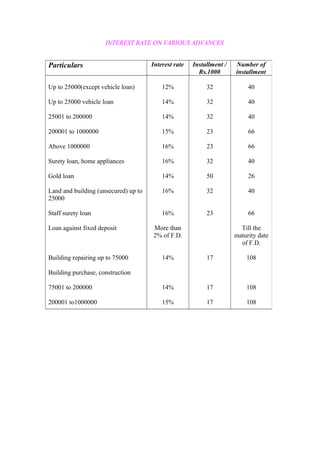
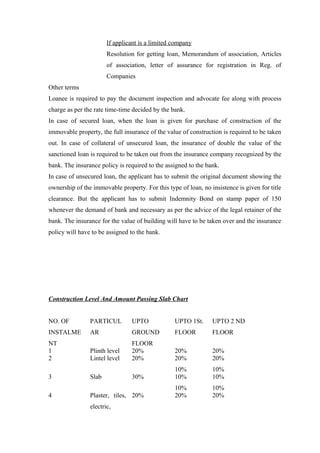
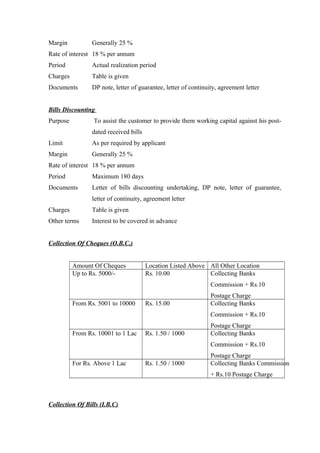
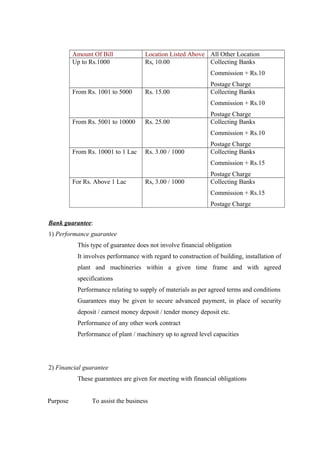
This document is a project report on credit management and non-performing assets (NPAs) of Rajkot District Co-operative Bank Ltd. (RDC Bank). It discusses the history and background of RDC Bank, which was established in 1959. It then covers various aspects of credit management at RDC Bank, including credit policies, appraisal, monitoring, NPAs, and recovery processes. The report aims to analyze credit management practices and suggest improvements to reduce NPAs.