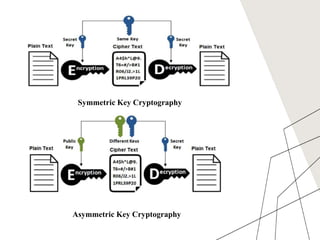
Cryptography is the technique of securing communication by converting readable text into an unreadable format using algorithms and protocols for confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. There are two main types of cryptography: symmetric key cryptography, which uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric key cryptography, which uses a pair of keys. Applications of cryptography include computer passwords, secure web browsing, electronic signatures, authentication, and end-to-end encryption for communications.