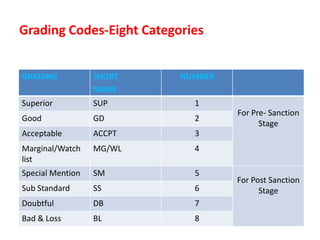
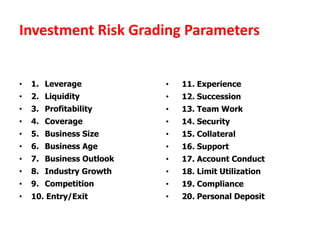
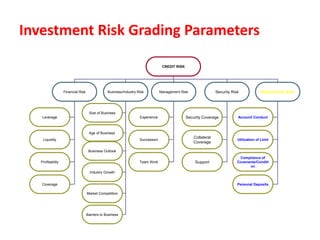
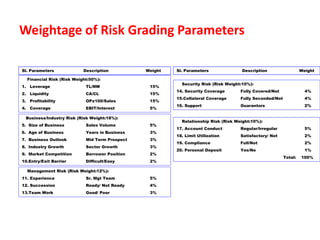
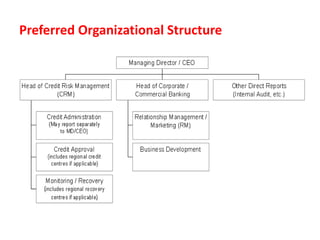
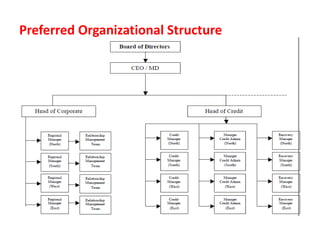
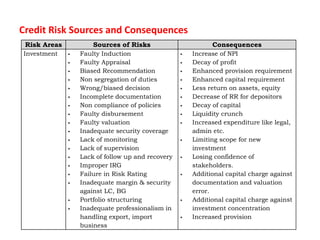
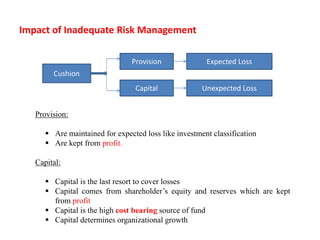
The document discusses credit risk management at a bank. It defines credit risk and outlines the bank's credit risk management framework, including having a credit risk policy, preferred organizational structure, and procedural guidelines. It emphasizes the importance of credit risk grading, monitoring, and mitigation. Key areas of responsibility for the investment risk management, relationship management, and credit administration teams are also outlined.





![Credit Risk Concept in Islam
“O you who have believed, when you contract a debt for a specified term,
write it down.” (mitigant of legal, residual, settlement risks etc.)
(Surah Al-Baqara 282)
"And if you are upon a journey and you do not find a scribe, then a security
may be taken into possession." (mitigant of credit default risks)
(Surah Al Baqara 283)
And he said, "O my sons, do not enter from one gate but enter from different
gates; and I cannot avail you against [the decree of] Allah at all. The decision
is only for Allah ; upon Him I have relied, and upon Him let those who would
rely [indeed] rely.“ (mitigant of concentration risk)
(Surah Al Yusuf 67)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creditriskmanagement-220826153208-464cc211/85/Credit-Risk-Management-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![Credit Risk Concept in Islam
“Then will come after that seven difficult [years] which will consume what you saved
for them, except a little from which you will store.”
(counter cyclical buffer, Capital Conservation Buffer for absorbing future loss)
(Sura Yusuf 48)
"Narrated Aisha, Ummul Mu'minin:
The Apostle of Allah (peace_be_upon_him) said: Profit follows responsibility of
bearing loss. “ (Importance of undertaking risks in business)
(Sunan e Ibn Majah Book 23, Number 3501)
Prophet (PBUH) once asked a Bedouin who had left his camel untied, “Why do you not
tie your camel?” The Bedouin answered, “I put my trust in God”.
Prophet (PBUH) then said, “tie up your camel first then put your trust in God”.
Knowing Sharia’h Ruling of the tasks that you do is a must being a Muslim.
So dependence on Allah only or Risk Management too?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creditriskmanagement-220826153208-464cc211/85/Credit-Risk-Management-pptx-7-320.jpg)


![Central Bank Initiatives in Investment Risk Mgt.
• 1993: Lending (Investment) Risk Analysis
Limitations: lot of Subjectivity, lack of objectivity, only decisive for lending or not,
indifference about limit utilization etc.
• 2003: Credit Risk Management Guideline [as
one of the 6 (six) Core Risks]
• 2005: Credit Risk Grading Manual
• 2011: Inclusion of Environmental Risk
Management in CRM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creditriskmanagement-220826153208-464cc211/85/Credit-Risk-Management-pptx-10-320.jpg)