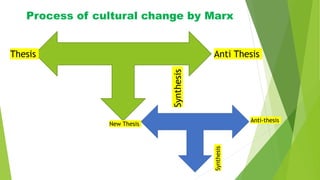
Cultural evolution is the idea that human cultural change resembles a darwinian evolutionary process, akin to biological evolution, and encompasses changes in beliefs, knowledge, and customs. Various theories explain cultural evolution, including unilineal, cyclical, diffusionist, and conflict theories, each addressing different aspects of social change and the dynamics of cultural conflict. Cultural diffusion facilitates the spread of cultural traits across societies, influenced by factors such as need, recognition, and social dynamics.