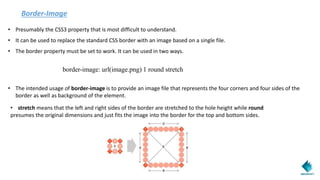
The document provides an introduction to CSS, specifically focusing on CSS3, which is backwards-compatible and introduces new features through modules. It details various CSS rules, properties, and functionalities such as border-radius, background images, transitions, and box shadows. The aim is to enhance web design while ensuring compatibility across different browsers.