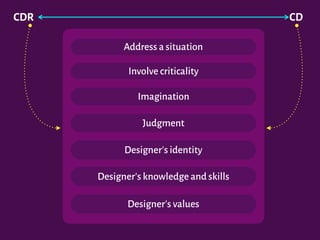
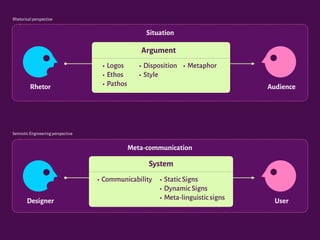
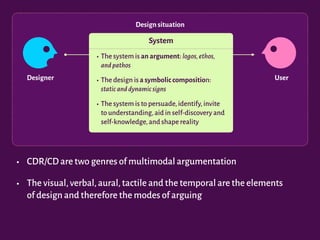
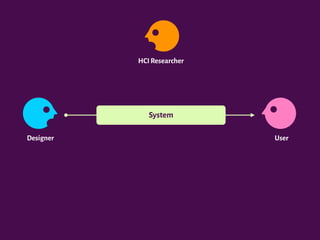
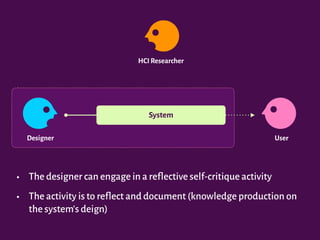
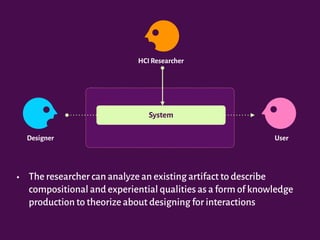
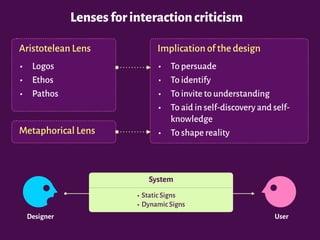
The document discusses the interplay between design, rhetoric, and semiotics in user interfaces, emphasizing the importance of meta-communication and the rhetorical nature of human-computer interaction (HCI). It outlines approaches such as semiotic engineering and rhetorical criticism, which aim to analyze and improve the communicability of design systems. The focus is on how design can persuade and facilitate understanding through various modes of argumentation, while also encouraging reflective critique from designers and researchers.