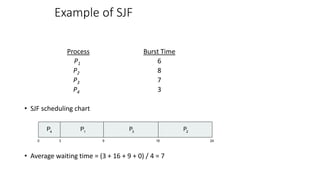
This document discusses CPU scheduling algorithms. It describes scheduling criteria like CPU utilization, throughput, turnaround time and waiting time. It then explains the First-Come, First-Served (FCFS) scheduling algorithm and provides an example. It also covers the Shortest-Job-First (SJF) and Priority scheduling algorithms, giving examples of each. The objectives are to describe various CPU scheduling algorithms, discuss evaluation criteria, and examine algorithms used by different operating systems.