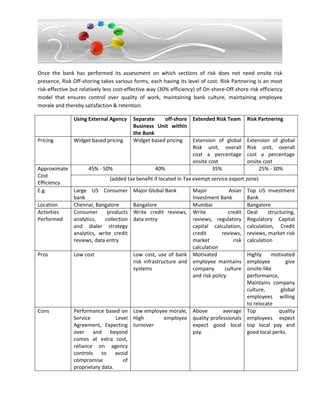
Risk offshoring brings cost benefits but also builds risk knowledge through centralization. It is important to set clear governance and ownership over processes, regardless of location. While market risk offshoring has been successful, credit risk results vary due to needing more client interaction. The document discusses different offshoring models and their tradeoffs regarding costs, efficiency, and challenges like cultural differences, motivation, and competitive demand for risk professionals.