Crct science review
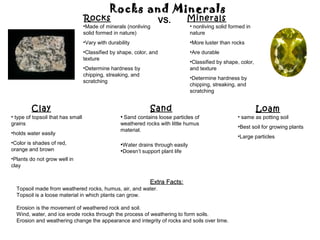
- 1. Rocks and Minerals Rocks VS. Minerals •Made of minerals (nonliving • nonliving solid formed in solid formed in nature) nature •Vary with durability •More luster than rocks •Classified by shape, color, and •Are durable texture •Classified by shape, color, •Determine hardness by and texture chipping, streaking, and •Determine hardness by scratching chipping, streaking, and scratching Clay Sand Loam • type of topsoil that has small • Sand contains loose particles of • same as potting soil grains weathered rocks with little humus •Best soil for growing plants material. •holds water easily •Large particles •Color is shades of red, •Water drains through easily orange and brown •Doesn’t support plant life •Plants do not grow well in clay Extra Facts: Topsoil made from weathered rocks, humus, air, and water. Topsoil is a loose material in which plants can grow. Erosion is the movement of weathered rock and soil. Wind, water, and ice erode rocks through the process of weathering to form soils. Erosion and weathering change the appearance and integrity of rocks and soils over time.
- 2. Fossils fossil is something that has lasted from a living thing that died long ago mold is the shape of a plant or cast mold animal left in sediments when the rock formed imprint are molds of leaves or other imprint thin objects (an imprint is a lot like a stamp) cast forms when mud or minerals cast mold fill a mold and hardens A fossil is the remains formed from a living thing (plant or animal) that died long ago. Mold, cast, and imprint are types of fossils. Fossils are formed when a living thing’s remains (bone/shell/stem/leaves) are covered with material from layers by nature.
- 3. Georgia Habitats • A habitat is a place where both plants and animals live. • Mountains are landforms that are much higher than the areas around it. • Marsh/swamp is a low lying wetland with grass plants. • Coastal land is located near a large body of water such as a sea or an ocean, and is known for its climate. • Atlantic Ocean is the body of salt water that contains marine animals. • Piedmont is land between the coastal plain and Appalachian Mountains. • Different organisms/plants live in different habitats. • Organisms/plants may not survive if their habitat is changed.
- 4. Heat Thermal energy (heat) • Heat is a form of energy is produced by: that is transferred by a difference in temperature. Burning sun oven • Friction is the force friction between two moving objects that prevents them from moving freely. • Insulation is material that heat cannot move through easily. • Radiation is heat energy Insulators vs. conductors that is passed without touching anything. • Heat is transferable through different objects. • A thermometer is a tool used to measure temperature.
- 5. Magnets • Magnets are usually Some things magnets are attracted to metallic objects that (stick to): metals attract each other and some other objects. • Some objects are attracted by magnets while some are not. • Magnets have two parts: a north pole and a south Some things magnets are NOT pole. attracted to: • The north pole of one magnet attracts the south pole of another magnet (opposites attract). • Similar poles of two magnets repel each other Opposite poles attract (come together): (alike repels). Like poles repel (push apart):
- 6. Pollution Types of Pollution: Some Facts • Pollution occurs when the environment is contaminated Air: with harmful substances. • Human behaviors such as littering, driving, industry, and development impact the environment. It effects plants and animals. • Conservation of resources and recycling of materials and Water: reusing materials are ways to protect the environment. . Things you can do to reduce: Say no to junk mail! Buy in bulk. Start a compost pile. Buy only what Land: you need, instead of what you want. Things you can reuse: Clothes, travel cups, shopping bags, washable eating utensils You can also donate items instead of throwing them away! Noise: Things you can recycle: Acid Batteries, Aluminum Cans , Building Materials, Cardboard, Chemicals, Electronic equipment, Glass (particularly bottles and jars), Lead, Magazines, Metal, Newspaper, Oil, Paint, Paper, Plastic Bags, Plastic Bottles, Steel Cans, Tires, White Goods (Appliances), Wood, Writing/Copy Paper, Yard Waste
- 7. Pollution Types of Pollution: Some Facts • Pollution occurs when the environment is contaminated Air: with harmful substances. • Human behaviors such as littering, driving, industry, and development impact the environment. It effects plants and animals. • Conservation of resources and recycling of materials and Water: reusing materials are ways to protect the environment. . Things you can do to reduce: Say no to junk mail! Buy in bulk. Start a compost pile. Buy only what Land: you need, instead of what you want. Things you can reuse: Clothes, travel cups, shopping bags, washable eating utensils You can also donate items instead of throwing them away! Noise: Things you can recycle: Acid Batteries, Aluminum Cans , Building Materials, Cardboard, Chemicals, Electronic equipment, Glass (particularly bottles and jars), Lead, Magazines, Metal, Newspaper, Oil, Paint, Paper, Plastic Bags, Plastic Bottles, Steel Cans, Tires, White Goods (Appliances), Wood, Writing/Copy Paper, Yard Waste