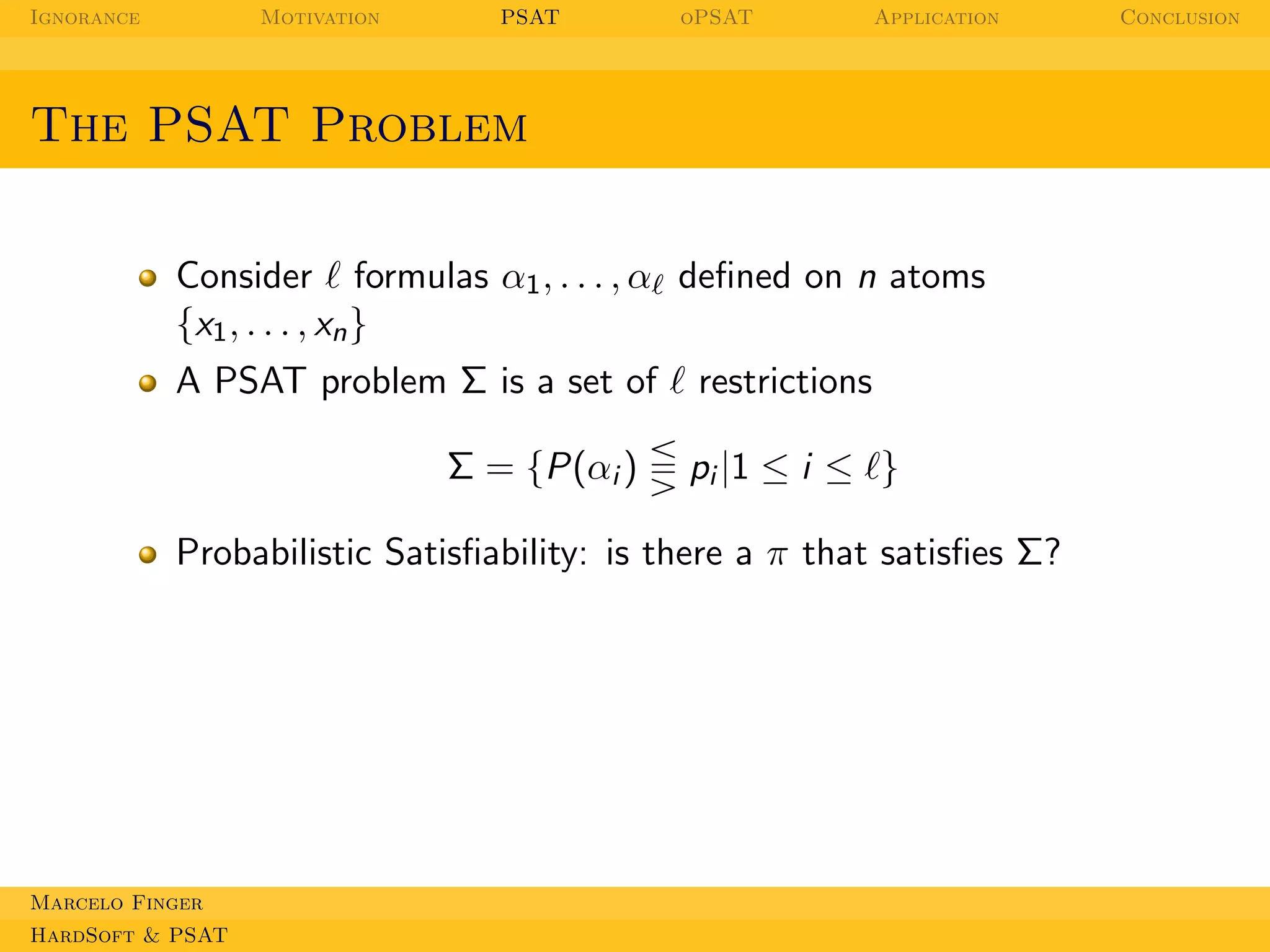
Formulas α1 , . . . , αℓ over logical variables P = {x1 , . . . , xn }
Propositional valuation v : P → {0, 1}
A probability distribution over propositional valuations
π : V → [0, 1]
2n
π(vi ) = 1
i=1
Marcelo Finger
HardSoft & PSAT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curitiba2013-materials-slides-131114122612-phpapp01/75/Applications-of-Probabilistic-Logic-to-Materials-Discovery-Solving-problems-with-hard-and-soft-constraints-33-2048.jpg)
![Ignorance
Motivation
PSAT
oPSAT
Application
Conclusion
The Setting
Formulas α1 , . . . , αℓ over logical variables P = {x1 , . . . , xn }
Propositional valuation v : P → {0, 1}
A probability distribution over propositional valuations
π : V → [0, 1]
2n
π(vi ) = 1
i=1
Probability of a formula α according to π
Pπ (α) =
Marcelo Finger
HardSoft & PSAT
{π(vi )|vi (α) = 1}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curitiba2013-materials-slides-131114122612-phpapp01/75/Applications-of-Probabilistic-Logic-to-Materials-Discovery-Solving-problems-with-hard-and-soft-constraints-34-2048.jpg)

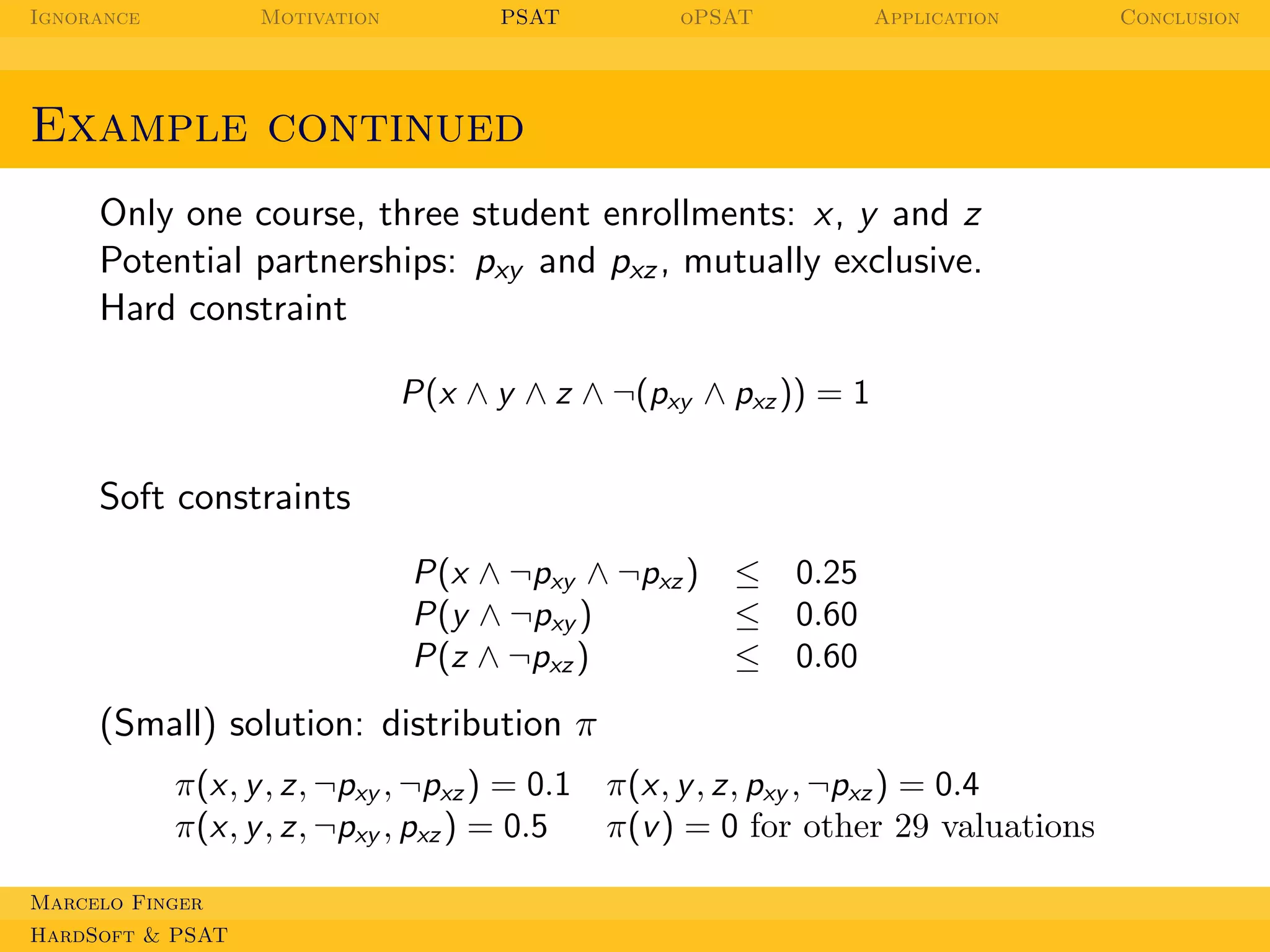

![Ignorance
Motivation
PSAT
oPSAT
Application
Conclusion
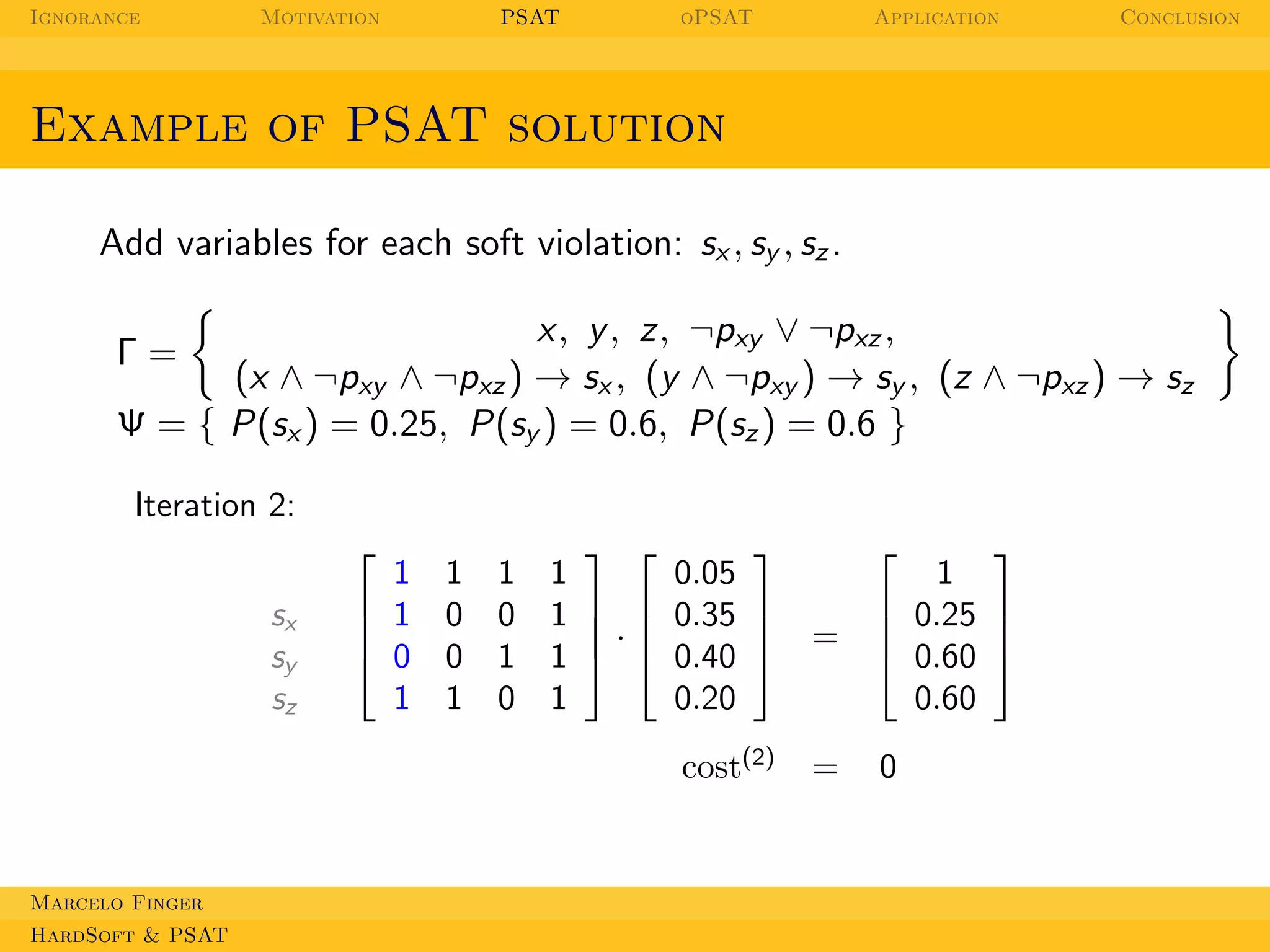
Example of PSAT solution
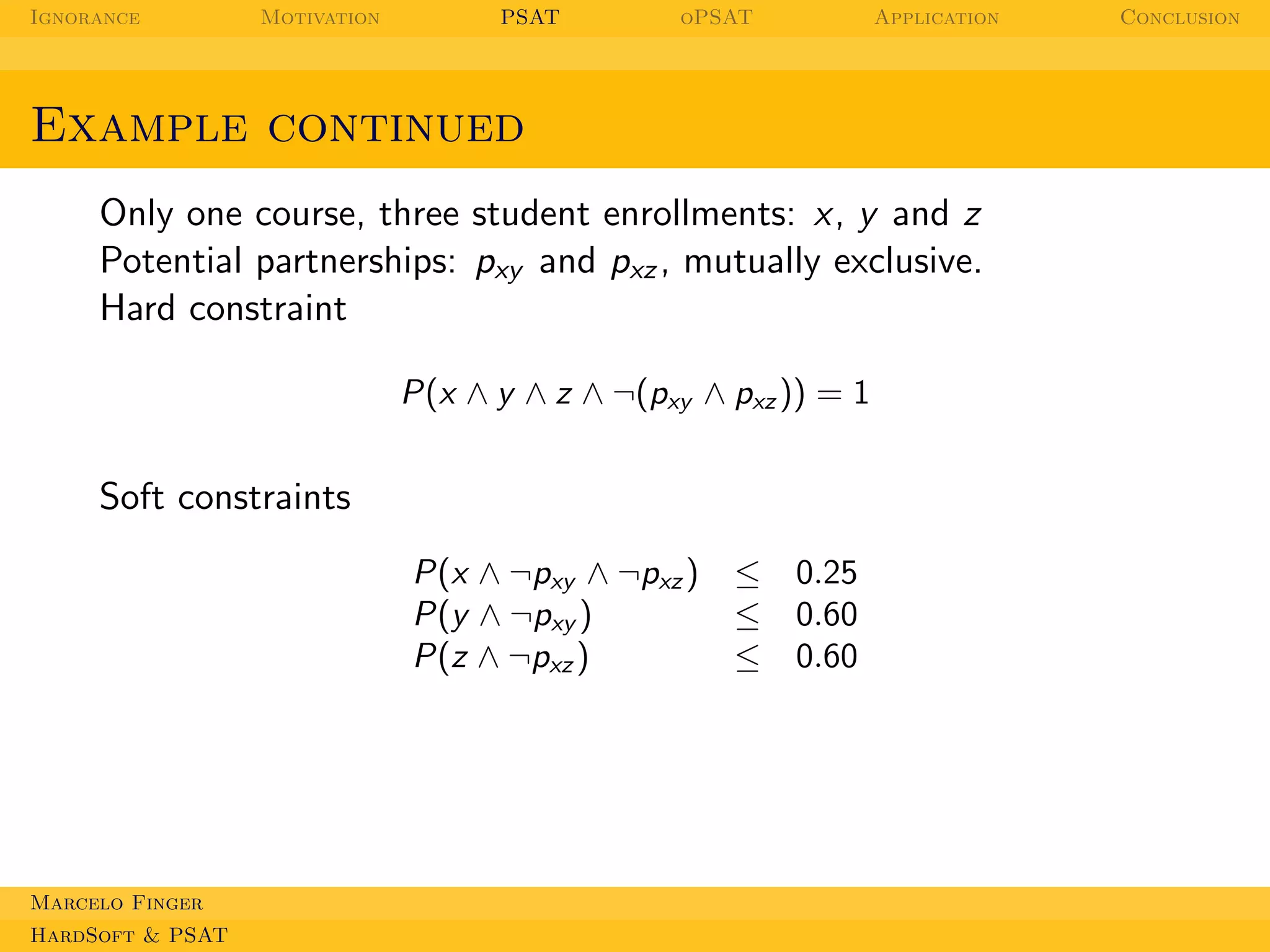
Add variables for each soft violation: sx , sy , sz .
x, y , z, ¬pxy ∨ ¬pxz ,
(x ∧ ¬pxy ∧ ¬pxz ) → sx , (y ∧ ¬pxy ) → sy , (z ∧ ¬pxz ) → sz
Ψ = { P(sx ) = 0.25, P(sy ) = 0.6, P(sz ) = 0.6 }
Γ=
Iteration 0:
sx
sy
sz
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0.4
1
1 0
·
1 0.35
0.25
1
HardSoft & PSAT
=
cost(0)
b (0)
Marcelo Finger
=
=
1
0.25
0.60
0.60
0.4
[1 0 1 0]′ : col 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curitiba2013-materials-slides-131114122612-phpapp01/75/Applications-of-Probabilistic-Logic-to-Materials-Discovery-Solving-problems-with-hard-and-soft-constraints-40-2048.jpg)
![Ignorance
Motivation
PSAT
oPSAT
Application
Conclusion
Example of PSAT solution
Add variables for each soft violation: sx , sy , sz .
x, y , z, ¬pxy ∨ ¬pxz ,
(x ∧ ¬pxy ∧ ¬pxz ) → sx , (y ∧ ¬pxy ) → sy , (z ∧ ¬pxz ) → sz
Ψ = { P(sx ) = 0.25, P(sy ) = 0.6, P(sz ) = 0.6 }
Γ=
Iteration 1:
sx
sy
sz
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0.05
1
1 0.35
·
1 0.35
0.25
1
HardSoft & PSAT
=
cost(1)
b (1)
Marcelo Finger
=
=
1
0.25
0.60
0.60
0.05
[1 1 0 1]′ : col 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/curitiba2013-materials-slides-131114122612-phpapp01/75/Applications-of-Probabilistic-Logic-to-Materials-Discovery-Solving-problems-with-hard-and-soft-constraints-41-2048.jpg)